Local data in Syncfusion ASP.NET Core Grid
16 May 202524 minutes to read
The Syncfusion ASP.NET Core Grid offers a straightforward way to bind local data, such as arrays or JSON objects, to the Grid. This feature allows you to display and manipulate data within the Grid without the need for external server calls, making it particularly useful for scenarios where you’re working with static or locally stored data.
To achieve this, you can assign a IEnumerable object to the dataSource property. Additionally, you have an option to provide the local data source using an instance of the DataManager.
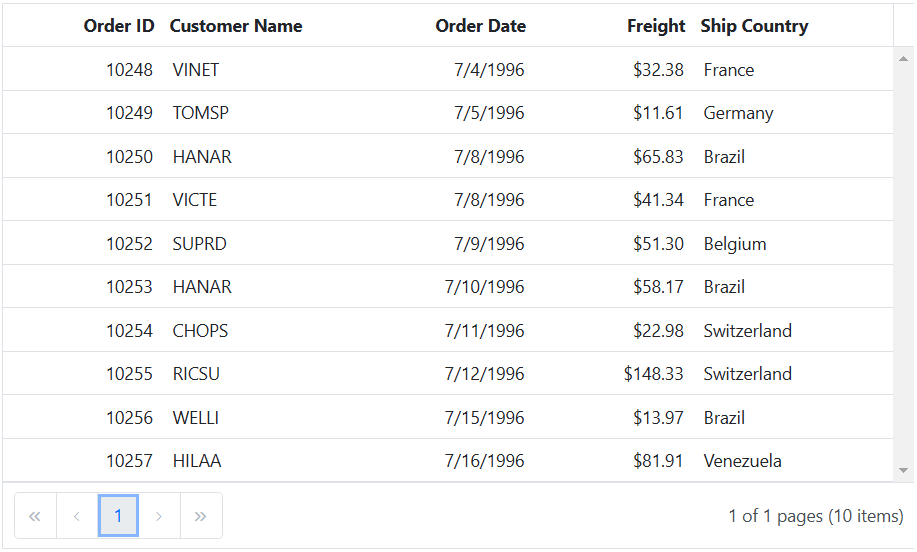
The following example demonstrates how to utilize the local data binding feature in the ASP.NET Core Grid:
<ejs-grid id="grid" dataSource="@ViewBag.DataSource" allowPaging="true" height="348px">
<e-grid-columns>
<e-grid-column field="OrderID" headerText="Order ID" textAlign="Right" width="120"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="CustomerID" headerText="Customer Name" width="150"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="OrderDate" headerText=" Order Date" textAlign="Right" format="yMd" width="130"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="Freight" headerText="Freight" textAlign="Right" format="C2" width="120"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="ShipCountry" headerText="Ship Country" width="150"></e-grid-column>
</e-grid-columns>
</ejs-grid>public void OnGet()
{
}
NOTE
- By default,
DataManagerusesJsonAdaptorfor list data-binding.
Data binding with SignalR
The Syncfusion ASP.NET Core Grid provides support for real-time data binding using SignalR, allowing you to update the Grid automatically as data changes on the server-side. This feature is particularly useful for applications requiring live updates and synchronization across multiple clients.
To achieve real-time data binding with SignalR in your Grid, follow the steps below:
Step 1: To create a new ASP.NET Core Web App(Razor Pages) project named signalR, follow these steps:
- Open Visual Studio.
- Select “Create a new project”
- Choose ASP.NET Core Web App(Razor Pages) project template.
- Name the project signalR.
- Click “Create”
Step 2: Create a simple Grid by following the Getting Started documentation link.
Step 3: Install the SignalR Client Library by following these steps:
-
In Solution Explorer, right-click the project and choose Add > Client-Side Library.
-
In the Add Client-Side Library dialog:
- Choose unpkg as the provider.
- Type @microsoft/signalr@latest in the library field.
- Choose Select specific files, expand dist/browser, and check signalr.js and signalr.min.js.
- Specify wwwroot/js/signalr/* as the target location.
- Click Install.
Step 4: Add the Microsoft.AspNetCore.SignalR NuGet package to the project:
In Solution Explorer, right-click the project node and select Manage NuGet Packages. In the Browse tab, search for Microsoft.AspNetCore.SignalR and then select Install on the right to install the package.
Step 5: In the Index.cshtml.cs file, manage data operations such as fetching, updating, inserting, and deleting records. Add the following code to define methods for sending data updates to clients.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using Syncfusion.EJ2.Base;
using signalR.Models;
using System.Collections;
namespace signalR.Pages
{
public class IndexModel : PageModel
{
private readonly ILogger<IndexModel> _logger;
public IndexModel(ILogger<IndexModel> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
public void OnGet()
{
}
public JsonResult OnPostUrlDatasource([FromBody] DataManagerRequest dataManagerRequest)
{
IEnumerable DataSource = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords();
DataOperations operation = new DataOperations();
if (dataManagerRequest.Search != null && dataManagerRequest.Search.Count > 0)
{
DataSource = operation.PerformSearching(DataSource, dataManagerRequest.Search);
}
if (dataManagerRequest.Sorted != null && dataManagerRequest.Sorted.Count > 0)
{
DataSource = operation.PerformSorting(DataSource, dataManagerRequest.Sorted);
}
if (dataManagerRequest.Where != null && dataManagerRequest.Where.Count > 0)
{
DataSource = operation.PerformFiltering(DataSource, dataManagerRequest.Where, dataManagerRequest.Where[0].Operator);
}
int count = DataSource.Cast<OrdersDetails>().Count();
if (dataManagerRequest.Skip != 0)
{
DataSource = operation.PerformSkip(DataSource, dataManagerRequest.Skip);
}
if (dataManagerRequest.Take != 0)
{
DataSource = operation.PerformTake(DataSource, dataManagerRequest.Take);
}
return dataManagerRequest.RequiresCounts ? new JsonResult(new { result = DataSource, count = count }) : new JsonResult(DataSource);
}
public JsonResult OnPostGetdata()
{
IEnumerable DataSource = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords();
return new JsonResult(DataSource);
}
//update the record.
public JsonResult OnPostUpdate([FromBody] CRUDModel<OrdersDetails> value)
{
var ord = value.value;
OrdersDetails val = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Where(or => or.OrderID == ord.OrderID).FirstOrDefault();
val.OrderID = ord.OrderID;
val.EmployeeID = ord.EmployeeID;
val.CustomerID = ord.CustomerID;
val.Freight = ord.Freight;
val.OrderDate = ord.OrderDate;
val.ShipCity = ord.ShipCity;
val.ShipCountry = ord.ShipCountry;
return new JsonResult(value.value);
}
//Insert the record.
public JsonResult OnPostInsert([FromBody] CRUDModel<OrdersDetails> value)
{
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Insert(0, value.value);
return new JsonResult(value.value);
}
//Delete the record.
public JsonResult OnPostDelete([FromBody] CRUDModel<OrdersDetails> value)
{
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Remove(OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Where(or => or.OrderID == int.Parse(value.key.ToString())).FirstOrDefault());
return new JsonResult(value);
}
}
public class CRUDModel<T> where T : class
{
public string? action { get; set; }
public string? keyColumn { get; set; }
public object? key { get; set; }
public T? value { get; set; }
public List<T>? added { get; set; }
public List<T>? changed { get; set; }
public List<T>? deleted { get; set; }
public IDictionary<string, object>? @params { get; set; }
}
}Step 6: Create a model class named OrdersDetails.cs under the Models folder in the server-side project to represent the order data. Add the following code:
namespace signalR.Models
{
public class OrdersDetails
{
public static List<OrdersDetails> order = new List<OrdersDetails>();
public OrdersDetails()
{
}
public OrdersDetails(int OrderID, string CustomerId, int EmployeeId, double Freight, bool Verified, DateTime OrderDate, string ShipCity, string ShipName, string ShipCountry, DateTime ShippedDate, string ShipAddress)
{
this.OrderID = OrderID;
this.CustomerID = CustomerId;
this.EmployeeID = EmployeeId;
this.Freight = Freight;
this.ShipCity = ShipCity;
this.Verified = Verified;
this.OrderDate = OrderDate;
this.ShipName = ShipName;
this.ShipCountry = ShipCountry;
this.ShippedDate = ShippedDate;
this.ShipAddress = ShipAddress;
}
public static List<OrdersDetails> GetAllRecords()
{
if (order.Count() == 0)
{
int code = 10000;
for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++)
{
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 1, "ALFKI", i + 0, 2.3 * i, false, new DateTime(1991, 05, 15), "Berlin", "Simons bistro", "Denmark", new DateTime(1996, 7, 16), "Kirchgasse 6"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 2, "ANATR", i + 2, 3.3 * i, true, new DateTime(1990, 04, 04), "Madrid", "Queen Cozinha", "Brazil", new DateTime(1996, 9, 11), "Avda. Azteca 123"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 3, "ANTON", i + 1, 4.3 * i, true, new DateTime(1957, 11, 30), "Cholchester", "Frankenversand", "Germany", new DateTime(1996, 10, 7), "Carrera 52 con Ave. Bolívar #65-98 Llano Largo"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 4, "BLONP", i + 3, 5.3 * i, false, new DateTime(1930, 10, 22), "Marseille", "Ernst Handel", "Austria", new DateTime(1996, 12, 30), "Magazinweg 7"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 5, "BOLID", i + 4, 6.3 * i, true, new DateTime(1953, 02, 18), "Tsawassen", "Hanari Carnes", "Switzerland", new DateTime(1997, 12, 3), "1029 - 12th Ave. S."));
code += 5;
}
}
return order;
}
public int? OrderID { get; set; }
public string CustomerID { get; set; }
public int? EmployeeID { get; set; }
public double? Freight { get; set; }
public string ShipCity { get; set; }
public bool Verified { get; set; }
public DateTime OrderDate { get; set; }
public string ShipName { get; set; }
public string ShipCountry { get; set; }
public DateTime ShippedDate { get; set; }
public string ShipAddress { get; set; }
}
}Step 7: In your client-side code, establish a connection to the SignalR hub and configure Grid data binding in the Pages/Index.cshtml file. Add the following code:s
<script src="js/microsoft/signalr/dist/browser/signalr.js"></script>
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<ejs-grid id="grid" load="gridload" created="onCreated" actionComplete="actionComplete" height="348px" toolbar="@(new List<string>() { "Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Cancel", "Update" })">
<e-grid-editSettings allowAdding="true" allowDeleting="true" allowEditing="true" mode="Normal"></e-grid-editSettings>
<e-data-manager url="/Index?handler=UrlDatasource" insertUrl="/Index?handler=Insert" updateUrl="/Index?handler=Update" removeUrl="/Index?handler=Delete" adaptor="UrlAdaptor"></e-data-manager>
<e-grid-columns>
<e-grid-column field="OrderID" headerText="Order ID" isPrimaryKey="true" textAlign="Right" width="120"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="CustomerID" headerText="Customer ID" width="150"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="ShipCity" headerText="Ship City" width="150"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="ShipCountry" headerText="ShipCountry" width="150"></e-grid-column>
</e-grid-columns>
</ejs-grid>
<script>
function gridload() {
this.dataSource.dataSource.headers = [{ 'XSRF-TOKEN': document.querySelector('input[type="hidden"][name="__RequestVerificationToken"]').value }];
}
let connection = new signalR.HubConnectionBuilder().withUrl("/ChatHub").build();
function onCreated() {
connection.on("ReceiveMessage", (message) => {
var grid = document.getElementById("grid").ej2_instances[0];
if (grid) {
grid.refresh();
}
});
connection.start()
.then(() => {
console.log("SignalR connection established successfully");
connection.invoke('SendMessage', "refreshPages")
.catch((err) => {
console.error("Error sending data:", err.toString());
});
})
.catch((err) => {
console.error("Error establishing SignalR connection:", err.toString());
});
}
function actionComplete(args) {
if (args.requestType === "save" || args.requestType === "delete") {
connection.invoke('SendMessage', "refreshPages")
.catch((err) => {
console.error(err.toString());
});
}
}
</script>Step 8: Create a SignalR hub on the server-side to manage communication between clients and the server. You can create a ChatHub.cs file under the Hubs folder. Add the following code to define methods for sending data updates to clients:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.SignalR;
namespace signalR.Hubs
{
public class ChatHub:Hub
{
public async Task SendMessage(string message)
{
await Clients.All.SendAsync("ReceiveMessage", message);
}
}
}Step 9: Configure the SignalR server to route requests to the SignalR hub. In the Program.cs file, add the following code:
using signalR.Hubs;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddSignalR(); // Add SignalR services.
