UML diagram in Vue Diagram component
25 Apr 202524 minutes to read
UML Class Diagram
A class diagram visually depicts the static structure of an application and is extensively employed in modeling object-oriented systems. It holds a unique position in UML diagrams, as it directly aligns with object-oriented languages. The diagram also facilitates automatic generation of class diagram shapes based on business logic, streamlining the translation from conceptual models to practical implementation.
UML Class Diagram Shapes
The UML class diagram shapes are explained as follows.
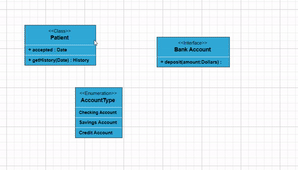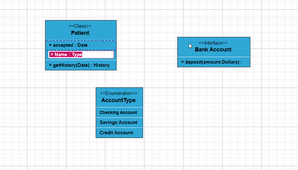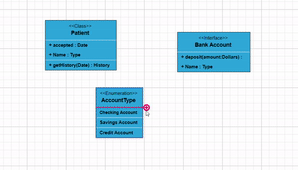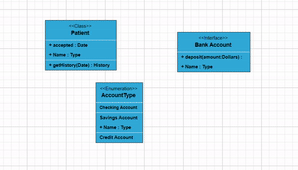
Class
A class defines a group of objects that share common specifications, features, constraints, and semantics. To create a class object, the classifier should be defined using the class notation. This notation serves as a foundational element in object-oriented programming, encapsulating the Essential® characteristics and behavior that objects belonging to the class will exhibit.
Also, define the name, attributes, and methods of the class using the class property of node.
The attribute’s name, type, and scope properties allow you to define the name, data type, and visibility of the attribute.
The method’s name, parameters, type, and scope properties allow you to define the name, parameter, return type, and visibility of the methods.
-
The method
parametersobject properties allow you to define the name and type of the parameter. -
The following code example illustrates how to create a class.
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :nodes='nodes'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const nodes = [{
id: "Patient",
//Position of the node
offsetX: 200,
offsetY: 200,
style: {
fill: '#26A0DA',
},
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
//Define class object
classShape: {
name: "Patient",
//Define class attributes
attributes: [{ name: "accepted", type: "Date" }],
//Define class methods
methods: [{ name: "getHistory", type: "getHistory" }]
},
classifier: "Class"
} as UmlClassifierShapeModel
}]
const width = "100%";
const height = "350px";
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :nodes='nodes'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
let nodes = [{
id: "Patient",
//Position of the node
offsetX: 200,
offsetY: 200,
style: {
fill: '#26A0DA',
},
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
//Define class object
classShape: {
name: "Patient",
//Define class attributes
attributes: [{ name: "accepted", type: "Date" }],
//Define class methods
methods: [{ name: "getHistory", type: "getHistory" }]
},
classifier: "Class"
}
}]
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "350px",
nodes: nodes
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style>Interface
- An
interfaceis a specific type of classifier that signifies a declaration of a cohesive set of public features and obligations. When creating an interface, it involves defining the classifier property using the interface notation. This Essential® concept in object-oriented programming outlines a contract for classes to adhere to, specifying the required methods and behaviors without delving into the implementation details.
Additionally, you can define the name, attributes, and methods of the interface using the interface property of the node.
The attributes’ name, type, and scope properties allow you to specify the name, data type, and visibility of each attribute.
Similarly, the methods’ name, parameters, type, and scope properties enable you to define the name, parameters, return type, and visibility of the methods.
The parameters object within methods allows you to specify the name and type of each parameter.
