How can I help you?
Getting Started with the Vue Diagram Component in Vue 2
10 Feb 202624 minutes to read
This guide walks you through creating a Vue 2 application using Vue-CLI and integrating the Syncfusion® Vue Diagram component
Ready to streamline your Syncfusion® Vue development? Discover the full potential of Syncfusion® Vue components with Syncfusion® AI Coding Assistant. Effortlessly integrate, configure, and enhance your projects with intelligent, context-aware code suggestions, streamlined setups, and real-time insights—all seamlessly integrated into your preferred AI-powered IDEs like VS Code, Cursor, Syncfusion® CodeStudio and more. Explore Syncfusion® AI Coding Assistant
Prerequisites
System requirements for Syncfusion® Vue UI components
Dependencies
The following list of dependencies are required to use the Diagram component in your application.
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-base
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-data
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-navigations
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-inputs
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-popups
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-buttons
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-lists
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-diagrams
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-vue-baseSetup Vue Environment
Use Vue CLI to set up your Vue project. Install Vue CLI globally with the following command:
npm install -g @vue/clior
yarn global add @vue/cliCreate a Vue 2 Application
Create a new project using the vue create command.
vue create my-diagram-appWhen creating a new project, choose the option Default ([Vue 2] babel, eslint) from the menu.
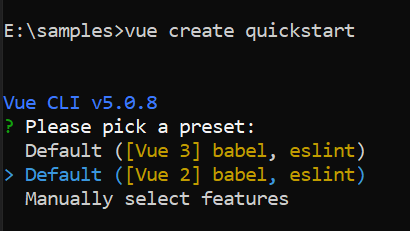
once the my-diagram-app project is created, navigate to the project folder:
cd my-diagram-appAdd Syncfusion® Vue Diagram packages
All Syncfusion® packages are published to the npmjs.com registry.
Install the @syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams package by running the following command:
npm install @syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams --saveor
yarn add @syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagramsImport Syncfusion® CSS styles
You can import themes for the Syncfusion® Vue component in multiple ways—CSS/SASS from npm packages, CDN, CRG and Theme Studio. Refer to themes topic to know more about built-in themes and different ways to refer to themes in a Vue project.
In this guide, the Tailwind 3 theme is applied using CSS files available in the installed packages. Add the following imports in the <style> section of src/App.vue:
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/tailwind3.css";
</style>Diagram components use other Syncfusion® components internally. So, CSS references for dependent components must be added to ensure all features render correctly.
Add the Syncfusion® Vue Diagram component
Follow these steps to render the Diagram component in your Vue app.
Import and register the component
In src/App.vue, import and register DiagramComponent in the <script> section:
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
export default {
components: {
'ejs-diagram': DiagramComponent
}
}
</script>Add the Diagram in the template
Define the Diagram component with height and width.
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' ></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>Provide values for height and width
Declare width and height in the data() section:
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "350px",
}
}
}
</script>Run the project
Use either npm or yarn:
npm run serveor
yarn run serveNOTE
Vue CLI projects automatically rebuild when you save changes—no need to rerun the command each time.
Defining Basic Diagram
The below examples shows the basic diagram component which renders an empty diagram.
<template>
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height'></ejs-diagram>
</template>
<script setup>
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const width = "100%";
const height = "350px";
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/tailwind3.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "350px"
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/tailwind3.css";
</style>Module Injection
Diagram component are segregated into individual feature-wise modules. In order to use a particular feature, you need to inject the required module. Please find relevant feature service name and description as follows.
-
BpmnDiagrams- Inject this provider to add built-in BPMN Shapes to diagrams. -
ConnectorBridging- Inject this provider to add bridges to connectors. -
ConnectorEditing- Inject this provider to edit the segments for connector. -
ComplexHierarchicalTree- Inject this provider to complex hierarchical tree like structure. -
DataBinding- Inject this provider to populate nodes from given data source. -
DiagramContextMenu- Inject this provider to manipulate context menu. -
HierarchicalTree- Inject this provider to use hierarchical tree like structure. -
LayoutAnimation- Inject this provider animation to layouts. -
MindMap- Inject this provider to use mind map. -
PrintAndExport- Inject this provider to print or export the objects. -
RadialTree- Inject this provider to use Radial tree like structure. -
Snapping- Inject this provider to Snap the objects. -
SymmetricLayout- Inject this provider to render layout in symmetrical method. -
UndoRedo- Inject this provider to revert and restore the changes. -
Ej1Serialization- Inject this provider to load ej1 diagram json in ej2 diagram.