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
builder.Services.AddAntiforgery(o => o.HeaderName = "XSRF-TOKEN");
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.MapHub<ChatHub>("/chatHub"); // Map the ChatHub.
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapRazorPages();
app.Run();The following screenshot represents the addition, editing, and deletion operations performed, reflecting changes across all client sides:

You can find a complete sample for signalR on GitHub.
Binding data from excel file
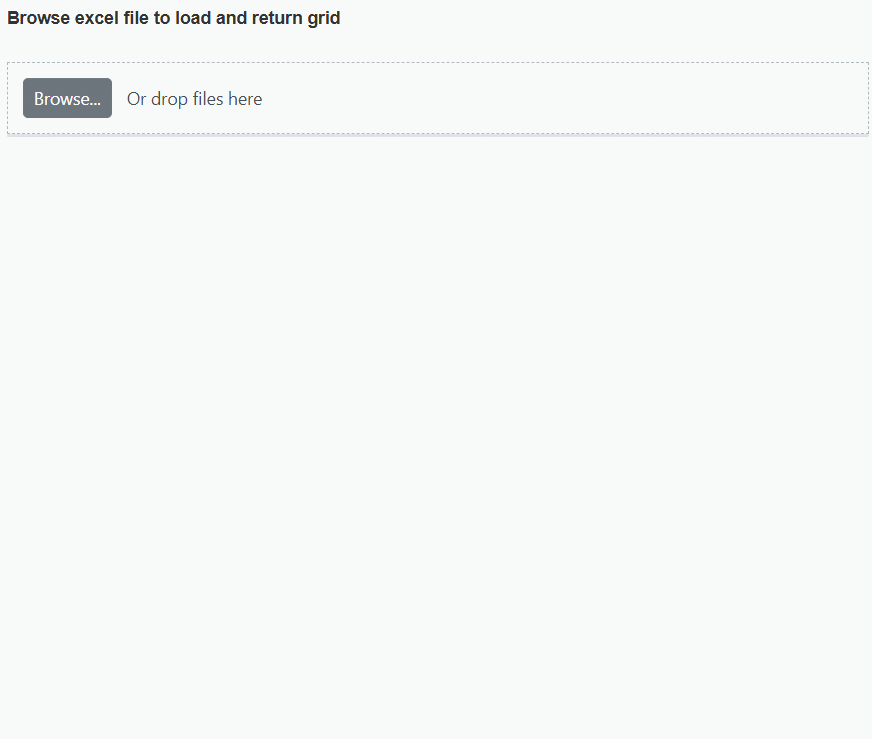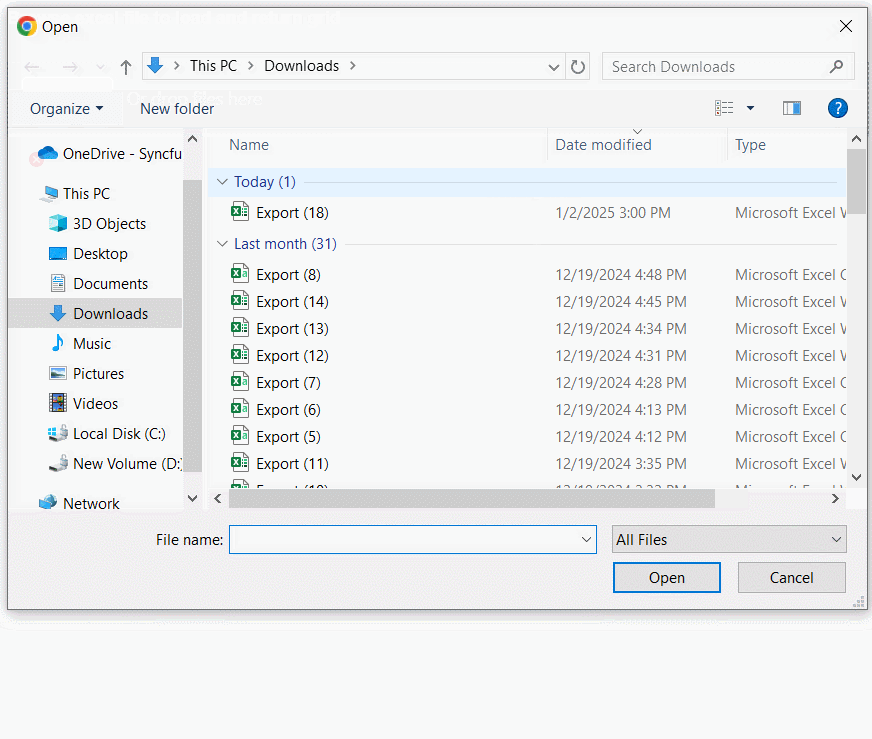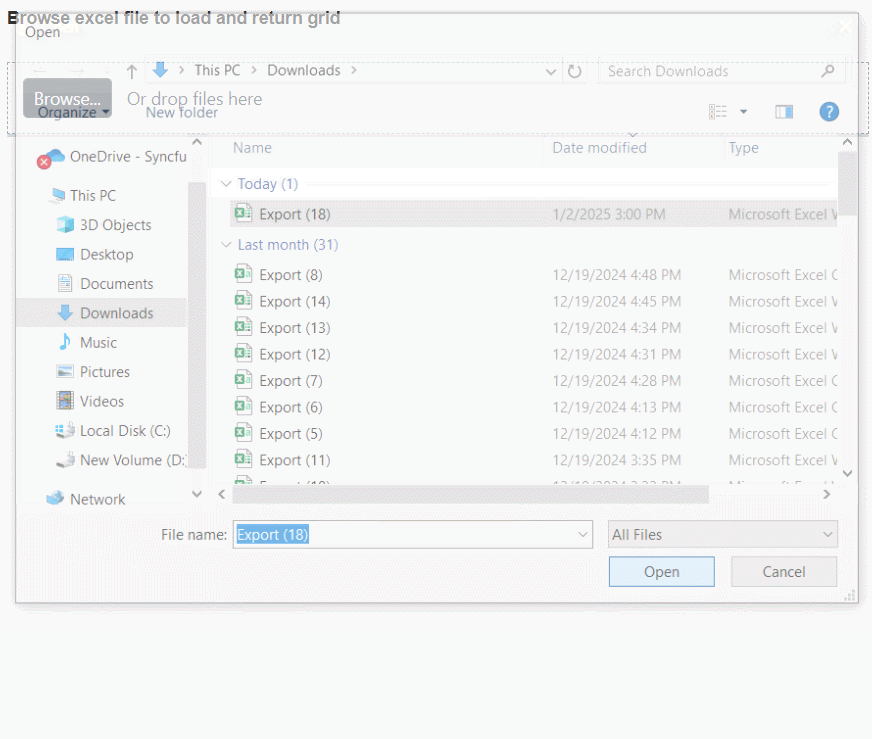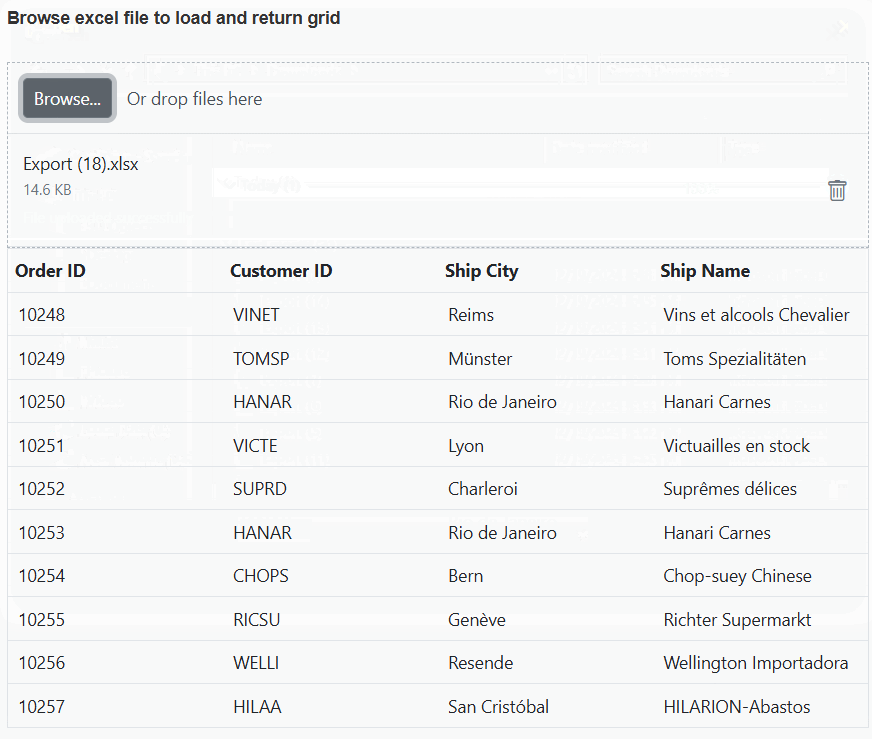
The Syncfusion ASP.NET Core Grid allows you to import data from Excel files into your web application for display and manipulation within the Grid. This feature streamlines the process of transferring Excel data to a web-based environment. This can be achieved by using uploader change event.
To import excel data in to Grid, you can follow these steps:
- Import excel file using Uploader.
- Parse the excel file data using XLSX library.
- Bind the JSON to the Grid.