The following code example illustrates how to create an interface:
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :nodes='nodes'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const nodes = [{
id: "Patient",
//Position of the node
offsetX: 200,
offsetY: 200,
style: {
fill: '#26A0DA',
},
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
//Define interface object
interfaceShape: {
name: "Patient",
//Define interface attributes
attributes: [{ name: "owner", type: "String[*]" }],
//Define interface methods
methods: [
{
name: "deposit",
parameters: [
{
name: "amount",
type: "Dollars"
}
]
}
]
},
classifier: "Interface"
} as UmlClassifierShapeModel
}]
const width = "100%";
const height = "350px";
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :nodes='nodes'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
let nodes = [{
id: "Patient",
//Position of the node
offsetX: 200,
offsetY: 200,
style: {
fill: '#26A0DA',
},
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
//Define interface object
interfaceShape: {
name: "Patient",
//Define interface attributes
attributes: [{ name: "owner", type: "String[*]" }],
//Define interface methods
methods: [
{
name: "deposit",
parameters: [
{
name: "amount",
type: "Dollars"
}
]
}
]
},
classifier: "Interface"
}
}]
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "350px",
nodes: nodes
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style>Enumeration
To establish an enumeration, designate the classifier property of the node as enumeration. Additionally, define the name and enumerate the members of the enumeration using the appropriate enumeration property of the node. This process encapsulates a set of distinct values within the enumeration, allowing for a clear representation of specific and named constants within a system.
You can set a name for the enumeration members collection using the name property of members collection.
The following code example illustrates how to create an enumeration.
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :nodes='nodes'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const nodes = [{
id: "Patient",
offsetX: 200,
offsetY: 200,
style: {
fill: '#26A0DA',
},
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
//Define enumeration object
enumerationShape: {
name: "AccountType",
//set the members of enumeration
members: [
{
name: "Checking Account",
},
{
name: "Savings Account"
},
{
name: "Credit Account"
}
]
},
classifier: "Enumeration"
} as UmlClassifierShapeModel
}];
const width = "100%";
const height = "350px";
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :nodes='nodes'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
let nodes = [{
id: "Patient",
offsetX: 200,
offsetY: 200,
style: {
fill: '#26A0DA',
},
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
//Define enumeration object
enumerationShape: {
name: "AccountType",
//set the members of enumeration
members: [
{
name: "Checking Account",
},
{
name: "Savings Account"
},
{
name: "Credit Account"
}
]
},
classifier: "Enumeration"
}
}]
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "350px",
nodes: nodes
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style>UML Class Relationships
A class may be involved in one or more relationships with other classes. A relationship can be one of the following types:
| Shape | Image |
|---|---|
| Association |  |
| Aggregation |  |
| Composition |  |
| Inheritance |  |
| Dependency |  |
Association
Association is basically a set of links that connects elements of a UML model. The type of association is as follows.
1. Directional
2. BiDirectional
The association property allows you to define the type of association. The default value of association is “Directional”. The following code example illustrates how to create an association.
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :connectors='connectors'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const connectors = [{
id: "connector1",
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 300, y: 300 },
type: "Straight",
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
relationship: "Association",
//Define type of association
association: "BiDirectional"
}
},
{
id: 'connector2',
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 200, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 400, y: 300 },
type: 'Straight',
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
relationship: 'Association',
associationType: 'BiDirectional',
},
}]
const width = "100%";
const height = "600px";
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :connectors='connectors'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
let connectors = [{
id: "connector1",
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 300, y: 300 },
type: "Straight",
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
relationship: "Association",
//Define type of association
association: "BiDirectional"
}
},
{
id: 'connector2',
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 200, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 400, y: 300 },
type: 'Straight',
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
relationship: 'Association',
associationType: 'BiDirectional',
},
}]
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "600px",
connectors: connectors
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style>Aggregation
Aggregation is a binary association between a property and one or more composite objects that group together a set of instances. Aggregation is decorated with a hollow diamond. To create an aggregation shape, define the relationship of connector shape as “Aggregation”.
The following code example illustrates how to create an aggregation.
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :connectors='connectors'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
let connectors = [{
id: "connector",
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 300, y: 300 },
type: "Straight",
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
//Set an relationship for connector
relationship: "Aggregation"
}
}]
const width = "100%";
const height = "350px";
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :connectors='connectors'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
let connectors = [{
id: "connector",
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 300, y: 300 },
type: "Straight",
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
//Set an relationship for connector
relationship: "Aggregation"
}
}]
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "350px",
connectors: connectors
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style>Composition
Composition is a strong form of aggregation. The composition is decorated with a black diamond. To create a composition shape, define the relationship property of the connector shape as “Composition”.
