How can I help you?
Ports in React Diagram Component
21 Oct 202524 minutes to read
Ports are specialized connection points on nodes that provide precise control over where connectors attach. Unlike node-to-node connections that automatically adjust their attachment points, ports maintain fixed connection locations even when nodes are moved, rotated, or resized. This makes ports essential for creating stable, predictable diagram layouts and professional flowcharts.
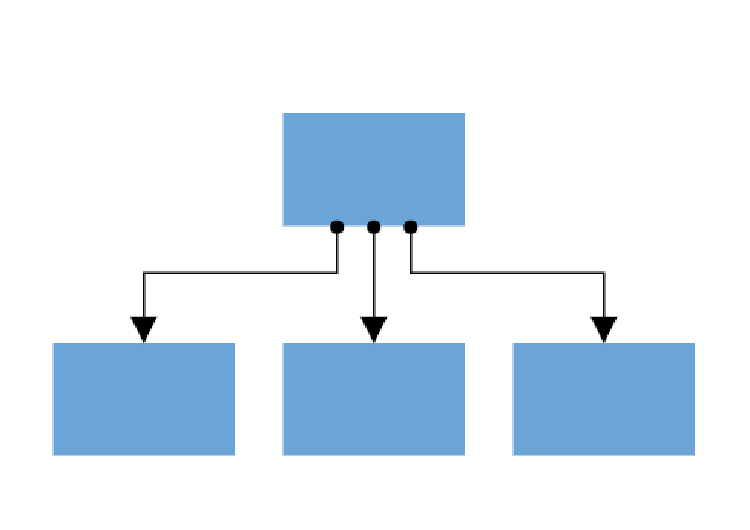
Types of Connections
The Diagram component supports two distinct connection methods, each serving different use cases depending on the level of connection control required.
Node to Node Connection
Node to node connections automatically find the optimal attachment point on a node’s boundary. When either connected node moves, the connector dynamically repositions to maintain the shortest path between nodes. This connection type works best for simple diagrams where precise connection points are not critical.