The following example demonstrates how to import Excel data into the Grid by utilizing the Uploader change event along with the XLSX library:
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://unpkg.com/[email protected]/dist/xlsx.full.min.js"></script>
@{
var asyncSettings = new Syncfusion.EJ2.Inputs.UploaderAsyncSettings { SaveUrl = "https://services.syncfusion.com/aspnet/production/api/FileUploader/Save", RemoveUrl = "https://services.syncfusion.com/aspnet/production/api/FileUploader/Remove" };
}
<div>
<label style="font-weight: bold">Browse excel file to load and return grid</label>
<div style="padding:20px 0 0 0">
<ejs-uploader id="upload" removing="onRemove" change="onSuccess" asyncSettings="@asyncSettings"></ejs-uploader>
</div>
</div>
<ejs-grid id="grid"></ejs-grid>
<ejs-dialog id="dialog" header="Alert" showCloseIcon="true" content="Invalid JSON" visible="false" width="250px"></ejs-dialog>
<script>
function onRemove(args) {
var grid = document.getElementById("grid").ej2_instances[0];
grid.dataSource = [''];
grid.columns = [];
}
function onSuccess(args) {
var files = args.file;
if (files) {
parseExcel(files[0]);
}
}
function parseExcel(file) {
var grid = document.getElementById("grid").ej2_instances[0];
var dialog = document.getElementById("dialog").ej2_instances[0];
if (file && file.type == 'xlsx') {
var reader = new FileReader();
reader.onload = (e) => {
var data = (e.target).result;
var workbook = XLSX.read(data, { type: 'array' });
workbook.SheetNames.forEach((sheetName) => {
var XL_row_object = XLSX.utils.sheet_to_json(workbook.Sheets[sheetName]);
if (Array.isArray(XL_row_object) && XL_row_object.length > 0) {
grid.dataSource = XL_row_object;
} else {
dialog.content = "Invalid JSON";
dialog.show();
}
});
};
reader.readAsArrayBuffer(file.rawFile);
} else {
dialog.content = 'Please upload only .xlsx format';
dialog.show();
}
}
</script>public void OnGet()
{
}
Binding data and performing CRUD actions via Fetch request
The Syncfusion ASP.NET Core Grid provides a seamless way to bind data from external sources using Fetch requests, facilitating CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations with data retrieved from a server. This feature is particularly valuable for sending data to a server for database updates and asynchronously retrieving data without refreshing the entire web page
To achieve data binding and perform CRUD actions using Fetch requests in the Grid, follow these steps:
Step 1: To create a new ASP.NET Core Web App(Razor Pages) project named FetchRequest, follow these steps:
- Open Visual Studio.
- Select “Create a new project”
- Choose ASP.NET Core Web App(Razor Pages) project template.
- Name the project FetchRequest.
- Click “Create”
Step 2: Create a simple Grid by following the Getting Started documentation link.
Step 3: In the Pages/Index.cshtml file, follow the steps below.
A. To bind data from an external Fetch request, utilize the dataSource property of the Grid. Fetch data from the server and provide it to the dataSource property using the onSuccess event of the Fetch request.
B. To perform CRUD actions, leverage the actionBegin event. You can cancel the default CRUD operations by utilizing the cancel argument provided by this event. This allows you to dynamically call your server-side method using Fetch, along with the relevant data received from the actionBegin event, to update your server data accordingly.
C. In the Fetch success event, you have the flexibility to utilize the Grid endEdit and deleteRecord methods to handle the addition, editing, and deletion of corresponding data in the Grid. However, invoking these methods triggers the actionBegin event once again to save the changes in the Grid. To prevent this behavior and maintain control over the execution flow, you can employ a flag variable and manage it within the actionComplete and Fetch failure events: The following code snippet demonstrates this approach:
@{
string fullUrl = $"{Request.Scheme}://{Request.Host}{Request.PathBase}{Request.Path}";
}
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<div style="padding: 10px 0px 20px 0px">
<ejs-button id="sample" cssClass="e-success" content="Bind data via Fetch"></ejs-button>
</div>
<ejs-grid id="grid" height="348px" actionComplete="actionComplete" actionBegin="actionBegin" toolbar="@(new List<string>() { "Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Cancel", "Update" })">
<e-grid-editSettings allowAdding="true" allowDeleting="true" allowEditing="true"></e-grid-editSettings>
<e-grid-columns>
<e-grid-column field="OrderID" headerText="Order ID" isPrimaryKey="true" textAlign="Right" width="120"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="CustomerID" headerText="Customer Name" width="150"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="ShipCity" headerText="Ship City" width="150"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="ShipCountry" headerText="ShipCountry" width="150"></e-grid-column>
</e-grid-columns>
</ejs-grid>
<script>
let flag = false;
document.getElementById('sample').onclick = function () {
var grid = document.getElementById("grid").ej2_instances[0];
const fetchRequest = new ej.base.Fetch({
url: '@fullUrl?handler=Getdata',
type: "POST",
beforeSend: function (args) {
args.fetchRequest.headers.set('XSRF-TOKEN', document.querySelector('input[type = "hidden"][name = "__RequestVerificationToken"]').value);
},
});
fetchRequest.send();
fetchRequest.onSuccess = (data) => {
grid.dataSource = data;
};
};
function actionComplete(e) {
if (e.requestType === 'save' || e.requestType === 'delete') {
flag = false;
}
}
function actionBegin(e) {
var grid = document.getElementById("grid").ej2_instances[0];
if (!flag) {
if (e.requestType == 'save' && (e.action == 'add')) {
var editedData = e.data;
e.cancel = true;
var fetchRequest = new ej.base.Fetch({
url: '@fullUrl?handler=Insert',
type: 'POST',
beforeSend: function (args) {
args.fetchRequest.headers.set('XSRF-TOKEN', document.querySelector('input[type = "hidden"][name = "__RequestVerificationToken"]').value);
},
contentType: 'application/json; charset=utf-8',
data: JSON.stringify({ value: editedData })
});
fetchRequest.onSuccess = () => {
flag = true;
grid.endEdit();
};
fetchRequest.onFailure = () => {
flag = false;
};
fetchRequest.send();
}
if (e.requestType == 'save' && (e.action == "edit")) {
var editedData = e.data;
e.cancel = true;
var fetchRequest = new ej.base.Fetch({
url: '@fullUrl?handler=Update',
type: 'POST',
beforeSend: function (args) {
args.fetchRequest.headers.set('XSRF-TOKEN', document.querySelector('input[type = "hidden"][name = "__RequestVerificationToken"]').value);
},
contentType: 'application/json; charset=utf-8',
data: JSON.stringify({ value: editedData })
});
fetchRequest.onSuccess = () => {
flag = true;
grid.endEdit();
};
fetchRequest.onFailure = () => {
flag = false;
};
fetchRequest.send();
}
if (e.requestType == 'delete') {
var editedData = e.data;
e.cancel = true;
var fetchRequest = new ej.base.Fetch({
url: '@fullUrl?handler=Delete',
type: 'POST',
beforeSend: function (args) {
args.fetchRequest.headers.set('XSRF-TOKEN', document.querySelector('input[type = "hidden"][name = "__RequestVerificationToken"]').value);
},
contentType: 'application/json; charset=utf-8',
data: JSON.stringify({ key: editedData[0][grid.getPrimaryKeyFieldNames()[0]] })
});
fetchRequest.onSuccess = () => {
flag = true;
grid.deleteRecord();
};
fetchRequest.onFailure = () => {
flag = false;
};
fetchRequest.send();
}
}
}
</script>Step 5: In the Index.cshtml.cs file, there is a method named OnPostGetdata that provides the data source for the Grid. When the button is clicked, an Fetch request is sent to retrieve the data from the server and bind it to the Grid. Additionally, implement server-side logic to perform add, edit, and delete operations. Add the following code:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using System.Collections;
using FetchRequest.Models;
namespace FetchRequest.Pages
{
public class IndexModel : PageModel
{
public void OnGet()
{
}
public ActionResult OnPostGetdata()
{
IEnumerable DataSource = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords();
return new JsonResult(DataSource);
}
public ActionResult OnPostUpdate([FromBody] CRUDModel<OrdersDetails> value)
{
var ord = value.value;
OrdersDetails val = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Where(or => or.OrderID == ord.OrderID).FirstOrDefault();
val.OrderID = ord.OrderID;
val.EmployeeID = ord.EmployeeID;
val.CustomerID = ord.CustomerID;
val.Freight = ord.Freight;
val.OrderDate = ord.OrderDate;
val.ShipCity = ord.ShipCity;
val.ShipCountry = ord.ShipCountry;
return new JsonResult(value.value);
}
//Insert the record.
public ActionResult OnPostInsert([FromBody] CRUDModel<OrdersDetails> value)
{
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Insert(0, value.value);
return new JsonResult(value.value);
}
//Delete the record.
public ActionResult OnPostDelete(int key)
{
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Remove(OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Where(or => or.OrderID == key).FirstOrDefault());
var data = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords();
return new JsonResult(data);
}
public class CRUDModel<T> where T : class
{
public string action { get; set; }
public string table { get; set; }
public string keyColumn { get; set; }
public object key { get; set; }
public T value { get; set; }
public List<T> added { get; set; }
public List<T> changed { get; set; }
public List<T> deleted { get; set; }
public IDictionary<string, object> @params { get; set; }
}
}
}Step 6: Create a model class named OrdersDetails.cs under the Models folder in the server-side project to represent the order data. Add the following code:
namespace FetchRequest.Models
{
public class OrdersDetails
{
public static List<OrdersDetails> order = new List<OrdersDetails>();
public OrdersDetails()
{
}
public OrdersDetails(int OrderID, string CustomerId, int EmployeeId, double Freight, bool Verified, DateTime OrderDate, string ShipCity, string ShipName, string ShipCountry, DateTime ShippedDate, string ShipAddress)
{
this.OrderID = OrderID;
this.CustomerID = CustomerId;
this.EmployeeID = EmployeeId;
this.Freight = Freight;
this.ShipCity = ShipCity;
this.Verified = Verified;
this.OrderDate = OrderDate;
this.ShipName = ShipName;
this.ShipCountry = ShipCountry;
this.ShippedDate = ShippedDate;
this.ShipAddress = ShipAddress;
}
public static List<OrdersDetails> GetAllRecords()
{
if (order.Count() == 0)
{
int code = 10000;
for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++)
{
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 1, "ALFKI", i + 0, 2.3 * i, false, new DateTime(1991, 05, 15), "Berlin", "Simons bistro", "Denmark", new DateTime(1996, 7, 16), "Kirchgasse 6"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 2, "ANATR", i + 2, 3.3 * i, true, new DateTime(1990, 04, 04), "Madrid", "Queen Cozinha", "Brazil", new DateTime(1996, 9, 11), "Avda. Azteca 123"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 3, "ANTON", i + 1, 4.3 * i, true, new DateTime(1957, 11, 30), "Cholchester", "Frankenversand", "Germany", new DateTime(1996, 10, 7), "Carrera 52 con Ave. Bolívar #65-98 Llano Largo"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 4, "BLONP", i + 3, 5.3 * i, false, new DateTime(1930, 10, 22), "Marseille", "Ernst Handel", "Austria", new DateTime(1996, 12, 30), "Magazinweg 7"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 5, "BOLID", i + 4, 6.3 * i, true, new DateTime(1953, 02, 18), "Tsawassen", "Hanari Carnes", "Switzerland", new DateTime(1997, 12, 3), "1029 - 12th Ave. S."));
code += 5;
}
}
return order;
}
public int? OrderID { get; set; }
public string CustomerID { get; set; }
public int? EmployeeID { get; set; }
public double? Freight { get; set; }
public string ShipCity { get; set; }
public bool Verified { get; set; }
public DateTime OrderDate { get; set; }
public string ShipName { get; set; }
public string ShipCountry { get; set; }
public DateTime ShippedDate { get; set; }
public string ShipAddress { get; set; }
}
}Step 9: In the Program.cs file, add the following code:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
builder.Services.AddAntiforgery(o => o.HeaderName = "XSRF-TOKEN");
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapRazorPages();
app.Run();The following screenshot represents loading data when the button is clicked and CRUD operations are performed:

You can find a complete sample for Fetch request on GitHub.
Display the loading indicator with local data
The Syncfusion ASP.NET Core Grid allows you to display a loading indicator while loading local data. This feature is useful when there is a delay in loading data from a local source, and you want to inform the you that the data is being fetched.
To display the loading indicator with local data, you need to set the showSpinner property to true. This property controls the visibility of the loading indicator.