Register the required array of modules under the key diagram in the provide section.
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent, HierarchicalTree, MindMap, RadialTree, ComplexHierarchicalTree, DataBinding, Snapping, PrintAndExport, BpmnDiagrams, SymmetricLayout, ConnectorBridging, UndoRedo, LayoutAnimation, DiagramContextMenu, ConnectorEditing,Ej1Serialization } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "350px"
}
},
provide:{
diagram: [BpmnDiagrams, ConnectorBridging, ConnectorEditing, ComplexHierarchicalTree, DataBinding,DiagramContextMenu, HierarchicalTree, LayoutAnimation, MindMap, PrintAndExport, RadialTree, Snapping, SymmetricLayout, UndoRedo,Ej1Serialization]
},
}
</script>Basic Diagram elements
Diagrams are built using the following core elements:
-
Node: Visualizes any graphical object using nodes, which can be arranged and manipulated on a diagram page. -
Connector: Represents the relationship between two nodes. Three types of connectors provided as follows:- Orthogonal
- Bezier
- Straight
-
Port: Acts as connection points on nodes or connectors, allowing connections only at specific points. -
Annotation: Shows additional information by adding text or labels on nodes and connectors.
Flow Diagram
Create and Add Node
Create and add a node (JSON data) with specific position, size, label, and shape.
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :nodes='nodes'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const nodes = [
{
id: "node1",
width: 100,
height: 60,
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 80,
annotations: [
{
content: "start"
}
]
}
];
const width = "100%";
const height = "350px";
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/tailwind3.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :nodes='nodes'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const nodes = [
{
id: "node1",
width: 100,
height: 60,
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 80,
annotations: [
{
content: "start"
}
]
}
];
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "350px",
nodes: nodes
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/tailwind3.css";
</style>Apply shape and style to node
Syncfusion® diagram control provides support to render many built-in shapes in diagram.
Please refer to Shapes to know about built-in Shapes.
Customize the appearance of a node by changing its fill color, strokeColor, strokeWidth, borderColor, borderWidth, strokeDashArray, opacity, and shadow properties:
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :nodes='nodes'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const nodes = [
{
id: "node1",
height: 60,
width: 100,
offsetX: 200,
offsetY: 100,
shape: { type: 'Flow', shape: 'Terminator'},
style:{ fill:'red', strokeColor:'green', strokeWidth:5, strokeDashArray:'2,2' },
borderWidth: 10,
borderColor: 'orange',
annotations: [{content: 'Start '}]
}
];
const width = "100%";
const height = "350px";
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/tailwind3.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :nodes='nodes'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
let nodes = [
{
id: "node1",
height: 60,
width: 100,
offsetX: 200,
offsetY: 100,
shape: { type: 'Flow', shape: 'Terminator'},
style:{ fill:'red', strokeColor:'green', strokeWidth:5, strokeDashArray:'2,2' },
borderWidth: 10,
borderColor: 'orange',
annotations: [{content: 'Start '}]
}
];
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "350px",
nodes: nodes,
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/tailwind3.css";
</style>Add other flowchart nodes to the diagram
Add multiple nodes with different shapes to create a comprehensive diagram:
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :nodes='nodes'
:getNodeDefaults='getNodeDefaults'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const nodes = [
{
id: "node1",
offsetY: 50,
shape: { type: "Flow", shape: "Terminator" },
annotations: [{
content: "Start"
}]
},
{
id: "node2",
offsetY: 140,
shape: { type: "Flow", shape: "Process" },
annotations: [{
content: "var i = 0;"
}]
},
{
id: "node3",
offsetY: 230,
shape: { type: "Flow", shape: "Decision" },
annotations: [{
content: "i < 10?"
}]
},
];
const getNodeDefaults = (node) => {
node.height = 50;
node.width = 140;
node.style = { fill: "skyblue", strokeColor: "skyblue" };
node.offsetX = 300;
return node;
}
const width = "100%";
const height = "350px";
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/tailwind3.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :nodes='nodes'
:getNodeDefaults='getNodeDefaults'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const nodes = [
{
id: "node1",
offsetY: 50,
shape: { type: "Flow", shape: "Terminator" },
annotations: [{
content: "Start"
}]
},
{
id: "node2",
offsetY: 140,
shape: { type: "Flow", shape: "Process" },
annotations: [{
content: "var i = 0;"
}]
},
{
id: "node3",
offsetY: 230,
shape: { type: "Flow", shape: "Decision" },
annotations: [{
content: "i < 10?"