The following code example illustrates how to create a composition.
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :connectors='connectors'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const connectors = [{
id: "connector",
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 300, y: 300 },
type: "Straight",
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
//Set an relationship for connector
relationship: "Composition"
}
}]
const width = "100%"
const height = "350px"
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :connectors='connectors'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
let connectors = [{
id: "connector",
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 300, y: 300 },
type: "Straight",
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
//Set an relationship for connector
relationship: "Composition"
}
}]
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "350px",
connectors: connectors
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style>Inheritance
Inheritance is also called as “generalization”. Inheritance is a binary taxonomic directed relationship between a more general classifier (super class) and a more specific classifier (subclass). Inheritance is shown as a line with hollow triangle.
To create an inheritance, define the relationship as “inheritance”.
The following code example illustrates how to create an inheritance.
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :connectors='connectors'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const connectors = [{
id: "connector",
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 300, y: 300 },
type: "Straight",
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
//Set an relationship for connector
relationship: "Inheritance"
}
}]
const width = "100%";
const height = "350px";
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :connectors='connectors'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
let connectors = [{
id: "connector",
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 300, y: 300 },
type: "Straight",
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
//Set an relationship for connector
relationship: "Inheritance"
}
}]
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "350px",
connectors: connectors,
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style>Dependency
Dependency is a directed relationship, which is used to show that some UML elements needs or depends on other model elements for specifications. Dependency is shown as dashed line with opened arrow. To create a dependency, define the relationship property of connector shape as “dependency”.
The following code example illustrates how to create an dependency.
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :connectors='connectors'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const connectors = [{
id: "connector",
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 300, y: 300 },
type: "Straight",
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
//Set an relationship for connector
relationship: "Dependency"
}
}]
const width = "100%";
const height = "350px";
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :connectors='connectors'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
let connectors = [{
id: "connector",
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 300, y: 300 },
type: "Straight",
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
//Set an relationship for connector
relationship: "Dependency"
}
}]
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "350px",
connectors: connectors
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style>Multiplicity
Multiplicity is a definition of an inclusive interval of non-negative integers to specify the allowable number of instances of described element. The type of multiplicity are as follows.
1. OneToOne
2. ManyToOne
3. OneToMany
4. ManyToMany
By default the multiplicity will be considered as “OneToOne”.
The multiplicity property in UML allows you to specify large number of elements or some collection of elements.
The shape multiplicity’s source property is used to set the source label to connector and the target property is used to set the target label to connector.
To set an optionality or cardinality for the connector source label, use optional property.
The lowerBounds and upperBounds could be natural constants or constant expressions evaluated to natural (non negative) number. Upper bound could be also specified as asterisk ‘*’ which denotes unlimited number of elements. Upper bound should be greater than or equal to the lower bound.
- The following code example illustrates how to customize the multiplicity.