When a connector is connected between two nodes, its end points are automatically docked to the node’s nearest boundary as shown in the following gif.
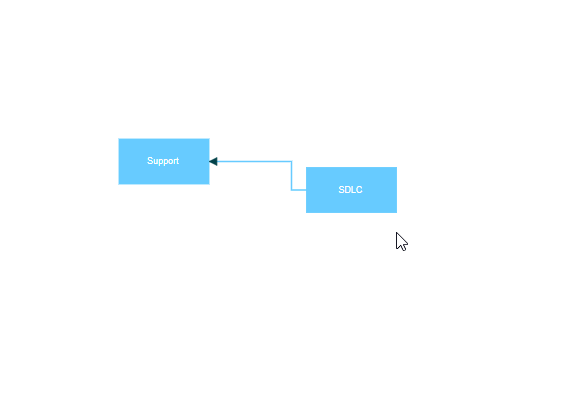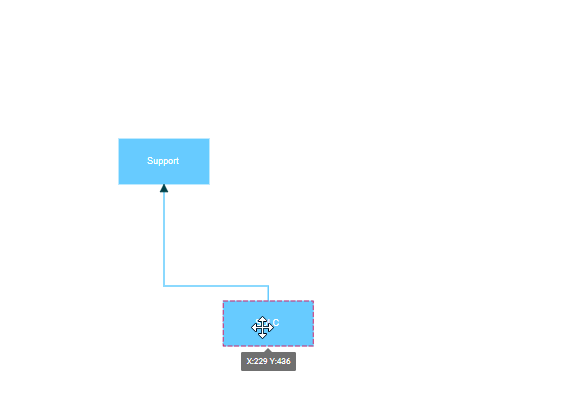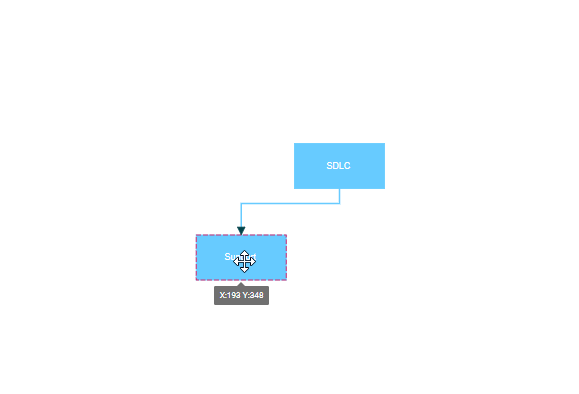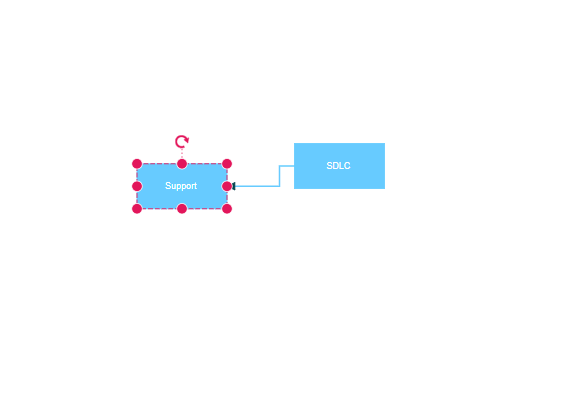
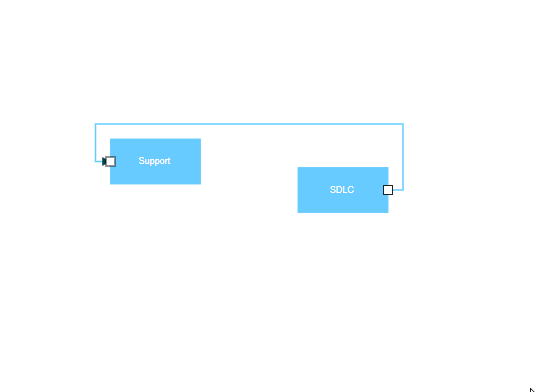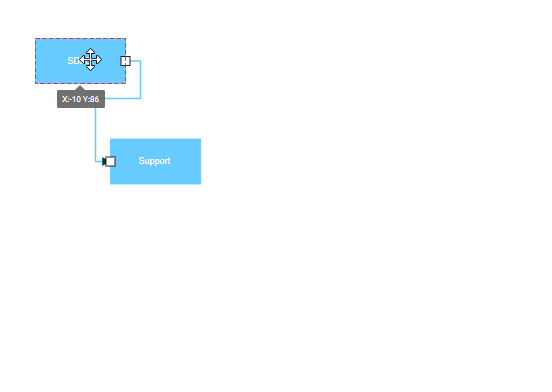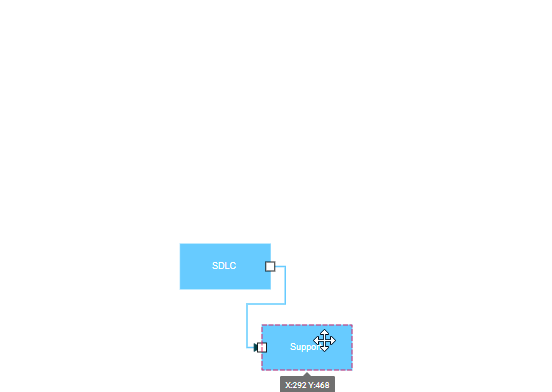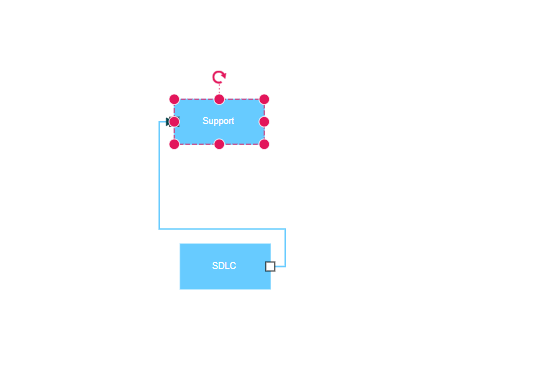
Port to Port Connection
Port to port connections attach to specific, predefined points on nodes. These connections remain fixed to their designated ports regardless of node movement, ensuring consistent diagram appearance and reliable connector behavior. This connection type is ideal for technical diagrams, flowcharts, and any scenario requiring precise connector placement.
Create Port
Ports are defined as objects within a node’s ports collection. The offset property accepts fractional values (0 to 1) that determine the port’s position relative to the node’s bounds, where (0,0) represents the top-left corner and (1,1) represents the bottom-right corner.