}]
},
];
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "350px",
nodes: nodes,
getNodeDefaults: (node) => {
node.height = 50;
node.width = 140;
node.style = { fill: "skyblue", strokeColor: "skyblue" };
node.offsetX = 300;
return node;
},
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/tailwind3.css";
</style>Connect flow chart nodes
Connect nodes by adding connectors using the connectors property of the diagram. Reference the source and target endpoints using the sourceID and targetID properties.
Combine the required nodes and connectors to form a complete flow diagram:
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :nodes='nodes' :connectors='connectors'
:getNodeDefaults='getNodeDefaults' :getConnectorDefaults='getConnectorDefaults'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const nodes = [
{
id: 'Start',
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 50,
annotations: [{ content: 'Start' }],
shape: { type: 'Flow', shape: 'Terminator' },
style: { fill: '#d0f0f1', strokeColor: '#797979' },
},
{
id: 'Init',
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 140,
annotations: [{ content: 'var i = 0;' }],
shape: { type: 'Flow', shape: 'Process' },
style: { fill: '#fbfdc5', strokeColor: '#797979' },
},
{
id: 'Condition',
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 230,
annotations: [{ content: 'i < 10?' }],
shape: { type: 'Flow', shape: 'Decision' },
style: { fill: '#c5efaf', strokeColor: '#797979' },
},
{
id: 'Print',
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 320,
annotations: [{ content: "print('Hello!!');" }],
shape: { type: 'Flow', shape: 'PreDefinedProcess' },
style: { fill: '#f8eee5', strokeColor: '#797979' },
},
{
id: 'Increment',
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 410,
annotations: [{ content: 'i++;' }],
shape: { type: 'Flow', shape: 'Process' },
style: { fill: '#fbfdc5', strokeColor: '#797979' },
},
{
id: 'End',
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 500,
annotations: [{ content: 'End' }],
shape: { type: 'Flow', shape: 'Terminator' },
style: { fill: '#d0f0f1', strokeColor: '#797979' },
},
];
const connectors = [
{ id: 'connector1', sourceID: 'Start', targetID: 'Init' },
{ id: 'connector2', sourceID: 'Init', targetID: 'Condition' },
{
id: 'connector3',
sourceID: 'Condition',
targetID: 'Print',
annotations: [{ content: 'Yes' }],
},
{
id: 'connector4',
sourceID: 'Condition',
targetID: 'End',
annotations: [{ content: 'No' }],
type: 'Orthogonal',
segments: [
{ type: 'Orthogonal', length: 30, direction: 'Right' },
{ type: 'Orthogonal', length: 300, direction: 'Bottom' },
],
},
{ id: 'connector5', sourceID: 'Print', targetID: 'Increment' },
{
id: 'connector6',
sourceID: 'Increment',
targetID: 'Condition',
type: 'Orthogonal',
segments: [
{ type: 'Orthogonal', length: 30, direction: 'Left' },
{ type: 'Orthogonal', length: 200, direction: 'Top' },
],
},
];
const width = "100%";
const height = "600px";
const getNodeDefaults = (node) => {
node.height = 50;
node.width = 140;
node.offsetX = 300;
return node;
}
const getConnectorDefaults = (obj) => {
obj.type = 'Orthogonal';
obj.targetDecorator = { shape: 'Arrow', width: 10, height: 10 };
return obj;
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/tailwind3.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :nodes='nodes' :connectors='connectors'
:getNodeDefaults='getNodeDefaults' :getConnectorDefaults='getConnectorDefaults'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const nodes = [
{
id: 'Start',
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 50,
annotations: [{ content: 'Start' }],
shape: { type: 'Flow', shape: 'Terminator' },
style: { fill: '#d0f0f1', strokeColor: '#797979' },
},
{
id: 'Init',
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 140,
annotations: [{ content: 'var i = 0;' }],
shape: { type: 'Flow', shape: 'Process' },
style: { fill: '#fbfdc5', strokeColor: '#797979' },
},
{
id: 'Condition',
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 230,
annotations: [{ content: 'i < 10?' }],
shape: { type: 'Flow', shape: 'Decision' },
style: { fill: '#c5efaf', strokeColor: '#797979' },
},
{
id: 'Print',
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 320,
annotations: [{ content: "print('Hello!!');" }],
shape: { type: 'Flow', shape: 'PreDefinedProcess' },
style: { fill: '#f8eee5', strokeColor: '#797979' },
},
{
id: 'Increment',