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :connectors='connectors'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const connectors = [{
id: 'connector1',
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 300, y: 300 },
type: 'Straight',
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
relationship: 'Dependency',
multiplicity: {
//Set multiplicity type
type: 'OneToOne',
},
},
},
{
id: 'connector2',
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 200, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 400, y: 300 },
type: 'Straight',
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
relationship: 'Dependency',
multiplicity: {
//Set multiplicity type
type: 'ManyToOne',
//Set source label to connector
source: {
optional: true,
lowerBounds: '89',
upperBounds: '67',
},
//Set target label to connector
target: {
optional: true,
lowerBounds: '78',
upperBounds: '90',
},
},
},
},
{
id: 'connector3',
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 300, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 500, y: 300 },
type: 'Straight',
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
relationship: 'Dependency',
multiplicity: {
//Set multiplicity type
type: 'OneToMany',
//Set source label to connector
source: {
optional: true,
lowerBounds: '89',
upperBounds: '67',
},
//Set target label to connector
target: {
optional: true,
lowerBounds: '78',
upperBounds: '90',
},
},
},
},
{
id: 'connector4',
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 400, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 600, y: 300 },
type: 'Straight',
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
relationship: 'Dependency',
multiplicity: {
//Set multiplicity type
type: 'ManyToMany',
//Set source label to connector
source: {
optional: true,
lowerBounds: '89',
upperBounds: '67',
},
//Set target label to connector
target: {
optional: true,
lowerBounds: '78',
upperBounds: '90',
},
},
},
}]
const width = "100%";
const height = "600px";
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :connectors='connectors'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
let connectors = [{
id: 'connector1',
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 300, y: 300 },
type: 'Straight',
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
relationship: 'Dependency',
multiplicity: {
//Set multiplicity type
type: 'OneToOne',
},
},
},
{
id: 'connector2',
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 200, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 400, y: 300 },
type: 'Straight',
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
relationship: 'Dependency',
multiplicity: {
//Set multiplicity type
type: 'ManyToOne',
//Set source label to connector
source: {
optional: true,
lowerBounds: '89',
upperBounds: '67',
},
//Set target label to connector
target: {
optional: true,
lowerBounds: '78',
upperBounds: '90',
},
},
},
},
{
id: 'connector3',
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 300, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 500, y: 300 },
type: 'Straight',
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
relationship: 'Dependency',
multiplicity: {
//Set multiplicity type
type: 'OneToMany',
//Set source label to connector
source: {
optional: true,
lowerBounds: '89',
upperBounds: '67',
},
//Set target label to connector
target: {
optional: true,
lowerBounds: '78',
upperBounds: '90',
},
},
},
},
{
id: 'connector4',
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 400, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 600, y: 300 },
type: 'Straight',
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
relationship: 'Dependency',
multiplicity: {
//Set multiplicity type
type: 'ManyToMany',
//Set source label to connector
source: {
optional: true,
lowerBounds: '89',
upperBounds: '67',
},
//Set target label to connector
target: {
optional: true,
lowerBounds: '78',
upperBounds: '90',
},
},
},
}]
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "600px",
connectors: connectors
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style>How to add UML child at runtime
In UML nodes, child elements such as member, method and attribute can be added either programmatically or interactively.
Adding UML child through code
The addChildToUmlNode method is employed for dynamically adding a child to the UML node during runtime, providing flexibility in modifying the diagram structure programmatically.
The following code example illustrates how to add members, methods and attributes to UML node at rumtime.
<template>
<div id="app">
<button @click="addMethod">addMethod</button>
<button @click="addAttribute">addAttribute</button>
<button @click="addMember">addMember</button>
<ejs-diagram
id="diagram"
ref="diagramObj"
:width="width"
:height="height"
:nodes="nodes"
