How can I help you?
Connecting GraphQL Service with EJ2 TypeScript Grid Control
7 May 202524 minutes to read
GraphQL is a powerful query language for APIs, designed to provide a more efficient alternative to traditional REST APIs. It allows you to precisely fetch the data you need, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching of data. GraphQL provides a flexible and expressive syntax for querying, enabling clients to request only the specific data they require.
Syncfusion’s® Grid control seamlessly integrates with GraphQL servers using the GraphQLAdaptor in the DataManager. This specialized adaptor simplifies the interaction between the Syncfusion® Grid and GraphQL servers, allowing efficient data retrieval with support for various operations like CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete), paging, sorting, and filtering.
This section describes a step-by-step process for retrieving data from GraphQL service using GraphQLAdaptor, then binding it to the Grid control to facilitate data and CRUD operations.
Configure GraphQL Server
To configure a GraphQL server with Syncfusion® Grid, you need to follow the below steps:
Step 1: Create Service for GraphQL
-
Create a new folder named GraphQLServer specifically for your GraphQL server.
-
Install the graph pack npm package. Open your terminal and navigate to the server folder, then run:
npm i graphpack -
To utilize Syncfusion’s® ej2-data package, you need to include it as a dependency in your project’s package.json file. Here’s how you can mention it in the configuration:
{ "name": "graphql-server", "version": "1.0.0", "description": "", "scripts": { "dev": "graphpack --port 4205", "build": "graphpack build" }, "devDependencies": { "graphpack": "^1.0.9" }, "dependencies": { "@syncfusion/ej2-data": "24.1.41" } } -
Create a database file (src/db.js) to store your data.
export let OrderData = [ { OrderID: 10248, CustomerID: 'VINET', EmployeeID: 5, OrderDate: new Date("07 12 1996 02:00:23"), ShipName: 'Vins et alcools Chevalier', ShipCity: 'Reims', ShipAddress: '59 rue de l Abbaye', ShipRegion: 'CJ', ShipPostalCode: '51100', ShipCountry: 'France', Freight: 32.38, Verified: !0 }, { OrderID: 10249, CustomerID: 'TOMSP', EmployeeID: 6, OrderDate: new Date("07 12 1996 00:03:23"), ShipName: 'Toms Spezialitäten', ShipCity: 'Münster', ShipAddress: 'Luisenstr. 48', ShipRegion: 'CJ', ShipPostalCode: '44087', ShipCountry: 'Germany', Freight: 11.61, Verified: !1 }, { OrderID: 10250, CustomerID: 'HANAR', EmployeeID: 4, OrderDate: new Date("07 12 1996 00:00:23"), ShipName: 'Hanari Carnes', ShipCity: 'Rio de Janeiro', ShipAddress: 'Rua do Paço, 67', ShipRegion: 'RJ', ShipPostalCode: '05454-876', ShipCountry: 'Brazil', Freight: 65.83,Verified: !0 }, .... ];Ensure that the GraphQL server is properly configured and dependencies are installed to proceed with the next steps.
Step 2: Schema Definition for GraphQL Server
In the context of GraphQL, a schema defines the structure of the data that clients can query from the server. It serves as a contract between the client and the server, outlining the types of data available, the operations that can be performed, and how the data is related.
When integrating GraphQL with the Syncfusion® Grid, defining a schema involves specifying the types of data the Grid expects to receive from the GraphQL server, along with any additional parameters for operations like sorting, filtering, and paging.
Here’s how you can define a schema for the Syncfusion® Grid:
-
Define Types: Create types representing the structure of data retrieved from GraphQL queries. Since the
GraphQLAdaptorin Syncfusion® extends fromUrlAdaptor, it expects a JSON response with specific properties:- result: An array containing the data entities.
- count: The total number of records.
- aggregates: Contains total aggregate data(optional).