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 410,
annotations: [{ content: 'i++;' }],
shape: { type: 'Flow', shape: 'Process' },
style: { fill: '#fbfdc5', strokeColor: '#797979' },
},
{
id: 'End',
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 500,
annotations: [{ content: 'End' }],
shape: { type: 'Flow', shape: 'Terminator' },
style: { fill: '#d0f0f1', strokeColor: '#797979' },
},
];
const connectors = [
{ id: 'connector1', sourceID: 'Start', targetID: 'Init' },
{ id: 'connector2', sourceID: 'Init', targetID: 'Condition' },
{
id: 'connector3',
sourceID: 'Condition',
targetID: 'Print',
annotations: [{ content: 'Yes' }],
},
{
id: 'connector4',
sourceID: 'Condition',
targetID: 'End',
annotations: [{ content: 'No' }],
type: 'Orthogonal',
segments: [
{ type: 'Orthogonal', length: 30, direction: 'Right' },
{ type: 'Orthogonal', length: 300, direction: 'Bottom' },
],
},
{ id: 'connector5', sourceID: 'Print', targetID: 'Increment' },
{
id: 'connector6',
sourceID: 'Increment',
targetID: 'Condition',
type: 'Orthogonal',
segments: [
{ type: 'Orthogonal', length: 30, direction: 'Left' },
{ type: 'Orthogonal', length: 200, direction: 'Top' },
],
},
];
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "600px",
nodes: nodes,
connectors: connectors,
getNodeDefaults: (node) => {
node.height = 50;
node.width = 140;
node.offsetX = 300;
return node;
},
getConnectorDefaults: (obj) => {
obj.type = 'Orthogonal';
obj.targetDecorator = { shape: 'Arrow', width: 10, height: 10 };
return obj;
},
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/tailwind3.css";
</style>Set default values for all nodes and connectors using the getNodeDefaults and getConnectorDefaults properties, respectively. For example, if all nodes have the same width and height, move such properties into getNodeDefaults.
Automatic Organization Chart
The previous ‘Flow Diagram’ section explained how to create a diagram manually. This section demonstrates how to create and position diagrams automatically using data binding.
Create Business object (Employee information)
Define Employee Information as JSON data. The following code example shows an employee array where Name serves as a unique identifier and ReportingPerson identifies the person to whom an employee reports in the organization:
let data = [
{
Name: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Director"
},
{
Name: "Christina",
ReportingPerson: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Manager"
},
{
Name: "Yoshi",
ReportingPerson: "Christina",
Role: "Lead"
},
{
Name: "Philip",
ReportingPerson: "Christina",
Role: "Lead"
},
{
Name: "Yang",
ReportingPerson: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Manager"
},
{
Name: "Roland",
ReportingPerson: "Yang",
Role: "Lead"
},
{
Name: "Yvonne",
ReportingPerson: "Yang",
Role: "Lead"
}
];Map data source
Configure the above “Employee Information” with the diagram so that nodes and connectors are automatically generated using the mapping properties.
The following code example demonstrates how to use dataSourceSettings to map id and parentId with the corresponding property names of employee information:
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :dataSourceSettings='dataSourceSettings'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent, HierarchicalTree, DataBinding } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
import { DataManager } from "@syncfusion/ej2-data";
export let localdata = [
{
Name: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Director",
},
{
Name: "Christina",
ReportingPerson: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Manager",
},
{
Name: "Yoshi",
ReportingPerson: "Christina",
Role: "Lead",
},
{
Name: "Philip",
ReportingPerson: "Christina",
Role: "Lead",
},
{
Name: "Yang",
ReportingPerson: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Manager",
},
{
Name: "Roland",
ReportingPerson: "Yang",
Role: "Lead",
},
{
Name: "Yvonne",
ReportingPerson: "Yang",
Role: "Lead",
}
];
export default {
components: {
'ejs-diagram': DiagramComponent
},
name: 'app',
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "350px",
dataSourceSettings: {
id: 'Name', parentId: 'ReportingPerson',
dataManager: new DataManager(localdata),
}
}
},
provide: { diagram: [DataBinding, HierarchicalTree] },
}
</script>Rendering layout with Datasource
To create an organizational chart, set the type of layout as OrganizationalChart.