The following code demonstrates how to add ports during node initialization:
import * as React from "react";
import * as ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import {DiagramComponent, PortVisibility} from "@syncfusion/ej2-react-diagrams";
let node = [{
offsetX: 250,
offsetY: 250,
width: 100,
height: 100,
// Initialize port collection
ports: [{
// Sets the position for the port
offset: {
x: 0.5,
y: 0.5
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
}]
}];
// initialize Diagram component
function App() {
return (
<DiagramComponent
id="container"
width={'100%'}
height={'600px'}
nodes={node}
// render initialized Diagram
/>
);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('diagram'));
root.render(<App />);import * as React from "react";
import * as ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import {DiagramComponent, PortVisibility, NodeModel} from "@syncfusion/ej2-react-diagrams";
let node: NodeModel[] = [{
offsetX: 250,
offsetY: 250,
width: 100,
height: 100,
// Initialize port collection
ports: [{
// Sets the position for the port
offset: {
x: 0.5,
y: 0.5
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
}]
}];
// initialize Diagram component
function App() {
return (
<DiagramComponent
id="container"
width={'100%'}
height={'600px'}
nodes={node}
// render initialized Diagram
/>
);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('diagram'));
root.render(<App />);NOTE
When setting a Port’s ID, ensure that it does not contain white spaces, does not start with numbers or special characters, and does not include special characters like underscores (_) or spaces.
Add Ports at Runtime
The addPorts method enables dynamic port creation after the diagram has been initialized. This functionality is useful for interactive applications where users can customize node connection points or when ports need to be added based on business logic.
The port’s ID property defines a unique identifier that can be used to reference the port in subsequent operations. If no ID is specified, the system automatically generates a default ID.
import * as React from "react";
import * as ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import {DiagramComponent,PortVisibility} from "@syncfusion/ej2-react-diagrams";
import { ButtonComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-buttons';
let diagramInstance;
let node = [{
offsetX: 250,
offsetY: 250,
width: 100,
height: 100,
}];
let port = [{
id: 'port1',
offset: {
x: 0,
y: 0.5
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
}, {
id: 'port2',
offset: {
x: 1,
y: 0.5
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
},
{
id: 'port3',
offset: {
x: 0.5,
y: 0
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
},
{
id: 'port4',
offset: {
x: 0.5,
y: 1
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
}];
// Method to add ports through run time
const addport = () => {
// Parameters:
// - node: The node to which the port will be added.
// - port: The port collection to be added to the node.
diagramInstance.addPorts(diagramInstance.nodes[0], port);
}
// initialize Diagram component
function App() {
return (
<div>
<ButtonComponent content="Add Port" onClick={addport} />
<DiagramComponent
id="container"
ref={(diagram) => (diagramInstance = diagram)}
width={'100%'}
height={'600px'}
nodes={node}
// render initialized Diagram
/>
</div>
);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('diagram'));
root.render(<App />);import * as React from "react";
import * as ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import {Diagram, DiagramComponent,PortVisibility, NodeModel,PointPortModel,} from "@syncfusion/ej2-react-diagrams";
import { ButtonComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-buttons';
let diagramInstance:DiagramComponent;
let node: NodeModel[] = [{
offsetX: 250,
offsetY: 250,
width: 100,
height: 100,
}];
let port: PointPortModel[] = [{
id: 'port1',
offset: {
x: 0,
y: 0.5
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
}, {
id: 'port2',
offset: {
x: 1,
y: 0.5
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
},
{
id: 'port3',
offset: {
x: 0.5,
y: 0
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
},
{
id: 'port4',
offset: {
x: 0.5,
y: 1
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
}];
// Method to add ports through run time
const addport = () => {
// Parameters:
// - node: The node to which the port will be added.
// - port: The port collection to be added to the node.
diagramInstance.addPorts(diagramInstance.nodes[0], port);
}
// initialize Diagram component
function App() {
return (
<div>
<ButtonComponent content="Add Port" onClick={addport} />
<DiagramComponent
id="container"
ref={(diagram) => (diagramInstance = diagram)}
width={'100%'}
height={'600px'}
nodes={node}
// render initialized Diagram
/>
</div>
);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('diagram'));
root.render(<App />);Remove Ports at Runtime
TheremovePorts method allows dynamic removal of ports from nodes. When a port is removed, any connectors attached to that port are automatically disconnected. This method is particularly useful for creating adaptive interfaces or cleaning up unused connection points.
import * as React from "react";
import * as ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import { DiagramComponent, PortVisibility } from "@syncfusion/ej2-react-diagrams";
import { ButtonComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-buttons';
let diagramInstance;
let node = [{
offsetX: 250,
offsetY: 250,
width: 100,
height: 100,
// Initialize port collection
ports: [{
id: 'port1',
offset: {
x: 0,
y: 0.5
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
},
{
id: 'port2',
offset: {
x: 1,
y: 0.5
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
},
{
id: 'port3',
offset: {
x: 0.5,
y: 0
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
},
{
id: 'port4',
offset: {
x: 0.5,
y: 1
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
}
]
}];
// initialize Diagram component
let ports = [{
id: 'port1',
}, {
id: 'port2',
}, {
id: 'port3',
}, {
id: 'port4',
}];
// Method to add ports through run time
const removePort = () => {
// Parameters:
// - node: The node from which the ports will be removed.