For example, if your Grid displays orders, you might define types for ReturnType and Order:
type ReturnType { result: [Order] count: Int aggregates: String # Total records aggregates } type Order { OrderID: Int! CustomerID: String EmployeeID: Int Freight: Int ShipCity: String ShipCountry: String } -
Define Queries: Define queries that can be made to retrieve data from the server. In the case of a Grid, you may define a query to fetch orders, accepting parameters such as
DataManagerfor advanced data operations. To utilizeDatamanager, you need to install packages from@syncfusion/ej2-datatype Query { getOrders(datamanager: DataManager): ReturnType } -
Define DataManager Input: Define input types for
DataManager, specifying parameters for sorting, filtering, paging, aggregates, etc., to be used in queries. The query parameters will be send in a string format which contains the below details.Parameters Description requiresCountsIf it is true then the total count of records will be included in response. skipHolds the number of records to skip. takeHolds the number of records to take. sortedContains details about current sorted column and its direction. whereContains details about current filter column name and its constraints. groupContains details about current grouped column names. searchContains details about current search data. aggregatesContains details about aggregate data. input DataManager { skip: Int take: Int sorted: [Sort] group: [String] table: String select: [String] where: String search: String requiresCounts: Boolean aggregates: [Aggregate] params: String }
Create a schema file (e.g., src/schema.graphql) in your GraphQL server project and write the schema definition there.
#Grid Sort direction
input Sort {
name: String
direction: String
}
#Grid aggregates type
input Aggregate {
field: String!
type: String!
}
# Represents parameters for querying data, including sorting, filtering, etc.
input DataManager {
skip: Int
take: Int
sorted: [Sort]
group: [String]
table: String
select: [String]
where: String
search: String
requiresCounts: Boolean
aggregates: [Aggregate]
params: String
}
# Represents an order type
type Order {
OrderID: Int!
CustomerID: String
EmployeeID: Int
Freight: Int
ShipCity: String
ShipCountry: String
}
# Represents the result of a query, including the data and count
type ReturnType {
result: [Order]
count: Int
aggregates: String
}
# Represents a query to fetch orders with specified data manager parameters
type Query {
getOrders(datamanager: DataManager): ReturnType
}
Step 3: Implement Resolvers
To handle GraphQL queries and fetch data from your database, you need to create resolver functions. These resolver functions will be responsible for processing GraphQL queries and returning the appropriate data. In order to return data based on the grid expected result and count, utilize DataUtil from @syncfusion/ej2-data package.
Create a resolver file(src/resolvers.js) and implement the following code.
import { OrderData } from "./db";
import { DataUtil } from "@syncfusion/ej2-data";
const resolvers = {
Query: {
getOrders: (parent, { datamanager }, context, info) => {
var ret = DataUtil.processData(datamanager, OrderData);
return ret;
}
}
};
export default resolvers;Step 4: Run GraphQL Server
Install required packages and start the GraphQL server by running the following commands in your terminal:
npm install
npm run devThe server will be hosted at http://localhost:xxxx/. (where xxxx represents the port number).
Connecting grid to an GraphQL service
To integrate GraphQL with the Syncfusion® Grid in your EJ2 TypeScript application, follow the below steps:
Step 1: Set up development environment
Open the command prompt from the required directory, and run the following command to clone the Syncfusion® JavaScript (Essential® JS 2) quickstart project from GitHub.
git clone https://github.com/SyncfusionExamples/ej2-quickstart-webpack- GridClient
cd GridClientStep 2: Add Syncfusion® Grid packages
npm installStep 3: Import the Syncfusion® CSS styles
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/bootstrap5.css';
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-buttons/styles/bootstrap5.css';
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-calendars/styles/bootstrap5.css';
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-dropdowns/styles/bootstrap5.css';
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-inputs/styles/bootstrap5.css';
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/bootstrap5.css';
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/bootstrap5.css';
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/bootstrap5.css';
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-notifications/styles/bootstrap5.css';
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-grids/styles/bootstrap5.css';Step 3: Adding Grid control
To get started, add the grid control in app.ts and index.html files using the following code.