The following code example shows how DataManager generates layouts based on the DataSourceSettings of the Diagram:
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :getNodeDefaults='getNodeDefaults'
:getConnectorDefaults='getConnectorDefaults' :layout='layout'
:dataSourceSettings='dataSourceSettings'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { provide } from "vue";
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram, DataBinding, HierarchicalTree } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
import { DataManager } from "@syncfusion/ej2-data";
let localdata = [
{
Name: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Director"
},
{
Name: "Christina",
ReportingPerson: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Manager"
},
{
Name: "Yoshi",
ReportingPerson: "Christina",
Role: "Lead"
},
{
Name: "Philip",
ReportingPerson: "Christina",
Role: "Lead"
},
{
Name: "Yang",
ReportingPerson: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Manager"
},
{
Name: "Roland",
ReportingPerson: "Yang",
Role: "Lead"
},
{
Name: "Yvonne",
ReportingPerson: "Yang",
Role: "Lead"
}
];
const width = "100%";
const height = "350px";
const getNodeDefaults = (node) => {
let codes = {
Director: "rgb(0, 139,139)",
Manager: "rgb(30, 30,113)",
Lead: "rgb(0, 100,0)"
};
node.width = 70;
node.height = 30;
node.annotations = [
{ content: node.data.Name, style: { color: "white" } }
];
node.style.fill = codes[node.data.Role];
return node;
}
const getConnectorDefaults = (connector) => {
connector.type = "Orthogonal";
connector.cornerRadius = 7;
return connector;
}
const layout = {
type: "OrganizationalChart",
}
const dataSourceSettings = {
id: 'Name', parentId: 'ReportingPerson',
dataManager: new DataManager(localdata),
}
provide('diagram', [DataBinding, HierarchicalTree]);
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/tailwind3.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :getNodeDefaults='getNodeDefaults'
:getConnectorDefaults='getConnectorDefaults' :layout='layout'
:dataSourceSettings='dataSourceSettings'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent, HierarchicalTree, DataBinding } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
import { DataManager } from "@syncfusion/ej2-data";
export let localdata = [
{
Name: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Director",
},
{
Name: "Christina",
ReportingPerson: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Manager",
},
{
Name: "Yoshi",
ReportingPerson: "Christina",
Role: "Lead",
},
{
Name: "Philip",
ReportingPerson: "Christina",
Role: "Lead",
},
{
Name: "Yang",
ReportingPerson: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Manager",
},
{
Name: "Roland",
ReportingPerson: "Yang",
Role: "Lead",
},
{
Name: "Yvonne",
ReportingPerson: "Yang",
Role: "Lead",
}
];
export default {
components: {
'ejs-diagram': DiagramComponent
},
name: 'app',
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "350px",
getNodeDefaults: (node) => {
let codes = {
Director: "rgb(0, 139,139)",
Manager: "rgb(30, 30,113)",
Lead: "rgb(0, 100,0)"
};
node.width = 70;
node.height = 30;
node.annotations = [
{ content: node.data.Name, style: { color: "white" } }
];
node.style.fill = codes[node.data.Role];
return node;
},
getConnectorDefaults: (connector) => {
connector.type = "Orthogonal";
connector.cornerRadius = 7;
return connector;
},
layout: {
type: "OrganizationalChart",
},
dataSourceSettings: {
id: 'Name', parentId: 'ReportingPerson',
dataManager: new DataManager(localdata),
}
}
},
provide: { diagram: [DataBinding, HierarchicalTree] },
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/tailwind3.css";
</style>Customize employee appearance
The following code examples show how to define the default appearance of nodes and connectors. The setNodeTemplate method updates each node based on employee data:
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :getNodeDefaults='getNodeDefaults'
:getConnectorDefaults='getConnectorDefaults' :setNodeTemplate="setNodeTemplate" :layout='layout'
:dataSourceSettings='dataSourceSettings'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { provide } from "vue";
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram, HierarchicalTree, DataBinding, StackPanel, TextElement, ImageElement } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
import { DataManager } from "@syncfusion/ej2-data";
let localdata = [
{
Name: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Director"
},
{
Name: "Christina",