// - ports: The collection of ports to be removed from the node.
diagramInstance.removePorts(diagramInstance.nodes[0], ports);
}
function App() {
return (
<div>
<ButtonComponent content="Remove Port" onClick={removePort} />
<DiagramComponent id="container" ref={(diagram) => (diagramInstance = diagram)} width={'100%'} height={'600px'} nodes={node} />
</div>);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('diagram'));
root.render(<App />);import * as React from "react";
import * as ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import { DiagramComponent, PortVisibility,NodeModel } from "@syncfusion/ej2-react-diagrams";
import { ButtonComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-buttons';
let diagramInstance: DiagramComponent;
let node: NodeModel[] = [{
offsetX: 250,
offsetY: 250,
width: 100,
height: 100,
// Initialize port collection
ports: [{
id: 'port1',
offset: {
x: 0,
y: 0.5
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
},
{
id: 'port2',
offset: {
x: 1,
y: 0.5
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
},
{
id: 'port3',
offset: {
x: 0.5,
y: 0
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
},
{
id: 'port4',
offset: {
x: 0.5,
y: 1
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
}
]
}];
// initialize Diagram component
let ports = [{
id: 'port1',
}, {
id: 'port2',
}, {
id: 'port3',
}, {
id: 'port4',
}];
// Method to add ports through run time
const removePort = () => {
// Parameters:
// - node: The node from which the ports will be removed.
// - ports: The collection of ports to be removed from the node.
diagramInstance.removePorts(diagramInstance.nodes[0], ports);
}
function App() {
return (
<div>
<ButtonComponent content="Remove Port" onClick={removePort} />
<DiagramComponent id="container" ref={(diagram) => (diagramInstance = diagram)} width={'100%'} height={'600px'} nodes={node} />
</div>);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('diagram'));
root.render(<App />);Update Port at Runtime
Port properties can be modified at runtime by directly updating the port object and calling the [dataBind] method to apply the changes. This approach enables dynamic customization of port appearance, position, and behavior based on application state or user interactions.
The following code example illustrates how to change the port offset at runtime.
import * as React from "react";
import * as ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import {DiagramComponent,PortVisibility} from "@syncfusion/ej2-react-diagrams";
import { ButtonComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-buttons';
let diagramInstance;
let node = [{
offsetX: 250,
offsetY: 250,
width: 100,
height: 100,
ports: [{
offset: {
x: 0.5,
y: 0.5
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
}]
}];
// Method to update ports at run time
const updatePort = () => {
diagramInstance.nodes[0].ports[0].offset = {
x: 1,
y: 1
};
diagramInstance.dataBind();
}
// initialize Diagram component
function App() {
return (
<div>
<ButtonComponent content="update Port" onClick={updatePort} />
<DiagramComponent
id="container"
ref={(diagram) => (diagramInstance = diagram)}
width={'100%'}
height={'600px'}
nodes={node}
/>
</div>
);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('diagram'));
root.render(<App />);import * as React from "react";
import * as ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import {DiagramComponent,PortVisibility,NodeModel} from "@syncfusion/ej2-react-diagrams";
import { ButtonComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-buttons';
let diagramInstance: DiagramComponent;
let node: NodeModel[] = [{
offsetX: 250,
offsetY: 250,
width: 100,
height: 100,
ports: [{
offset: {
x: 0.5,
y: 0.5
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
}]
}];
// Method to update ports at run time
const updatePort = () => {
diagramInstance.nodes[0].ports[0].offset = {
x: 1,
y: 1
};
diagramInstance.dataBind();
}
// initialize Diagram component
function App() {
return (
<div>
<ButtonComponent content="update Port" onClick={updatePort} />
<DiagramComponent
id="container"
ref={(diagram) => (diagramInstance = diagram)}
width={'100%'}
height={'600px'}
nodes={node}
/>
</div>
);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('diagram'));
root.render(<App />);Specify Connection Direction to Port
The connectionDirection property controls the allowed connection flow through a port. This property accepts values that specify whether connectors can connect to the port (incoming), from the port (outgoing), or both directions. This feature is essential for creating directional flowcharts and enforcing proper data flow in technical diagrams.