The following example demonstrates how to display the loading indicator in the Grid using the load and created events:
@using Newtonsoft.Json;
<ejs-grid id="grid" height="348px" load="load" created="created" allowPaging="true">
<e-grid-columns>
<e-grid-column field="OrderID" headerText="Order ID" textAlign="Right" width="120"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="CustomerID" headerText="Customer Name" width="150"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="Freight" headerText="Freight" textAlign="Right" format="C2" width="120"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="ShipCity" headerText="Ship City" width="150"></e-grid-column>
</e-grid-columns>
</ejs-grid>
<script>
var isDataLoading =true
var data = JSON.parse('@Html.Raw(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(ViewBag.DataSource))');
function load() {
var grid = document.getElementById("grid").ej2_instances[0];
if (isDataLoading) {
grid.showSpinner();
}
}
function created(){
var grid = document.getElementById("grid").ej2_instances[0];
isDataLoading = true;
grid.dataSource = data;
}
</script>public void OnGet()
{
ViewData["DataSource"] = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords();
}Binding data and performing CRUD actions via AJAX request
The Syncfusion ASP.NET Core Grid provides a seamless way to bind data from external sources using AJAX requests, facilitating CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations with data retrieved from a server. This feature is particularly valuable for sending data to a server for database updates and asynchronously retrieving data without refreshing the entire web page
To achieve data binding and perform CRUD actions using AJAX requests in the Grid, follow these steps:
Step 1: To create a new ASP.NET Core Web App(Razor Pages) project named AJAX Request, follow these steps:
- Open Visual Studio.
- Select “Create a new project”
- Choose ASP.NET Core Web App(Razor Pages) project template.
- Name the project AJAXRequest.
- Click “Create”
Step 2: Create a simple Grid by following the Getting Started documentation link.
Step 3: In the Pages/Index.cshtml file, follow the steps below.
A. To bind data from an external AJAX request, utilize the dataSource property of the Grid. Get data from the server and provide it to the dataSource property using the onSuccess event of the AJAX request.
B. To perform CRUD actions, leverage the actionBegin event. You can cancel the default CRUD operations by utilizing the cancel argument provided by this event. This allows you to dynamically call your server-side method using Fetch, along with the relevant data received from the actionBegin event, to update your server data accordingly.
C. In the AJAX success event, you have the flexibility to utilize the Grid endEdit and deleteRecord methods to handle the addition, editing, and deletion of corresponding data in the Grid. However, invoking these methods triggers the actionBegin event once again to save the changes in the Grid. To prevent this behavior and maintain control over the execution flow, you can employ a flag variable and manage it within the actionComplete and AJAX failure events: The following code snippet demonstrates this approach:
@{
string fullUrl = $"{Request.Scheme}://{Request.Host}{Request.PathBase}{Request.Path}";
}
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<div style="padding: 10px 0px 20px 0px">
<ejs-button id="sample" cssClass="e-success" content="Bind data via ajax"></ejs-button>
</div>
<ejs-grid id="grid" height="348px" actionComplete="actionComplete" actionBegin="actionBegin" toolbar="@(new List<string>() { "Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Cancel", "Update" })">
<e-grid-editSettings allowAdding="true" allowDeleting="true" allowEditing="true" mode="Normal"></e-grid-editSettings>
<e-grid-columns>
<e-grid-column field="OrderID" headerText="Order ID" isPrimaryKey="true" textAlign="Right" width="120"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="CustomerID" headerText="Customer ID" width="150"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="ShipCity" headerText="Ship City" width="150"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="ShipCountry" headerText="ShipCountry" width="150"></e-grid-column>
</e-grid-columns>
</ejs-grid>
<script>
let flag = false;
document.getElementById('sample').onclick = function () {
var grid = document.getElementById("grid").ej2_instances[0];
const ajax = new ej.base.Ajax({
url: '@fullUrl?handler=Getdata',
type: "POST",
beforeSend: function (xhr) {
ajax.httpRequest.setRequestHeader("XSRF-TOKEN",document.querySelector('input[type="hidden"][name="__RequestVerificationToken"]').value);
},
contentType: "application/json",
});
ajax.send();
ajax.onSuccess = (data) => {
grid.dataSource = JSON.parse(data);
};
};
function actionComplete(e) {
if (e.requestType === 'save' || e.requestType === 'delete') {
flag = false;
}
}
function actionBegin(e) {
var grid = document.getElementById("grid").ej2_instances[0];
if (!flag) {
if (e.requestType == 'save' && (e.action == 'add')) {
var editedData = e.data;
e.cancel = true;
var ajax = new ej.base.Ajax({
url: '@fullUrl?handler=Insert',
type: 'POST',
beforeSend: function (xhr) {
ajax.httpRequest.setRequestHeader("XSRF-TOKEN",document.querySelector('input[type="hidden"][name="__RequestVerificationToken"]').value);
},
contentType: 'application/json; charset=utf-8',
data: JSON.stringify({ value: editedData })
});
ajax.onSuccess = () => {
flag = true;
grid.endEdit();
};
ajax.onFailure = () => {
flag = false;
};
ajax.send();
}
if (e.requestType == 'save' && (e.action == "edit")) {
var editedData = e.data;
e.cancel = true;
var ajax = new ej.base.Ajax({
url: '@fullUrl?handler=Update',
type: 'POST',
beforeSend: function (xhr) {
ajax.httpRequest.setRequestHeader("XSRF-TOKEN",document.querySelector('input[type="hidden"][name="__RequestVerificationToken"]').value);
},
contentType: 'application/json; charset=utf-8',
data: JSON.stringify({ value: editedData })
});
ajax.onSuccess = () => {
flag = true;
grid.endEdit();
};
ajax.onFailure = () => {
flag = false;
};
ajax.send();
}
if (e.requestType == 'delete') {
var editedData = e.data;
e.cancel = true;
var ajax = new ej.base.Ajax({