Place the following grid code in the app.ts.
import { Grid } from '@syncfusion/ej2-grids';
import { DataManager, GraphQLAdaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
let data: DataManager = new DataManager({
url: "http://localhost:xxxx", // Replace your hosted server link
adaptor: new GraphQLAdaptor({
response: {
result: 'getOrders.result',
count: 'getOrders.count'
},
query: `query getOrders($datamanager: DataManager) {
getOrders(datamanager: $datamanager) {
count,
result{
OrderID, CustomerID, ShipCity, ShipCountry}
}
}`,
}),
});
let grid: Grid = new Grid({
dataSource: data,
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, type: 'number', isPrimaryKey: true },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'ShipCity', headerText: 'Ship City', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'Ship Country', width: 140 }
],
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');Now, add an HTML div element with its ID attribute set to Grid in your index.html using the following code.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>EJ2 Grid</title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta name="description" content="Typescript Grid Control" />
<meta name="author" content="Syncfusion" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-base/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-grids/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-buttons/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-popups/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-richtexteditor/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-navigations/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-dropdowns/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-lists/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-inputs/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-calendars/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-notifications/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/systemjs/0.19.38/system.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/syncfusion-helper.js" type ="text/javascript"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id='container'>
<div id='Grid'></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Step 5: Run the Application:
Once the GraphQL server is running, assign its URL (e.g., http://localhost:xxxx/) to the dataManager.url property of the DataManager in your application.
npm startBy following these steps, you will successfully integrate GraphQL with the Syncfusion® Grid in your EJ2 TypeScript application. Ensure that the GraphQL server is running smoothly and is accessible at the specified URL.
You can find the complete GraphQLAdaptor sample in the GitHub link.
Handling searching operation
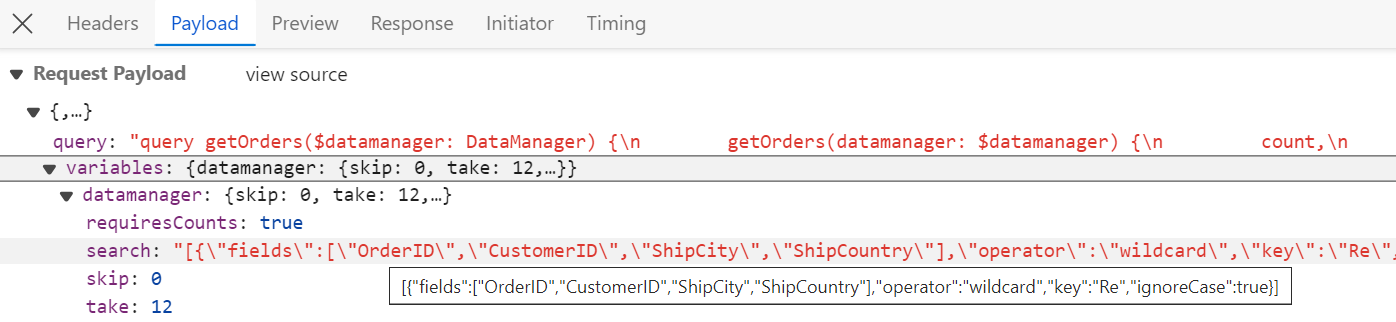
To handle search operation in the Syncfusion® Grid using the GraphQLAdaptor, by utilizing the datamanager.search parameters and executing the search operation with the search method. This feature allows users to efficiently search through the grid’s data and retrieve relevant information based on specified criteria.