></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from "vue";
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram } from "@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams";
const diagramObj = ref(null);
let nodes = [
{
id: "node1",
offsetX: 150,
offsetY: 150,
style: {
fill: "#26A0DA",
},
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
classShape: {
attributes: [{ name: "accepted", type: "Date" }],
methods: [
{
name: "getHistory",
style: {},
parameters: [{ name: "Date", style: {} }],
type: "History",
},
],
name: "Patient",
},
classifier: "Class",
},
},
{
id: "enumeration",
style: {
fill: "#26A0DA",
},
//Position of the node
offsetX: 400,
offsetY: 200,
shape: {
type: "UmlClassifier",
//Define enumeration object
enumerationShape: {
name: "AccountType",
//sets the members of enumeration
members: [
{
name: "Checking Account",
style: {},
},
{
name: "Savings Account",
},
{
name: "Credit Account",
},
],
},
classifier: "Enumeration",
},
},
];
const width = "1000px";
const height = "450px";
const addMethod = function () {
let diagram = diagramObj.value.ej2Instances;
let node = diagram.nodes[0];
let methods = {
name: "getHistory",
style: { color: "red" },
parameters: [{ name: "Date", style: {} }],
type: "History",
};
diagram.addChildToUmlNode(node, methods, "Method");
};
const addAttribute = function () {
let diagram = diagramObj.value.ej2Instances;
let node = diagram.nodes[0];
let attributes = { name: "accepted", type: "Date", style: { color: "red" } };
diagram.addChildToUmlNode(node, attributes, "Attribute");
};
const addMember = function () {
let diagram = diagramObj.value.ej2Instances;
let node = diagram.nodes[1];
let members = {
name: "Checking new",
style: { color: "red" },
isSeparator: true,
};
diagram.addChildToUmlNode(node, members, "Member");
};
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<button v-on:click="addMethod">add Method</button>
<button v-on:click="addAttribute">add Attribute</button>
<button v-on:click="addMember">add Member</button>
<ejs-diagram
id="diagram"
ref="diagramObj"
:width="width"
:height="height"
:nodes="nodes"
></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
import { ButtonComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-buttons';
let nodes = [{
id: 'node1',
offsetX: 150,
offsetY: 150,
style: {
fill: '#26A0DA',
},
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
classShape: {
attributes: [
{ name: 'accepted', type: 'Date', },
],
methods: [{ name: 'getHistory', style: {}, parameters: [{ name: 'Date', style: {} }], type: 'History' }],
name: 'Patient'
},
classifier: 'Class'
},
},
{
id: 'enumeration',
style: {
fill: '#26A0DA',
},
//Position of the node
offsetX: 400,
offsetY: 200,
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
//Define enumeration object
enumerationShape: {
name: 'AccountType',
//sets the members of enumeration
members: [
{
name: 'Checking Account',
style: {},
},
{
name: 'Savings Account',
},
{
name: 'Credit Account',
},
],
},
classifier: 'Enumeration',
},
},
]
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent,
'ejs-button': ButtonComponent,
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "600px",
nodes: nodes,
}
},
methods: {
addMethod: function () {
let diagram = this.$refs.diagramObj.ej2Instances;
let node = diagram.nodes[0];
let methods = {
name: 'getHistory',
style: { color: 'red' },
parameters: [{ name: 'Date', style: {} }],
type: 'History',
};
diagram.addChildToUmlNode(node, methods, 'Method');
},
addAttribute: function () {
let diagram = this.$refs.diagramObj.ej2Instances;
let node = diagram.nodes[0];
let attributes = { name: 'accepted', type: 'Date', style: { color: "red", } };
diagram.addChildToUmlNode(node, attributes, "Attribute");
},
addMember: function () {
let diagram = this.$refs.diagramObj.ej2Instances;
let node = diagram.nodes[1];
let members = { name: 'Checking new', style: { color: "red", }, isSeparator: true };
diagram.addChildToUmlNode(node, members, "Member");
},
},
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style>Adding UML child through user interaction
To include a child, select a node, move the mouse outside it, and position the pointer near the right side. A highlighter emerges between the two child elements. Click the highlighter to add a child type to the chosen UML node seamlessly. The following gif illustrates how to add Child through user interaction.
Adding UML Nodes in Symbol palette
UML built-in shapes are easily rendered in a symbol palette. The symbols property of palettes is used to define UML symbols with the necessary classes and methods. This feature allows you to add a collection of predefined UML symbols to the palette, making your UML diagramming application more versatile.
The following code example showcases the rendering of UML built-in shapes in a symbol palette.