url: '@fullUrl?handler=Delete',
beforeSend: function (xhr) {
ajax.httpRequest.setRequestHeader("XSRF-TOKEN",document.querySelector('input[type="hidden"][name="__RequestVerificationToken"]').value);
},
type: 'POST',
contentType: 'application/json; charset=utf-8',
data: JSON.stringify({ key: editedData[0][grid.getPrimaryKeyFieldNames()[0]] })
});
ajax.onSuccess = () => {
flag = true;
grid.deleteRecord();
};
ajax.onFailure = () => {
flag = false;
};
ajax.send();
}
}
}
</script>Step 5: In the Index.cshtml.cs file, there is a method named OnPostGetdata that provides the data source for the Grid. When the button is clicked, an AJAX request is sent to retrieve the data from the server and bind it to the Grid. Additionally, implement server-side logic to perform add, edit, and delete operations. Add the following code:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using System.Collections;
using AJAXRequest.Models;
namespace AJAXRequest.Pages
{
public class IndexModel : PageModel
{
public void OnGet()
{
}
public ActionResult OnPostGetdata()
{
IEnumerable DataSource = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords();
return new JsonResult(DataSource);
}
public ActionResult OnPostUpdate([FromBody] CRUDModel<OrdersDetails> value)
{
var ord = value.value;
OrdersDetails val = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Where(or => or.OrderID == ord.OrderID).FirstOrDefault();
val.OrderID = ord.OrderID;
val.EmployeeID = ord.EmployeeID;
val.CustomerID = ord.CustomerID;
val.Freight = ord.Freight;
val.OrderDate = ord.OrderDate;
val.ShipCity = ord.ShipCity;
val.ShipCountry = ord.ShipCountry;
return new JsonResult(value.value);
}
//Insert the record.
public ActionResult OnPostInsert([FromBody] CRUDModel<OrdersDetails> value)
{
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Insert(0, value.value);
return new JsonResult(value.value);
}
//Delete the record.
public ActionResult OnPostDelete(int key)
{
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Remove(OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Where(or => or.OrderID == key).FirstOrDefault());
var data = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords();
return new JsonResult(data);
}
public class CRUDModel<T> where T : class
{
public string action { get; set; }
public string table { get; set; }
public string keyColumn { get; set; }
public object key { get; set; }
public T value { get; set; }
public List<T> added { get; set; }
public List<T> changed { get; set; }
public List<T> deleted { get; set; }
public IDictionary<string, object> @params { get; set; }
}
}
}Step 6: Create a model class named OrdersDetails.cs under the Models folder in the server-side project to represent the order data. Add the following code:
namespace AJAXRequest.Models
{
public class OrdersDetails
{
public static List<OrdersDetails> order = new List<OrdersDetails>();
public OrdersDetails()
{
}
public OrdersDetails(int OrderID, string CustomerId, int EmployeeId, double Freight, bool Verified, DateTime OrderDate, string ShipCity, string ShipName, string ShipCountry, DateTime ShippedDate, string ShipAddress)
{
this.OrderID = OrderID;
this.CustomerID = CustomerId;
this.EmployeeID = EmployeeId;
this.Freight = Freight;
this.ShipCity = ShipCity;
this.Verified = Verified;
this.OrderDate = OrderDate;
this.ShipName = ShipName;
this.ShipCountry = ShipCountry;
this.ShippedDate = ShippedDate;
this.ShipAddress = ShipAddress;
}
public static List<OrdersDetails> GetAllRecords()
{
if (order.Count() == 0)
{
int code = 10000;
for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++)
{
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 1, "ALFKI", i + 0, 2.3 * i, false, new DateTime(1991, 05, 15), "Berlin", "Simons bistro", "Denmark", new DateTime(1996, 7, 16), "Kirchgasse 6"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 2, "ANATR", i + 2, 3.3 * i, true, new DateTime(1990, 04, 04), "Madrid", "Queen Cozinha", "Brazil", new DateTime(1996, 9, 11), "Avda. Azteca 123"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 3, "ANTON", i + 1, 4.3 * i, true, new DateTime(1957, 11, 30), "Cholchester", "Frankenversand", "Germany", new DateTime(1996, 10, 7), "Carrera 52 con Ave. Bolívar #65-98 Llano Largo"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 4, "BLONP", i + 3, 5.3 * i, false, new DateTime(1930, 10, 22), "Marseille", "Ernst Handel", "Austria", new DateTime(1996, 12, 30), "Magazinweg 7"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 5, "BOLID", i + 4, 6.3 * i, true, new DateTime(1953, 02, 18), "Tsawassen", "Hanari Carnes", "Switzerland", new DateTime(1997, 12, 3), "1029 - 12th Ave. S."));
code += 5;
}
}
return order;
}
public int? OrderID { get; set; }
public string CustomerID { get; set; }
public int? EmployeeID { get; set; }
public double? Freight { get; set; }
public string ShipCity { get; set; }
public bool Verified { get; set; }
public DateTime OrderDate { get; set; }
public string ShipName { get; set; }
public string ShipCountry { get; set; }
public DateTime ShippedDate { get; set; }
public string ShipAddress { get; set; }
}
}Step 9: In the Program.cs file, add the following code:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
builder.Services.AddAntiforgery(o => o.HeaderName = "XSRF-TOKEN");
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapRazorPages();
app.Run();The following screenshot represents loading data when the button is clicked and CRUD operations are performed:
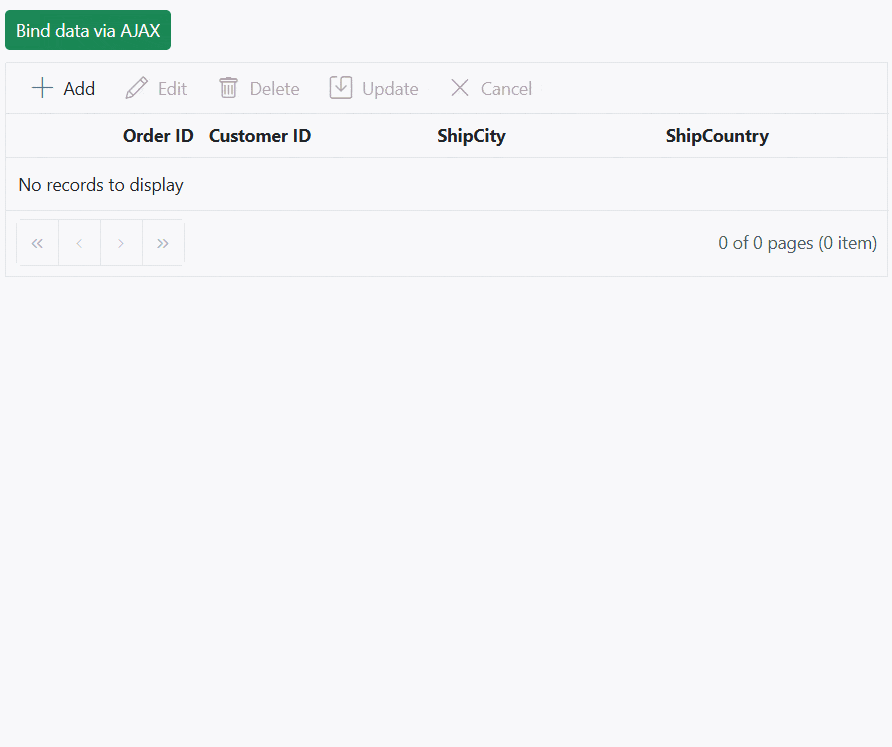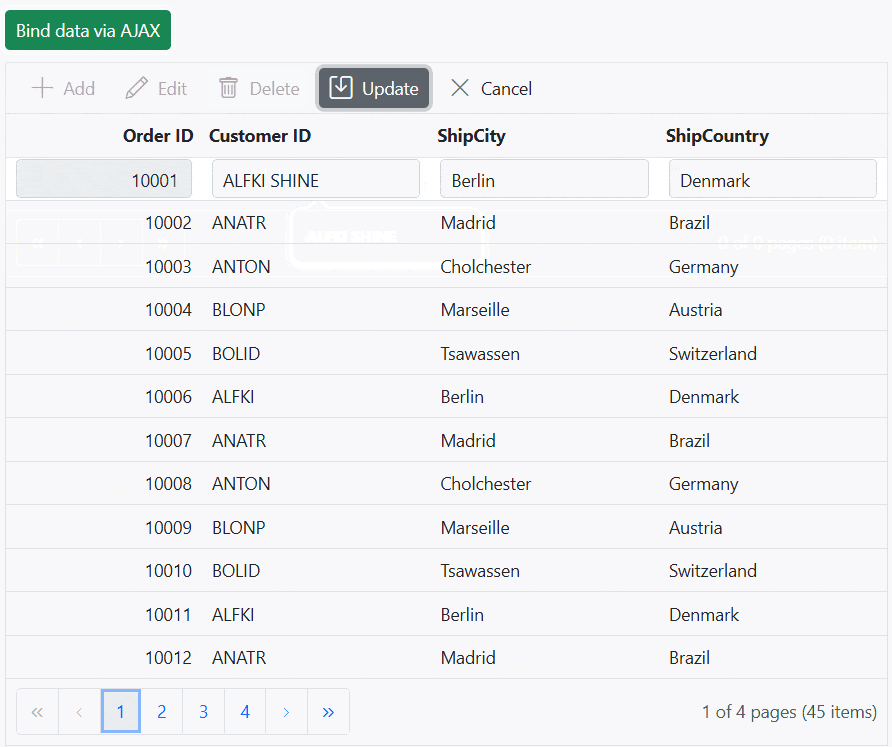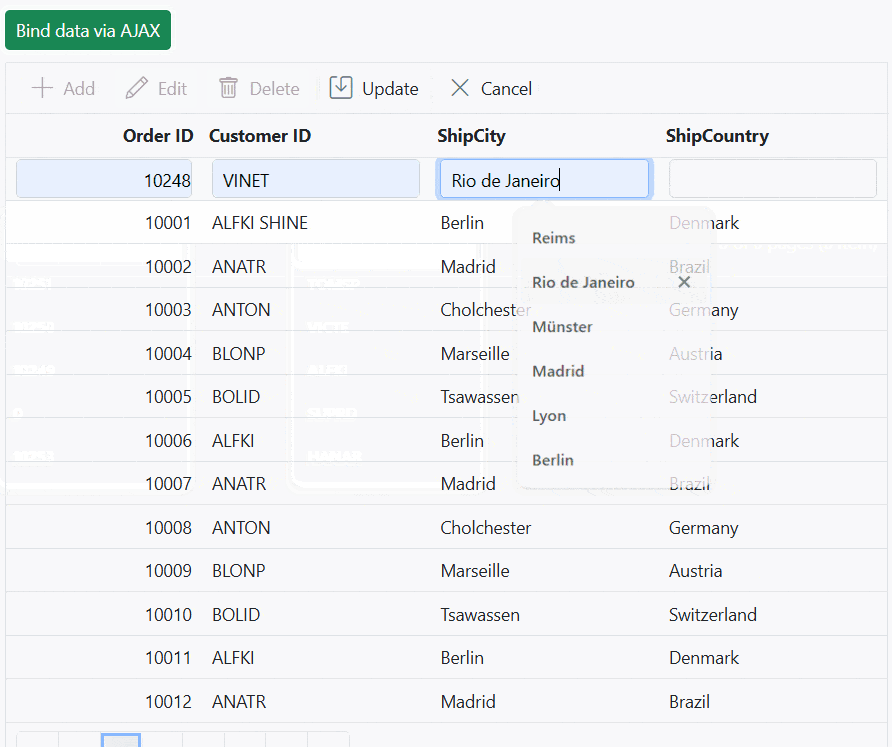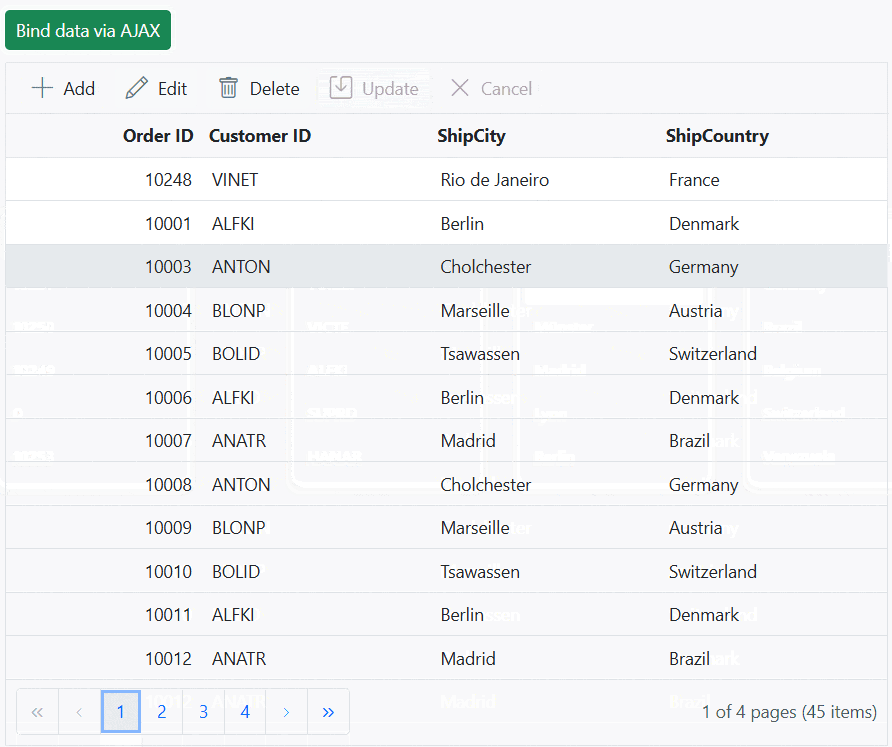
You can find a complete sample for AJAX request on GitHub.
Display the loading indicator using AJAX
The Syncfusion ASP.NET Core Grid allows you to display a loading indicator while loading data using AJAX. This feature is useful when there is a delay in loading data from data , and you want to inform the you that the data is being fetched. This is particularly beneficial when working with large datasets or under conditions of slower internet connections.
To display the loading indicator with local data, you need to set the showSpinner property to true. This property controls the visibility of the loading indicator.