ReportingPerson: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Manager"
},
{
Name: "Yoshi",
ReportingPerson: "Christina",
Role: "Lead"
},
{
Name: "Philip",
ReportingPerson: "Christina",
Role: "Lead"
},
{
Name: "Yang",
ReportingPerson: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Manager"
},
{
Name: "Roland",
ReportingPerson: "Yang",
Role: "Lead"
},
{
Name: "Yvonne",
ReportingPerson: "Yang",
Role: "Lead"
}
];
const width = "100%";
const height = "350px";
const getNodeDefaults = (node) => {
node.height = 60;
node.width = 100;
node.style = { fill: "#659be5", strokeColor: "none" };
return node;
}
const getConnectorDefaults = (obj) => {
obj.type = 'Orthogonal';
return obj;
}
const setNodeTemplate = (node) => {
let codes = {
Director: "rgb(0, 139,139)",
Manager: "rgb(30, 30,113)",
Lead: "rgb(0, 100,0)"
};
let content = new StackPanel();
content.id = node.id + "_outerstack";
content.orientation = "Horizontal";
content.style.strokeColor = "gray";
content.style.fill = codes[node.data.Role];
content.padding = { left: 5, right: 5, top: 5, bottom: 5 }
let innerContent = new ImageElement();
innerContent.style.strokeColor = "blue";
innerContent.id = node.id + "_innerstack";
innerContent.style.fill = "skyblue";
innerContent.width = 50;
innerContent.height = 50;
let text = new TextElement();
text.id = node.id + "_text";
text.content = node.data.Name;
text.margin = { left: 15, right: 5, top: 5, bottom: 5 }
text.style.color = "black";
content.children = [innerContent, text];
return content;
}
const layout = {
type: "OrganizationalChart",
}
const dataSourceSettings = {
id: 'Name', parentId: 'ReportingPerson',
dataManager: new DataManager(localdata),
doBinding: (nodeModel, localdata) => {
nodeModel.shape = {
type: "Text",
content: (localdata).Role,
}
}
}
provide('diagram', [DataBinding, HierarchicalTree]);
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/tailwind3.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :getNodeDefaults='getNodeDefaults'
:getConnectorDefaults='getConnectorDefaults' :setNodeTemplate='setNodeTemplate' :layout='layout'
:dataSourceSettings='dataSourceSettings'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent, HierarchicalTree, DataBinding, StackPanel, TextElement, ImageElement } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
import { DataManager } from "@syncfusion/ej2-data";
export let localdata = [
{
Name: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Director",
},
{
Name: "Christina",
ReportingPerson: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Manager",
},
{
Name: "Yoshi",
ReportingPerson: "Christina",
Role: "Lead",
},
{
Name: "Philip",
ReportingPerson: "Christina",
Role: "Lead",
},
{
Name: "Yang",
ReportingPerson: "Elizabeth",
Role: "Manager",
},
{
Name: "Roland",
ReportingPerson: "Yang",
Role: "Lead",
},
{
Name: "Yvonne",
ReportingPerson: "Yang",
Role: "Lead",
}
];
export default {
components: {
'ejs-diagram': DiagramComponent
},
name: 'app',
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "550px",
getNodeDefaults: (node) => {
node.height = 60;
node.width = 100;
node.style = { fill: "#659be5", strokeColor: "none" };
return node;
},
getConnectorDefaults: (obj) => {
obj.type = 'Orthogonal';
return obj;
},
setNodeTemplate: (node) => {
let codes = {
Director: "rgb(0, 139,139)",
Manager: "rgb(30, 30,113)",
Lead: "rgb(0, 100,0)"
};
let content = new StackPanel();
content.id = node.id + "_outerstack";
content.orientation = "Horizontal";
content.style.strokeColor = "gray";
content.style.fill = codes[node.data.Role];
content.padding = { left: 5, right: 5, top: 5, bottom: 5 }
let innerContent = new ImageElement();
innerContent.style.strokeColor = "blue";
innerContent.id = node.id + "_innerstack";
innerContent.style.fill = "skyblue";
innerContent.width = 50;
innerContent.height = 50;
let text = new TextElement();
text.id = node.id + "_text";
text.content = node.data.Name;
text.margin = { left: 15, right: 5, top: 5, bottom: 5 }
text.style.color = "black";
content.children = [innerContent, text];
return content;
},
layout: {
type: "OrganizationalChart",
},
dataSourceSettings: {
id: 'Name', parentId: 'ReportingPerson',
dataManager: new DataManager(localdata),
doBinding: (nodeModel, localdata) => {
nodeModel.shape = {
type: "Text",
content: (localdata).Role,
}
}
}
}
},
provide: { diagram: [DataBinding, HierarchicalTree] },
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/tailwind3.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/tailwind3.css";
</style>