<template>
<div style="width: 100%">
<div id="palette-space" class="sb-mobile-palette">
<ejs-symbolpalette id="symbolpalette" :palettes="palettes" :width="palettewidth" :height="paletteheight"
:getNodeDefaults="palettegetNodeDefaults" :getSymbolInfo="getSymbolInfo" :symbolMargin="symbolMargin"
:symbolHeight="symbolHeight" :symbolWidth="symbolWidth">
</ejs-symbolpalette>
</div>
<div id="diagram-space" class="sb-mobile-diagram">
<ejs-diagram style="display: block" ref="diagramObject" id="diagram" :width="width" :height="height">
</ejs-diagram>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram, SymbolPaletteComponent as EjsSymbolpalette } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const umlShapes = [
{
id: 'class',
style: {
fill: '#26A0DA',
},
borderColor: 'white',
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
classShape: {
attributes: [
{
name: 'accepted',
type: 'Date',
style: {
color: 'red',
fontFamily: 'Arial',
textDecoration: 'Underline',
italic: true,
},
isSeparator: true,
},
],
methods: [
{
name: 'getHistory',
style: {},
parameters: [{ name: 'Date', style: {} }],
type: 'History',
},
],
name: 'Patient',
},
classifier: 'Class',
},
},
{
id: 'Interface',
style: {
fill: '#26A0DA',
},
borderColor: 'white',
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
interfaceShape: {
name: 'Bank Account',
},
classifier: 'Interface',
},
},
{
id: 'Enumeration',
style: {
fill: '#26A0DA',
},
borderColor: 'white',
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
enumerationShape: {
name: 'AccountType',
members: [
{
name: 'Checking Account',
style: {},
},
],
},
classifier: 'Enumeration',
},
},
];
const width = '100%';
const height = '700px';
const palettes = [
{
id: 'uml',
expanded: true,
symbols: umlShapes,
title: 'UML Shapes',
},
]
const palettewidth = '100%';
const paletteheight = '700px';
const symbolHeight = 80;
const symbolWidth = 80;
const palettegetNodeDefaults = (symbol) => {
symbol.width = 100;
symbol.height = 100;
}
const symbolMargin = { left: 15, right: 15, top: 15, bottom: 15 };
const getSymbolInfo = (symbol) => {
return { fit: true, description: { text: symbol.id } };
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style><template>
<div style="width: 100%">
<div id="palette-space" class="sb-mobile-palette">
<ejs-symbolpalette id="symbolpalette" :palettes="palettes" :width="palettewidth" :height="paletteheight"
:getNodeDefaults="palettegetNodeDefaults" :getSymbolInfo="getSymbolInfo" :symbolMargin="symbolMargin"
:symbolHeight="symbolHeight" :symbolWidth="symbolWidth"></ejs-symbolpalette>
</div>
<div id="diagram-space" class="sb-mobile-diagram">
<ejs-diagram style="display: block" ref="diagramObject" id="diagram" :width="width"
:height="height"></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent, SymbolPaletteComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
let umlShapes = [
{
id: 'class',
style: {
fill: '#26A0DA',
},
borderColor: 'white',
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
classShape: {
attributes: [
{
name: 'accepted',