The following example demonstrates how to display the loading indicator in the Grid using the load and created events:
<ejs-grid id="grid" height="348px" load="load" created="created">
<e-grid-columns>
<e-grid-column field="OrderID" headerText="Order ID" textAlign="Right" width="120"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="CustomerID" headerText="Customer Name" width="150"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="Freight" headerText="Freight" textAlign="Right" format="C2" width="120"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="ShipCity" headerText="Ship City" width="150"></e-grid-column>
</e-grid-columns>
</ejs-grid>
<script>
var isDataLoading =true
function load() {
var grid = document.getElementById("grid").ej2_instances[0];
if (isDataLoading) {
grid.showSpinner();
isDataLoading = false;
}
}
function created() {
var grid = document.getElementById("grid").ej2_instances[0];
isDataLoading = true;
const ajax = new ej.base.Ajax( 'https://services.syncfusion.com/aspnet/production/api/orders', 'GET');
ajax.send();
ajax.onSuccess = (data) => {
grid.dataSource = JSON.parse(data);
};
}
</script>public void OnGet()
{
}Managing spinner visibility during data loading
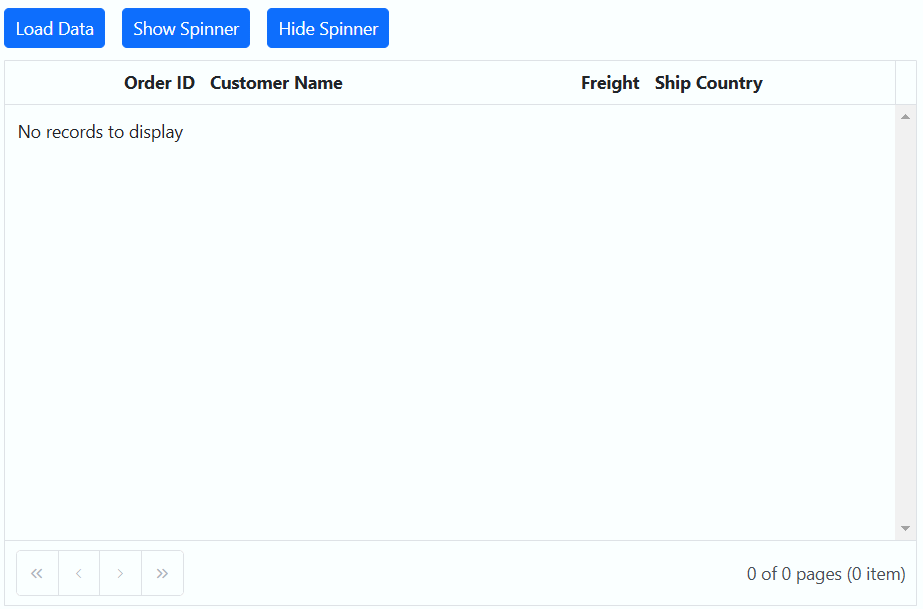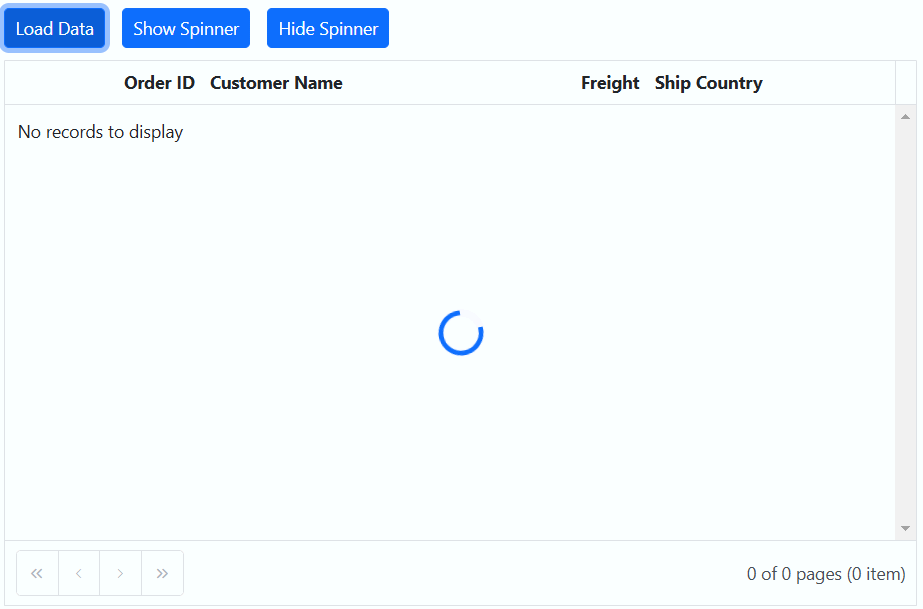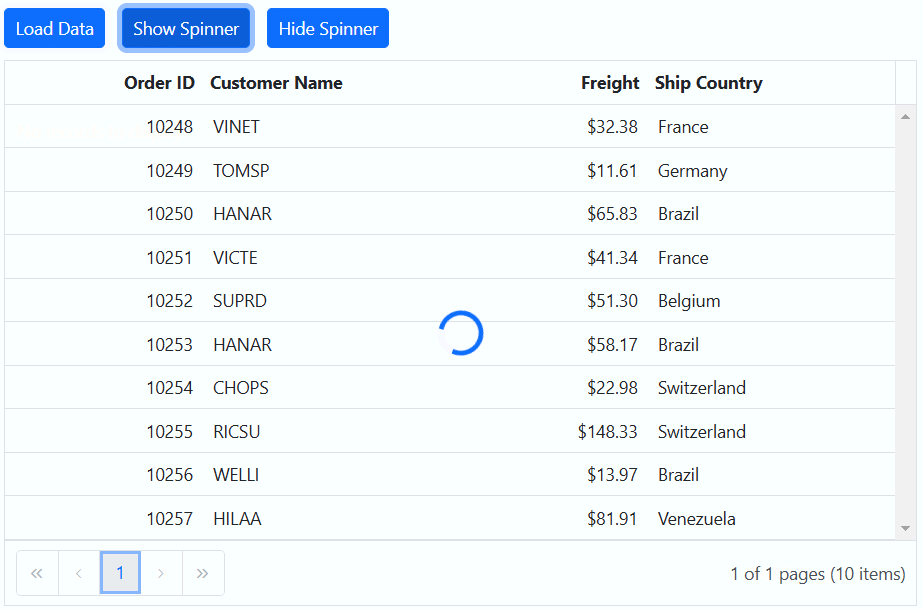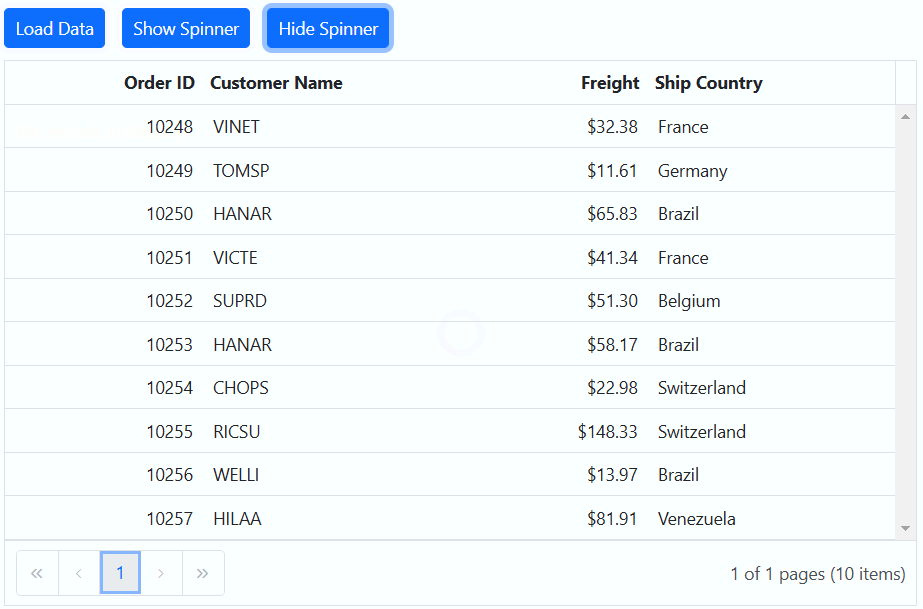
Showing a spinner during data loading in the Syncfusion ASP.NET Core Grid enhances the experience by providing a visual indication of the loading progress. This feature helps to understand that data is being fetched or processed.
To show or hide a spinner during data loading in the Grid, you can utilize the showSpinner and hideSpinner methods provided by the Grid.
The following example demonstrates how to show and hide the spinner during data loading using external buttons in a Grid:
@using Newtonsoft.Json
<div style="padding-bottom: 10px">
<ejs-button id="loadButton" cssClass="e-primary" content="Load Data"></ejs-button>
<ejs-button id="showButton" cssClass="e-primary custom" content="Show Spinner"></ejs-button>
<ejs-button id="hideButton" cssClass="e-primary custom" content="Hide Spinner"></ejs-button>
</div>
<ejs-grid id="grid" allowPaging="true" height="348px">
<e-grid-columns>
<e-grid-column field="OrderID" headerText="Order ID" textAlign="Right" width="120"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="CustomerID" headerText="Customer Name" width="150"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="Freight" headerText="Freight" textAlign="Right" format="C2" width="120"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="ShipCountry" headerText="Ship Country" width="150"></e-grid-column>
</e-grid-columns>
</ejs-grid>
<script>
document.getElementById('loadButton').onclick = handleButtonClick;
document.getElementById('showButton').onclick = handleButtonClick;
document.getElementById('hideButton').onclick = handleButtonClick;
function handleButtonClick(event){
var grid = document.getElementById("grid").ej2_instances[0];
if (event.target.id === "showButton") {
grid.showSpinner();
}
else if(event.target.id === "loadButton"){
grid.showSpinner();
setTimeout(() => {
grid.dataSource = @Html.Raw(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(ViewBag.DataSource));
grid.hideSpinner();
}, 1000);
}
else {
grid.hideSpinner();
}
}
</script>
<style>
.custom{
margin-left: 10px;
}
</style>public void OnGet()
{
ViewData["DataSource"] = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords();
}
Immutable mode
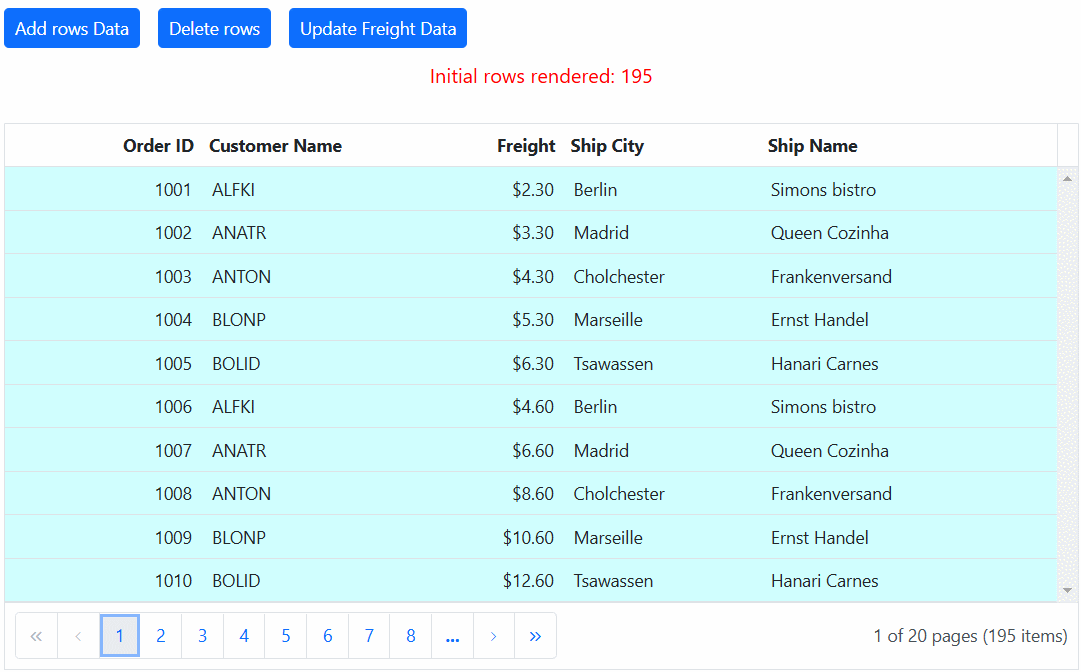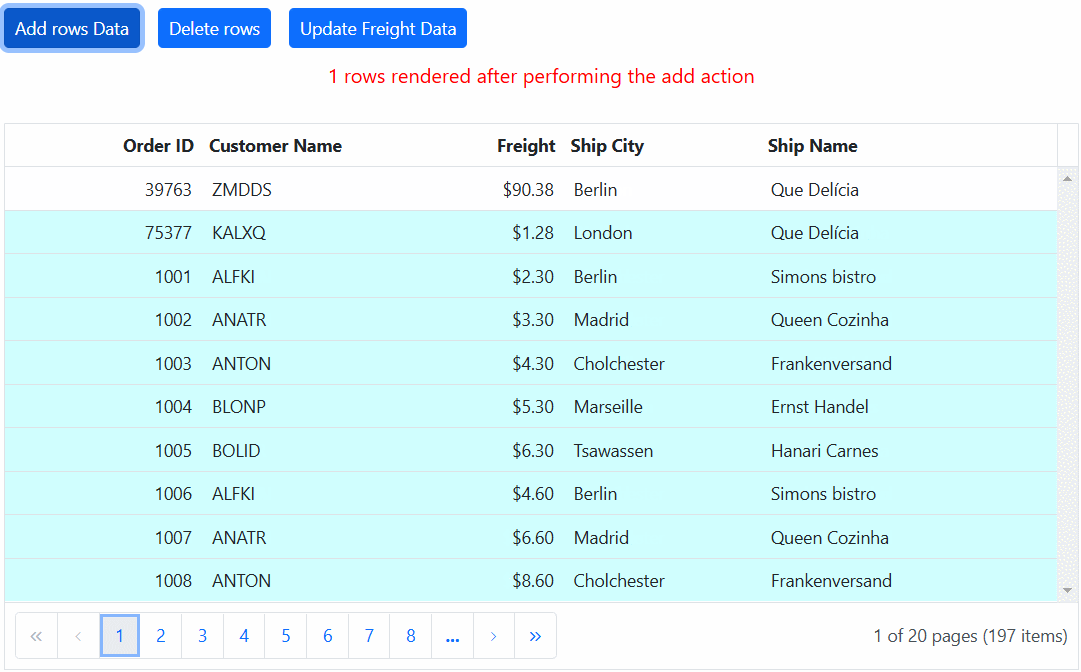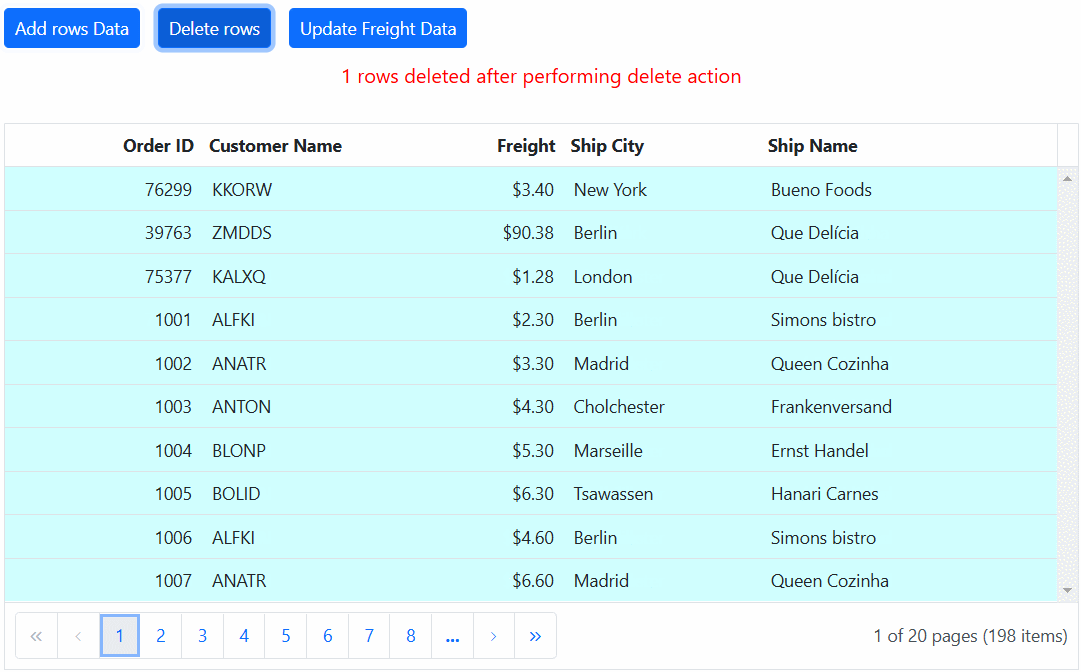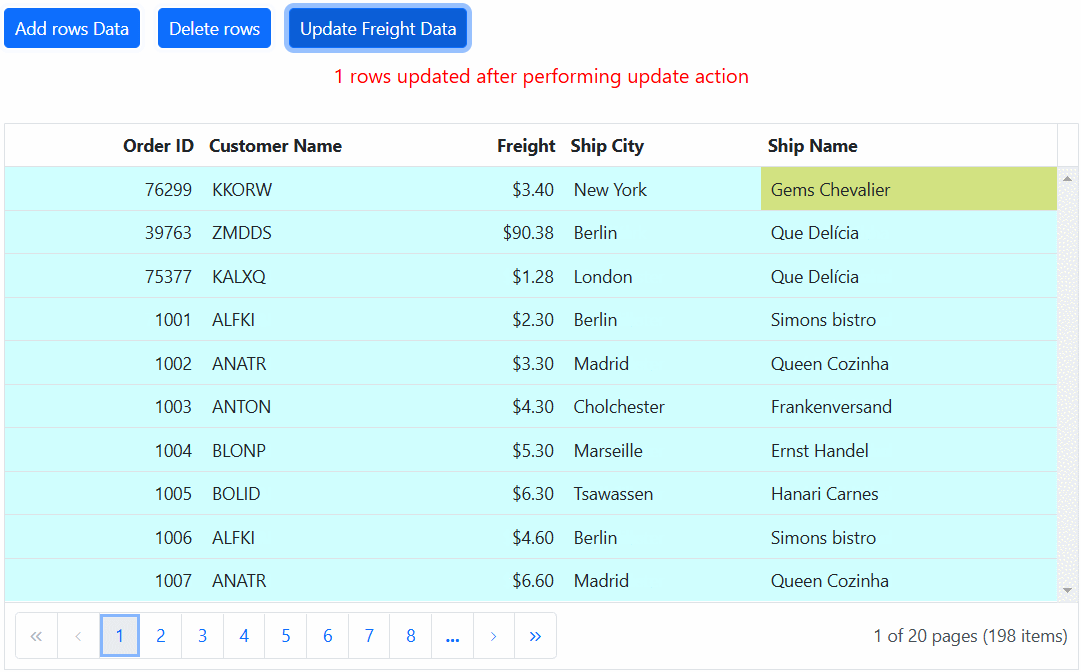
Immutable mode in the Syncfusion ASP.NET Core Grid is designed to optimize re-rendering performance by utilizing the object reference and deep compare concept. This mode ensures that when performing Grid actions, only the modified or newly added rows are re-rendered, preventing unnecessary re-rendering of unchanged rows.
To enable this feature, you need to set the enableImmutableMode property as true.
If immutable mode is enabled, when the datasource changes, only newly added rows are regenerated or reused. Consequently, the Grid queryCellInfo and rowDataBound events trigger only for newly generated rows, not for existing rows.
If immutable mode is not enabled, both newly added rows and existing rows are regenerated or reused when the datasource changes. As a result, the rowDataBound and queryCellInfo events trigger for both newly added and existing rows.
This feature uses the primary key value for data comparison. So, you need to provide the
isPrimaryKeycolumn.
The following example demonstrates how to enable immutable mode in an ASP.NET Core component. When add, delete, or update actions are performed, existing rows are not regenerated or reused, ensuring efficient rendering of only the modified or newly added rows:
@using Newtonsoft.Json;
<div style="padding-bottom: 10px">
<ejs-button id="addtop" cssClass="e-primary" content="Add rows Data"></ejs-button>
<ejs-button id="delete" cssClass="e-primary custom" content="Delete rows"></ejs-button>
<ejs-button id="update" cssClass="e-primary custom" content="Update Freight Data"></ejs-button>
</div>
<p style="color:red;text-align:center;padding-bottom:10px" id="message"></p>
<ejs-grid id="grid" dataSource="@ViewBag.DataSource" allowPaging="true" allowPaging="true" enableHover="true" enableImmutableMode="true" height="348px" load="load" rowDataBound="rowDataBound" queryCellInfo="queryCellInfo">
<e-grid-selectionsettings type="Multiple"></e-grid-selectionsettings>
<e-grid-pagesettings pageSize=10></e-grid-pagesettings>
<e-grid-columns>
<e-grid-column field="OrderID" headerText="Order ID" isPrimaryKey="true" textAlign="Right" width="120"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="CustomerID" headerText="Customer Name" width="150"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="Freight" headerText="Freight" width="150"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="ShipCity" headerText="Ship City" width="150"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="ShipName" headerText="Ship Name" width="150"></e-grid-column>
</e-grid-columns>
</ejs-grid>
<script>
var data = JSON.parse('@Html.Raw(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(ViewBag.DataSource))');
document.getElementById('addtop').onclick = handleButtonClick;
document.getElementById('delete').onclick = handleButtonClick;
document.getElementById('update').onclick = handleButtonClick;
function load(){
document.getElementById("message").innerText = `Initial rows rendered: ${data.length}`;
}
function queryCellInfo(args) {
if ( args.column.field === 'ShipName' && args.data.ShipName === 'Gems Chevalier') {
args.cell.style.backgroundColor = 'rgb(210, 226, 129)';
}
}
function rowDataBound (args) {
args.row.style.backgroundColor = args.data.isNewlyAdded ? '' : 'rgb(208, 255, 255)';
}
function handleButtonClick(event){
var grid = document.getElementById("grid").ej2_instances[0];
if (event.target.id === "addtop") {
grid.getAllDataRows().forEach(row => {
row.style.backgroundColor = 'rgb(208, 255, 255)';
});
var count = 0;
if (count < 1) {
var newRowData = [];
var addedRecords = {
OrderID: generateOrderId(),
CustomerID: generateCustomerId(),
ShipCity: generateShipCity(),
Freight: generateFreight(),
ShipName: generateShipName(),
isNewlyAdded: true,
};
newRowData.push(addedRecords);
grid.dataSource = [...newRowData, ...grid.dataSource];
count++;
document.getElementById("message").innerText = count + ' rows rendered after performing the add action';
}
}else if(event.target.id === "delete")
{
var count = 0;
if (count < 1 && data.length > 0) {
grid.dataSource = grid.dataSource.slice(1);
count++;
document.getElementById("message").innerText = count + ' rows deleted after performing delete action';
}
}else {
var count = 0;
var newRowData = grid.dataSource.map(function (row) {
if (row.ShipName === 'Bueno Foods') {
count++;
return { ...row, ShipName: 'Gems Chevalier' };
} else {
return row;
}
});
grid.dataSource = newRowData;
document.getElementById("message").innerText = count + ' rows updated after performing update action';
}
}
function generateOrderId() {
return Math.floor(10000 + Math.random() * 90000);
}
function generateCustomerId() {
var characters = 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ';
var result = '';
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
result += characters.charAt(Math.floor(Math.random() * characters.length));
}
return result;
}
function generateFreight() {
var randomValue = Math.random() * 100;
return parseFloat(randomValue.toFixed(2));
}
function generateShipCity() {
var cities = ['London', 'Paris', 'New York', 'Tokyo', 'Berlin'];
return cities[Math.floor(Math.random() * cities.length)];
}
function generateShipName() {
var names = ['Que Delícia', 'Bueno Foods', 'Island Trading', 'Laughing Bacchus Winecellars'];
return names[Math.floor(Math.random() * names.length)];
}
</script>
<style>
.custom{
margin-left: 10px;
}
</style>public void OnGet()
{
ViewData["DataSource"] = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords();
}
ExpandoObject binding
The Syncfusion ASP.NET Core Grid is typically bound to a specific model type. However, there are scenarios where the model type is unknown during compile time. In such cases, you can bind data to the Grid using a list of ExpandoObject. This allows for dynamic data structures that can adapt to various data shapes without a predefined schema.
To bind an ExpandoObject to the Grid, you need to assign it to the dataSource property. The Grid supports various data operations such as sorting, filtering, and editing when using ExpandoObject.