import * as React from "react";
import * as ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import { DiagramComponent, PortVisibility,PortConnectionDirection } from "@syncfusion/ej2-react-diagrams";
import { ButtonComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-buttons';
let diagramInstance;
var nodes = [
{
id: 'node1',
offsetX: 450,
offsetY: 200,
width: 100,
height: 100,
ports: [
{
id: 'port1',
offset: { x: 0, y: 0 },
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible,
},
],
},
{
id: 'node2',
offsetX: 270,
offsetY: 300,
width: 100,
height: 100,
ports: [
{
id: 'port3',
offset: { x: 0.5, y: 0.5 },
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible,
//Sets the connection direction as Left
connectionDirection: 'Left',
},
],
},
];
//initialize the connector to connect the nodes
let connectors = [
{
id: 'connector1',
type: 'Orthogonal',
sourceID: 'node2',
targetID: 'node1',
sourcePortID: 'port3',
targetPortID: 'port1',
}];
// Method to add ports through run time
const changeConnectionDirection = () => {
diagramInstance.nodes[1].ports[0].connectionDirection='Top'
}
function App() {
return (
<div>
<ButtonComponent content="Change Connection Direction" onClick={changeConnectionDirection} />
<DiagramComponent
id="container"
ref={(diagram) => (diagramInstance = diagram)}
width={'100%'}
height={'600px'}
nodes={nodes}
connectors={connectors}
// render initialized Diagram
/>
</div>
);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('diagram'));
root.render(<App />);import * as React from "react";
import * as ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import { DiagramComponent, PortVisibility,NodeModel,ConnectorModel } from "@syncfusion/ej2-react-diagrams";
import { ButtonComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-buttons';
let diagramInstance: DiagramComponent;
var nodes:NodeModel[] = [
{
id: 'node1',
offsetX: 450,
offsetY: 200,
width: 100,
height: 100,
ports: [
{
id: 'port1',
offset: { x: 0, y: 0 },
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible,
},
],
},
{
id: 'node2',
offsetX: 270,
offsetY: 300,
width: 100,
height: 100,
ports: [
{
id: 'port3',
offset: { x: 0.5, y: 0.5 },
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible,
//Sets the connection direction as Left
connectionDirection: 'Left',
},
],
},
];
let connectors: ConnectorModel[] = [
{
id: 'connector1',
type: 'Orthogonal',
sourceID: 'node2',
targetID: 'node1',
sourcePortID: 'port3',
targetPortID: 'port1',
}];
// Method to add ports through run time
const changeConnectionDirection = () => {
diagramInstance.nodes[1].ports[0].connectionDirection='Top'
}
function App() {
return (
<div>
<ButtonComponent content="Change Connection Direction" onClick={changeConnectionDirection} />
<DiagramComponent
id="container"
ref={(diagram) => (diagramInstance = diagram)}
width={'100%'}
height={'600px'}
nodes={nodes}
connectors={connectors}
// render initialized Diagram
/>
</div>
);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('diagram'));
root.render(<App />);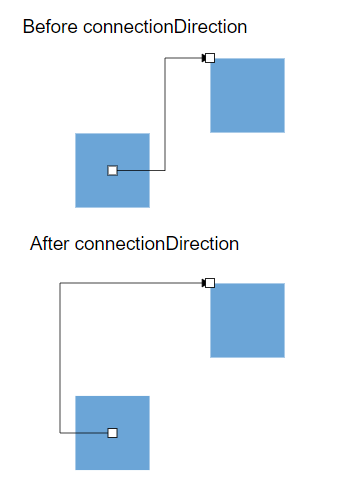
InEdges and OutEdges of Ports
Each port maintains collections of its connected connectors through read-only properties.The inEdges property contains the IDs of all connectors that terminate at the port, while outEdges contains the IDs of connectors that originate from the port. These properties are automatically maintained by the diagram and provide valuable information for traversing connection relationships.