type: 'Date',
style: {
color: 'red',
fontFamily: 'Arial',
textDecoration: 'Underline',
italic: true,
},
isSeparator: true,
},
],
methods: [
{
name: 'getHistory',
style: {},
parameters: [{ name: 'Date', style: {} }],
type: 'History',
},
],
name: 'Patient',
},
classifier: 'Class',
},
},
{
id: 'Interface',
style: {
fill: '#26A0DA',
},
borderColor: 'white',
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
interfaceShape: {
name: 'Bank Account',
},
classifier: 'Interface',
},
},
{
id: 'Enumeration',
style: {
fill: '#26A0DA',
},
borderColor: 'white',
shape: {
type: 'UmlClassifier',
enumerationShape: {
name: 'AccountType',
members: [
{
name: 'Checking Account',
style: {},
},
],
},
classifier: 'Enumeration',
},
},
];
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-symbolpalette": SymbolPaletteComponent,
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: '100%',
height: '700px',
palettes: [
{
id: 'uml',
expanded: true,
symbols: umlShapes,
title: 'UML Shapes',
},
],
palettewidth: '100%',
paletteheight: '700px',
symbolHeight: 80,
symbolWidth: 80,
palettegetNodeDefaults: (symbol) => {
symbol.width = 100;
symbol.height = 100;
},
symbolMargin: { left: 15, right: 15, top: 15, bottom: 15 },
getSymbolInfo: (symbol) => {
return { fit: true, description: { text: symbol.id } };
},
};
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style>Editing in UML nodes
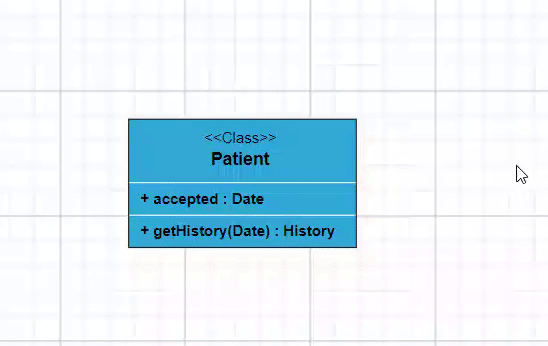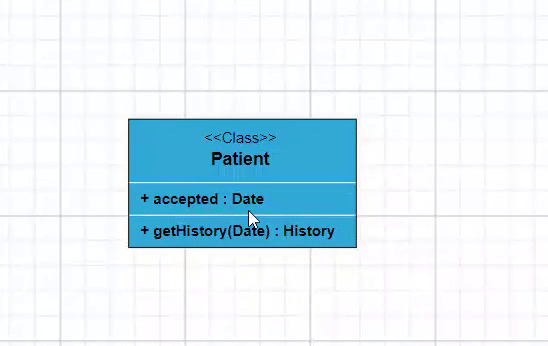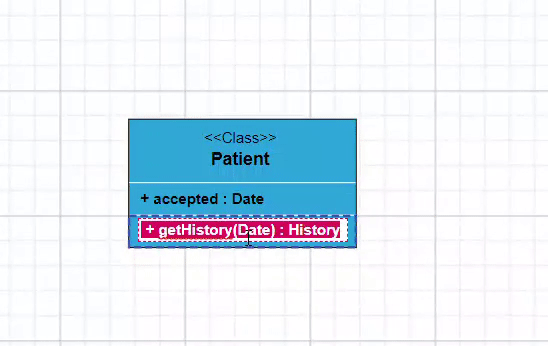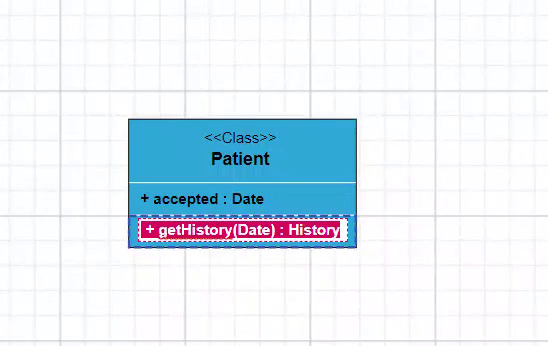
You can edit the name, attributes, and methods of the class diagram shapes just double clicking, similar to editing a node annotation.
The following image illustrates how the text editor looks in an edit mode.
UML Activity diagram
An Activity diagram functions as a visual flowchart, illustrating the progression from one activity to the next within a system. Each activity corresponds to a system operation, providing a clear depiction of the sequential flow in a dynamic process..
The purpose of an activity diagram can be described as follows.
1. Draw the activity flow of a system.
2. Describe the sequence from one activity to another.
3. Describe the parallel, branched, and concurrent flow of the system.
UML Activity diagram Shapes
To create a UmlActivity, define the type as “UmlActivity” and set the list of built-in shapes in the shape property as demonstrated below.
| Shape | Image |
|---|---|
| Action |  |
| Decision |  |
| MergeNode |  |
| InitialNode |  |
| FinalNode |  |
| ForkNode |  |
| JoinNode | 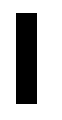 |
| TimeEvent | 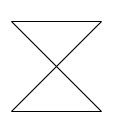 |
| AcceptingEvent | 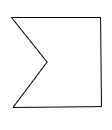 |
| SendSignal | 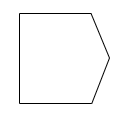 |
| ReceiveSignal | 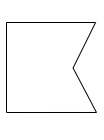 |
| StructuredNode | 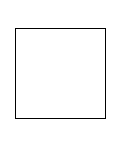 |
| Note | 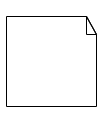 |
The following code illustrates how to create a UMLActivity shapes.