The following sample demonstrates ExpandoObject binding:
<ejs-grid id="grid" dataSource="ViewBag.ExpandoData" allowPaging="true" allowSorting="true" allowFiltering="true" toolbar="@(new List<string>() {"Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Update", "Cancel"})">
<e-grid-editSettings allowAdding="true" allowDeleting="true" allowEditing="true" mode="Normal"></e-grid-editSettings>
<e-grid-pageSettings pageSize=10> </e-grid-pageSettings>
<e-grid-columns>
<e-grid-column field="OrderID" headerText="Order ID" isPrimaryKey="true" validationRules="@(new { required=true, number=true})" width="140"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="CustomerID" headerText="Customer Name" validationRules="@(new { required=true})" width="150"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="Freight" headerText="Freight" validationRules="@(new { required=true})" textAlign="Right" editType="numericedit" format="C2" width="140"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="ShipCountry" headerText="Ship Country" editType="dropdownedit" width="150"></e-grid-column>
</e-grid-columns>
</ejs-grid>public static List<ExpandoObject> ExpandoOrders { get; set; } = new List<ExpandoObject>();
public ActionResult Index()
{
string[] customerIDs = { "ALFKI", "ANANTR", "ANTON", "BLONP", "BOLID" };
string[] shipCountrys = { "USA", "UK", "Denmark", "Australia", "India" };
ExpandoOrders = Enumerable.Range(1, 75).Select((x) =>
{
dynamic order = new ExpandoObject();
order.OrderID = 1000 + x;
order.CustomerID = customerIDs[x % customerIDs.Length];
order.Freight = (new double[] { 2, 1, 4, 5, 3 })[new Random().Next(5)] * x;
order.OrderDate = (new DateTime[] { new DateTime(2010, 11, 5), new DateTime(2018, 10, 3), new DateTime(1995, 9, 9), new DateTime(2012, 8, 2), new DateTime(2015, 4, 11) })[new Random().Next(5)];
order.ShipCountry = shipCountrys[x % shipCountrys.Length];
return order;
}).Cast<ExpandoObject>().ToList<ExpandoObject>();
ViewBag.ExpandoData = ExpandoOrders;
return View();
}ExpandoObject with complex column binding
This feature is useful for binding complex data structures to the Syncfusion ASP.NET Core Grid. You can achieve complex data binding with ExpandoObject by using the dot (.) operator in the column.field property. This allows you to access nested properties within the ExpandoObject.
In the following example, the fields Customer.CustomerID, Customer.OrderDate, Customer.Freight, and Customer.ShipCountry represent complex data bound to the Grid.
<ejs-grid id="grid" dataSource="ViewBag.ExpandoData" allowPaging="true" allowSorting="true" allowFiltering="true" toolbar="@(new List<string>() {"Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Update", "Cancel"})">
<e-grid-editSettings allowAdding="true" allowDeleting="true" allowEditing="true" mode="Normal"></e-grid-editSettings>
<e-grid-pageSettings pageSize=10> </e-grid-pageSettings>
<e-grid-columns>
<e-grid-column field="OrderID" headerText="Order ID" isPrimaryKey="true" validationRules="@(new { required=true, number=true})" width="140"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="Customer.CustomerID" headerText="Customer ID" width="150"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="Customer.Freight" headerText="Freight" validationRules="@(new { required=true})" textAlign="Right" editType="numericedit" format="C2" width="140"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="Customer.ShipCountry" headerText="Ship Country" editType="dropdownedit" width="150"></e-grid-column>
</e-grid-columns>
</ejs-grid>public List<ExpandoObject> ExpandoOrders { get; set; } = new List<ExpandoObject>();
public void OnGet()
{
string[] customerID = { "John Doe", "Jane Smith", "Alice Johnson", "Bob Brown", "Charlie Davis" };
string[] shipCountrys = { "USA", "UK", "Denmark", "Australia", "India" };
ExpandoOrders = Enumerable.Range(1, 75).Select((x) =>
{
dynamic order = new ExpandoObject();
order.OrderID = 1000 + x;
order.Customer = new ExpandoObject();
order.Customer.CustomerID = customerID[x % customerID.Length];
order.Customer.Freight = (new double[] { 2, 1, 4, 5, 3 })[new Random().Next(5)] * x;
order.Customer.OrderDate = (new DateTime[] { new DateTime(2010, 11, 5), new DateTime(2018, 10, 3), new DateTime(1995, 9, 9), new DateTime(2012, 8, 2), new DateTime(2015, 4, 11) })[new Random().Next(5)];
order.Customer.ShipCountry = shipCountrys[x % shipCountrys.Length];;
return order;
}).Cast<ExpandoObject>().ToList<ExpandoObject>();
ViewData["ExpandoData"] = ExpandoOrders;
}NOTE
Perform data and CRUD operations for complex ExpandoObject binding fields as well.
DynamicObject binding
The Syncfusion ASP.NET Core Grid is typically bound to a specific model type. However, there are scenarios where the model type is unknown during compile time. In such cases, you can bind data to the Grid using a list of ExpandoObject. This allows for dynamic data structures that can adapt to various data shapes without a predefined schema.
To bind an ExpandoObject to the Grid, you need to assign it to the dataSource property. This enables the Grid to perform various supported data operations and editing on the DynamicObject.
NOTE
You must override the GetDynamicMemberNames method of the DynamicObject class and return the property names to perform data operation and editing while using DynamicObject.
Here’s an example of how to bind a list of DynamicObject to the Grid:
<ejs-grid id="grid" dataSource="ViewBag.DynamicData" allowPaging="true" allowSorting="true" allowFiltering="true" toolbar="@(new List<string>() {"Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Update", "Cancel"})">
<e-grid-editSettings allowAdding="true" allowDeleting="true" allowEditing="true" mode="Normal" newRowPosition="Top"></e-grid-editSettings>
<e-grid-pageSettings pageSize=10> </e-grid-pageSettings>
<e-grid-columns>
<e-grid-column field="OrderID" headerText="Order ID" isPrimaryKey="true" validationRules="@(new { required=true, number=true})" width="140"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="CustomerID" headerText="Customer Name" validationRules="@(new { required=true})" width="150"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="Freight" headerText="Freight" validationRules="@(new { required=true})" textAlign="Right" editType="numericedit" format="C2" width="140"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="ShipCountry" headerText="Ship Country" editType="dropdownedit" width="150"></e-grid-column>
</e-grid-columns>
</ejs-grid>public static List<DynamicList> DynamicOrders { get; set; } = new List<DynamicList>();
public void OnGet()
{
string[] customerIDList = { "ALFKI", "ANANTR", "ANTON", "BLONP", "BOLID" };
string[] shipCountrys = { "USA", "UK", "Denmark", "Australia", "India" };
DynamicOrders = Enumerable.Range(1, 75).Select((x) =>
{
dynamic order = new DynamicList();
order.OrderID = 1000 + x;
order.CustomerID = customerIDList[x % customerIDList.Length];
order.Freight = (new double[] { 2, 1, 4, 5, 3 })[new Random().Next(5)] * x;
order.OrderDate = (new DateTime[] { new DateTime(2010, 11, 5), new DateTime(2018, 10, 3), new DateTime(1995, 9, 9), new DateTime(2012, 8, 2), new DateTime(2015, 4, 11) })[new Random().Next(5)];
order.ShipCountry = shipCountrys[x % shipCountrys.Length];
return order;
}).Cast<DynamicList>().ToList<DynamicList>();
ViewData["DynamicData"] = DynamicOrders;
}
public class DynamicList : DynamicObject
{
private List<KeyValuePair<string, object>> properties = new List<KeyValuePair<string, object>>();
public override bool TryGetMember(GetMemberBinder binder, out object result)
{
string name = binder.Name;
var property = properties.Find(propertyItem => propertyItem.Key == name);
result = property.Value;
return property.Key != null;
}
public override bool TrySetMember(SetMemberBinder binder, object value)
{
string name = binder.Name;
var property = properties.Find(propertyItem => propertyItem.Key == name);
if (property.Key != null)
{
properties.Remove(property);
}
properties.Add(new KeyValuePair<string, object>(name, value));
return true;
}
public override IEnumerable<string> GetDynamicMemberNames()
{
return properties.ConvertAll(propertyItem => propertyItem.Key);
}
}DynamicObject with complex column binding
You can achieve complex data binding with DynamicObject in the Syncfusion ASP.NET Core Grid by using the dot (.) operator in the column.field property. This allows you to access and bind to nested properties within the DynamicObject, enabling the display of structured data in the Grid.
In the following example, Customer.OrderDate, Customer.Freight, and Customer.ShipCountry are considered complex data fields that are bound to the Grid:
<ejs-grid id="grid" dataSource="ViewBag.DynamicData" allowPaging="true" allowSorting="true" allowFiltering="true" toolbar="@(new List<string>() {"Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Update", "Cancel"})">
<e-grid-editSettings allowAdding="true" allowDeleting="true" allowEditing="true"></e-grid-editSettings>
<e-grid-pageSettings pageSize=10> </e-grid-pageSettings>
<e-grid-columns>
<e-grid-column field="OrderID" headerText="Order ID" isPrimaryKey="true" validationRules="@(new { required=true, number=true})" width="140"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="Customer.CustomerID" headerText="Customer ID" width="150"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="Customer.Freight" headerText="Freight" validationRules="@(new { required=true})" textAlign="Right" editType="numericedit" format="C2" width="140"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="Customer.OrderDate" headerText="Order Date" editType="datetimepickeredit" customFormat="@(new {type = "datetime", format = "M/d/y hh:mm a" })" width="160"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="Customer.ShipCountry" headerText="Ship Country" editType="dropdownedit" width="150"></e-grid-column>
</e-grid-columns>
</ejs-grid>public static List<DynamicList> DynamicOrders { get; set; } = new List<DynamicList>();
public void OnGet()
{
string[] customerID = { "John Doe", "Jane Smith", "Alice Johnson", "Bob Brown", "Charlie Davis" };
string[] shipCountrys = { "USA", "UK", "Denmark", "Australia", "India" };
DynamicOrders = Enumerable.Range(1, 75).Select((x) =>
{
dynamic order = new DynamicList();
order.OrderID = 1000 + x;
order.Customer = new DynamicList();
order.Customer.CustomerID = customerID[x % customerID.Length];
order.Customer.Freight = (new double[] { 2, 1, 4, 5, 3 })[new Random().Next(5)] * x;
order.Customer.OrderDate = (new DateTime[] { new DateTime(2010, 11, 5), new DateTime(2018, 10, 3), new DateTime(1995, 9, 9), new DateTime(2012, 8, 2), new DateTime(2015, 4, 11) })[new Random().Next(5)];
order.Customer.ShipCountry = shipCountrys[x % shipCountrys.Length];
return order;
}).Cast<DynamicList>().ToList<DynamicList>();
ViewData["DynamicData"] = DynamicOrders;
}
public class DynamicList : DynamicObject
{
private List<KeyValuePair<string, object>> properties = new List<KeyValuePair<string, object>>();
public override bool TryGetMember(GetMemberBinder binder, out object result)
{
string name = binder.Name;
var property = properties.Find(propertyItem => propertyItem.Key == name);
result = property.Value;
return property.Key != null;
}
public override bool TrySetMember(SetMemberBinder binder, object value)
{
string name = binder.Name;
var property = properties.Find(propertyItem => propertyItem.Key == name);
if (property.Key != null)
{
properties.Remove(property);
}
properties.Add(new KeyValuePair<string, object>(name, value));
return true;
}
public override IEnumerable<string> GetDynamicMemberNames()
{
return properties.ConvertAll(propertyItem => propertyItem.Key);
}
}NOTE
Perform data and CRUD operations for complex DynamicObject binding fields as well.
Limitations
The following features are not supported in the immutable mode:
- Frozen rows and columns
- Grouping
- Row Template
- Detail Template
- Hierarchy Grid
- Scrolling
- Virtual scroll
- Infinite scroll
- Column reorder
- Rows,column spanning
- PDF export ,Excel export,Print
- Column Resize
- Drag and drop
- Column template
- Column chooser
- Clipboard
- AutoFit
- Filtering