The inEdges and outEdges of the port are read-only and cannot be customized.
import * as React from "react";
import * as ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import { DiagramComponent,PortVisibility} from "@syncfusion/ej2-react-diagrams";
import { ButtonComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-buttons';
let diagramInstance;
let nodes = [
{
id: 'node1',
offsetX: 250,
offsetY: 250,
width: 100,
height: 100,
ports: [
{
id: 'port1',
offset: { x: 0, y: 0.5 },
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible,
},
{
id: 'port2',
offset: { x: 0.5, y: 0 },
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible,
},
],
},
{
id: 'node2',
offsetX: 250,
offsetY: 400,
width: 100,
height: 100,
ports: [
{
id: 'port3',
offset: { x: 0, y: 0.5 },
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible,
},
{
id: 'port4',
offset: { x: 0.5, y: 1 },
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible,
},
],
},
];
let connectors = [
{
id: 'connector1',
sourceID: 'node1',
targetID: 'node2',
type: 'Orthogonal',
sourcePortID: 'port1',
targetPortID: 'port3',
annotations: [{ content: 'connector1' }],
},
{
id: 'connector2',
sourceID: 'node2',
targetID: 'node1',
type: 'Orthogonal',
sourcePortID: 'port4',
targetPortID: 'port2',
annotations: [{ content: 'connector2' }],
},
];
// Method for inEdges
const inEdges = () => {
let port1 = diagramInstance.nodes[0].ports[1];
console.log(port1.inEdges[0]);
}
// Method for outEdges
const outEdges = () => {
let port1 = diagramInstance.nodes[0].ports[0];
console.log(port1.outEdges[0]);
}
// initialize Diagram component
function App() {
return (
<div>
<ButtonComponent content="In Edges" onClick={inEdges} />
<ButtonComponent content="Out Edges" onClick={outEdges} />
<DiagramComponent
id="container"
ref={(diagram) => (diagramInstance = diagram)}
width={'100%'}
height={'600px'}
nodes={nodes}
connectors={connectors}
/>
</div>
);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('diagram'));
root.render(<App />);import * as React from "react";
import * as ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import { DiagramComponent,PortVisibility, ConnectorModel, NodeModel} from "@syncfusion/ej2-react-diagrams";
import { ButtonComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-buttons';
let diagramInstance: DiagramComponent;
let nodes: NodeModel[] = [
{
id: 'node1',
offsetX: 250,
offsetY: 250,
width: 100,
height: 100,
ports: [
{
id: 'port1',
offset: { x: 0, y: 0.5 },
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible,
},
{
id: 'port2',
offset: { x: 0.5, y: 0 },
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible,
},
],
},
{
id: 'node2',
offsetX: 250,
offsetY: 400,
width: 100,
height: 100,
ports: [
{
id: 'port3',
offset: { x: 0, y: 0.5 },
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible,
},
{
id: 'port4',
offset: { x: 0.5, y: 1 },
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible,
},
],
},
];
let connectors: ConnectorModel[]= [
{
id: 'connector1',
sourceID: 'node1',
targetID: 'node2',
type: 'Orthogonal',
sourcePortID: 'port1',
targetPortID: 'port3',
annotations: [{ content: 'connector1' }],
},
{
id: 'connector2',
sourceID: 'node2',
targetID: 'node1',
type: 'Orthogonal',
sourcePortID: 'port4',
targetPortID: 'port2',
annotations: [{ content: 'connector2' }],
},
];
// Method for inEdges
const inEdges = () => {
let port1 = diagramInstance.nodes[0].ports[1];
console.log(port1.inEdges[0]);
}
// Method for outEdges
const outEdges = () => {
let port1 = diagramInstance.nodes[0].ports[0];
console.log(port1.outEdges[0]);
}
// initialize Diagram component
function App() {
return (
<div>
<ButtonComponent content="In Edges" onClick={inEdges} />
<ButtonComponent content="Out Edges" onClick={outEdges} />
<DiagramComponent
id="container"
ref={(diagram) => (diagramInstance = diagram)}
width={'100%'}
height={'600px'}
nodes={nodes}
connectors={connectors}
/>
</div>
);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('diagram'));
root.render(<App />);The following code example shows how to get inEdges and outEdges of port.
Additional Information to Port
The addInfo property allows attachment of custom metadata to ports. This property accepts any object and is useful for storing application-specific data, configuration settings, or contextual information that needs to be associated with particular ports. The stored information persists with the port throughout its life cycle and can be accessed when processing port-related events or operations.
The following code example shows how to attach additional information to a port:
let port:PointPortModel = {id:'port1',offset:{x:0.5,y:0},addInfo:{position:'TopCenter',id:'port1'}};