In the image below, you can see the values of datamanager.search parameters:
import { OrderData } from "./db";
import { DataUtil, Query, DataManager } from "@syncfusion/ej2-data";
const resolvers = {
Query: {
getOrders: (parent, { datamanager }, context, info) => {
let orders = [...OrderData];
const query = new Query();
const performSearching = (searchParam) => {
const { fields, key } = JSON.parse(searchParam)[0];
query.search(key, fields);
}
// Perform Searching
if (datamanager.search) {
performSearching(datamanager.search);
}
orders = new DataManager(orders).executeLocal(query);
var count = orders.length;
return { result: orders, count: count }; // Return result and count
},
},
};
export default resolvers;import { Grid, Toolbar } from '@syncfusion/ej2-grids';
import { DataManager, GraphQLAdaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
let data: DataManager = new DataManager({
url: "http://localhost:xxxx", adaptor: new GraphQLAdaptor({
response: {
result: 'getOrders.result',
count: 'getOrders.count'
},
query: `query getOrders($datamanager: DataManager) {
getOrders(datamanager: $datamanager) {
count,
result{
OrderID, CustomerID, ShipCity, ShipCountry}
}
}`,
}),
});
Grid.Inject(Toolbar);
let grid: Grid = new Grid({
dataSource: data,
toolbar: ['Search'],
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, type: 'number', isPrimaryKey: true },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'ShipCity', headerText: 'Ship City', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'Ship Country', width: 140 }
],
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');Handling filtering operation
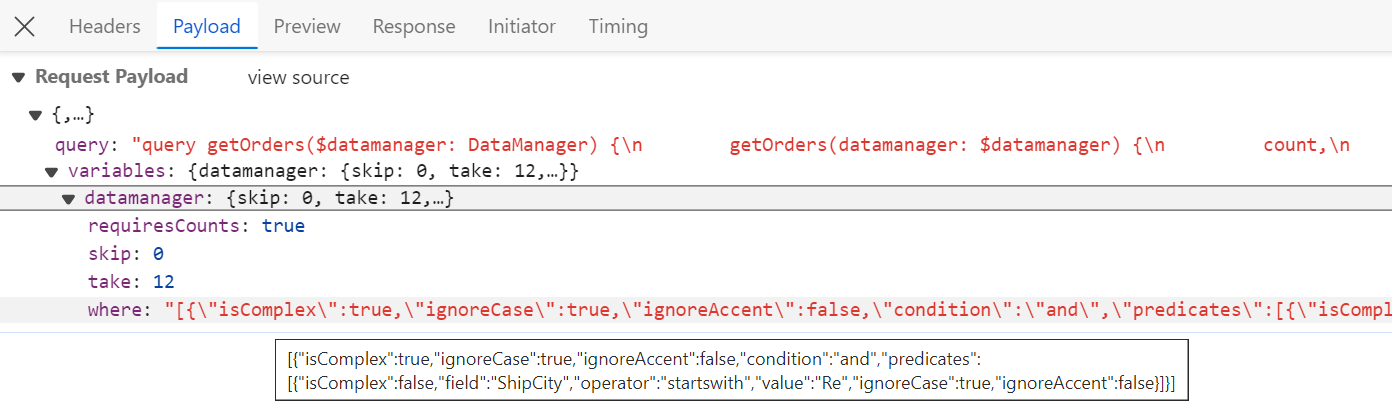
To handle filter operation in the Syncfusion® Grid using the GraphQLAdaptor, by utilizing the datamanager.where parameters and executing the filter operation with the where method. This feature allows you to efficiently filter through the grid’s data and retrieve relevant information based on specified criteria.