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :nodes='nodes'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const nodes = [
{ id: 'Action', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'Action' },offsetX:100,offsetY:100,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'Decision', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'Decision' },offsetX:300,offsetY:100,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'MergeNode', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'MergeNode' },offsetX:500,offsetY:100,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'InitialNode', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'InitialNode' },offsetX:100,offsetY:300,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'FinalNode', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'FinalNode' },offsetX:300,offsetY:300,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'ForkNode', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'ForkNode' },offsetX:500,offsetY:300,height:100,width:100},
{ id: 'JoinNode', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'JoinNode' },offsetX:100,offsetY:500,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'TimeEvent', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'TimeEvent' },offsetX:300,offsetY:500,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'AcceptingEvent', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'AcceptingEvent' },offsetX:500,offsetY:500,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'SendSignal', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'SendSignal' },offsetX:100,offsetY:700,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'ReceiveSignal', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'ReceiveSignal' },offsetX:300,offsetY:700,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'StructuredNode', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'StructuredNode' },offsetX:500,offsetY:700,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'Note', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'Note' },offsetX:100,offsetY:900,height:100,width:100 }
]
const width = "100%";
const height = "350px";
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :nodes='nodes'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
let nodes = [
{ id: 'Action', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'Action' },offsetX:100,offsetY:100,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'Decision', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'Decision' },offsetX:300,offsetY:100,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'MergeNode', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'MergeNode' },offsetX:500,offsetY:100,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'InitialNode', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'InitialNode' },offsetX:100,offsetY:300,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'FinalNode', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'FinalNode' },offsetX:300,offsetY:300,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'ForkNode', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'ForkNode' },offsetX:500,offsetY:300,height:100,width:100},
{ id: 'JoinNode', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'JoinNode' },offsetX:100,offsetY:500,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'TimeEvent', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'TimeEvent' },offsetX:300,offsetY:500,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'AcceptingEvent', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'AcceptingEvent' },offsetX:500,offsetY:500,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'SendSignal', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'SendSignal' },offsetX:100,offsetY:700,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'ReceiveSignal', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'ReceiveSignal' },offsetX:300,offsetY:700,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'StructuredNode', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'StructuredNode' },offsetX:500,offsetY:700,height:100,width:100 },
{ id: 'Note', shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', shape: 'Note' },offsetX:100,offsetY:900,height:100,width:100 }
]
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "600px",
nodes: nodes
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style>UMLActivity connector
To establish a UMLActivity connector, specify the type of connector shape as “UMLActivity” and define the flow as either “Exception,” “Control,” or “Object.” This configuration delineates the nature of the connection, allowing for a precise representation of the interaction within the activity diagram.
The following code illustrates how to create a UMLActivity connector.
<template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :connectors='connectors'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { DiagramComponent as EjsDiagram } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
let connectors = [{
id: 'connector',
type: 'Straight',
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 200, y: 200 },
shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', flow: 'Exception' }
}]
const width = "100%";
const height = "350px";
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style><template>
<div id="app">
<ejs-diagram id="diagram" :width='width' :height='height' :connectors='connectors'></ejs-diagram>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { DiagramComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams';
const connectors = [{
id: 'connector',
type: 'Straight',
//Define connector start and end points
sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 200, y: 200 },
shape: { type: 'UmlActivity', flow: 'Exception' }
}]
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-diagram": DiagramComponent
},
data() {
return {
width: "100%",
height: "350px",
connectors: connectors
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-vue-diagrams/styles/material.css";
</style>