In the image below, you can see the values of datamanager.where parameters:
import { OrderData } from "./db";
import { DataUtil, Query, DataManager } from "@syncfusion/ej2-data";
const resolvers = {
Query: {
getOrders: (parent, { datamanager }, context, info) => {
let orders = [...OrderData];
const query = new Query();
const performFiltering = (filterString) => {
const filter = JSON.parse(filterString);
// Iterating over each predicate
filter[0].predicates.forEach(predicate => {
const field = predicate.field;
const operator = predicate.operator;
const value = predicate.value;
query.where(field, operator, value);
});
}
// Perform filtering
if (datamanager.where) {
performFiltering(datamanager.where);
}
orders = new DataManager(orders).executeLocal(query);
var count = orders.length;
return { result: orders, count: count }; // Return result and count
},
},
};
export default resolvers;import { Grid, Filter } from '@syncfusion/ej2-grids';
import { DataManager, GraphQLAdaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
let data: DataManager = new DataManager({
url: "http://localhost:xxxx", adaptor: new GraphQLAdaptor({
response: {
result: 'getOrders.result',
count: 'getOrders.count'
},
query: `query getOrders($datamanager: DataManager) {
getOrders(datamanager: $datamanager) {
count,
result{
OrderID, CustomerID, ShipCity, ShipCountry}
}
}`,
}),
});
Grid.Inject(Filter);
let grid: Grid = new Grid({
dataSource: data,
allowFiltering: true,
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, type: 'number', isPrimaryKey: true },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'ShipCity', headerText: 'Ship City', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'Ship Country', width: 140 }
],
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');Handling sorting operation
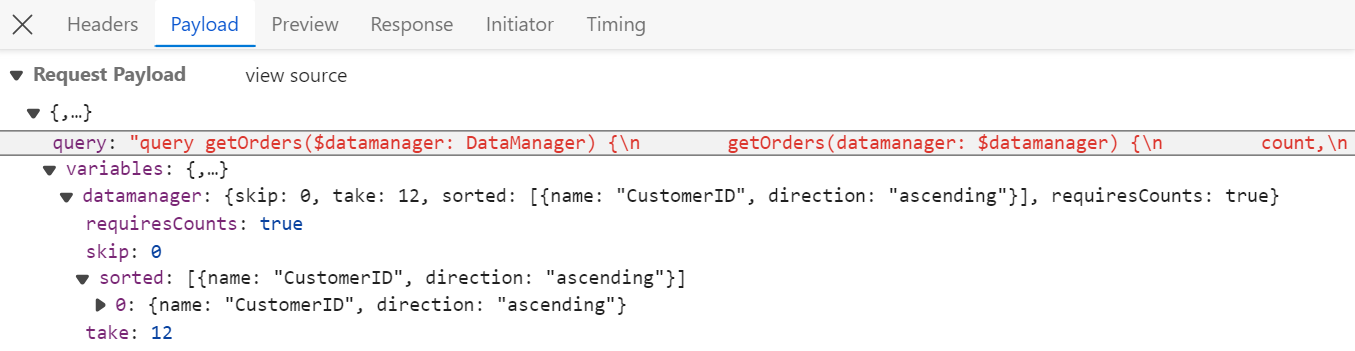
To handle sort operation in the Syncfusion® Grid using the GraphQLAdaptor, by utilizing the datamanager.sorted parameters and executing the sort operation with the sortBy method. This feature allows users to efficiently sort grid data based on specified criteria.
In the image below, you can see the values of datamanager.sorted parameters:
import { OrderData } from "./db";
import { DataUtil, Query, DataManager } from "@syncfusion/ej2-data";
const resolvers = {
Query: {
getOrders: (parent, { datamanager }, context, info) => {
let orders = [...OrderData];
const query = new Query();
const performSorting = (sorted) => {
for (let i = 0; i < sorted.length; i++) {
const { name, direction } = sorted[i];
query.sortBy(name, direction);
}
}
// Perform sorting
if (datamanager.sorted) {
performSorting(datamanager.sorted);
}
orders = new DataManager(orders).executeLocal(query);
var count = orders.length;
return { result: orders, count: count }; // Return result and count
},
},
};
export default resolvers;import { Grid, Sort } from '@syncfusion/ej2-grids';
import { DataManager, GraphQLAdaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
let data: DataManager = new DataManager({
url: "http://localhost:xxxx", adaptor: new GraphQLAdaptor({
response: {
result: 'getOrders.result',
count: 'getOrders.count'
},
query: `query getOrders($datamanager: DataManager) {
getOrders(datamanager: $datamanager) {
count,
result{
OrderID, CustomerID, ShipCity, ShipCountry}
}
}`,
}),
});
Grid.Inject(Sort);
let grid: Grid = new Grid({
dataSource: data,
allowSorting:true,
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, type: 'number', isPrimaryKey: true },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'ShipCity', headerText: 'Ship City', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'Ship Country', width: 140 }
],
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');Handling paging operation
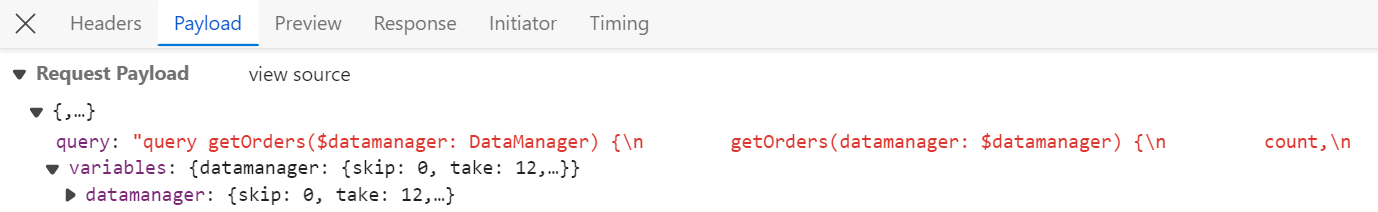
To handle page operation in the Syncfusion® Grid using the GraphQLAdaptor, by utilizing the datamanager.skip and datamanager.take parameters and executing the paging with the page method. This feature allows users to navigate through large datasets efficiently by dividing them into pages.
In the image below, you can see the value of datamanager.skip and datamanager.take parameters:
import { OrderData } from "./db";
import { DataUtil, Query, DataManager } from "@syncfusion/ej2-data";
const resolvers = {
Query: {
getOrders: (parent, { datamanager }, context, info) => {
let orders = [...OrderData];
const query = new Query();
// Perform paging
if (datamanager.skip && datamanager.take) {
const pageSkip = datamanager.skip / datamanager.take + 1;
const pageTake = datamanager.take;
query.page(pageSkip, pageTake);
} else if (datamanager.skip === 0 && datamanager.take) {
query.page(1, datamanager.take);
}
const currentResult = new DataManager(orders).executeLocal(query);
return { result: currentResult, count: count }; // Return result and count
},
},
};
export default resolvers;import { Grid, Group, Filter, Page, Sort, Edit, Toolbar } from '@syncfusion/ej2-grids';
import { DataManager, GraphQLAdaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
let data: DataManager = new DataManager({
url: "http://localhost:xxxx", adaptor: new GraphQLAdaptor({
response: {
result: 'getOrders.result',
count: 'getOrders.count'
},
query: `query getOrders($datamanager: DataManager) {
getOrders(datamanager: $datamanager) {
count,
result{
OrderID, CustomerID, ShipCity, ShipCountry}
}
}`,
}),
});
Grid.Inject(Page);
let grid: Grid = new Grid({
dataSource: data,
allowPaging: true,
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, type: 'number', isPrimaryKey: true },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'ShipCity', headerText: 'Ship City', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'Ship Country', width: 140 }
],
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');Handling CRUD operations
Syncfusion® Grid seamlessly integrates with GraphQL servers using the GraphQLAdaptor, enabling efficient CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations on your data. The below steps explains how to perform CRUD actions using GraphQLAdaptor in Syncfusion® Grid.
Insert operation
Adding a new record to the database involves the following steps:
-
Define the createOrder mutation in your GraphQL schema to handle creating a new order. This mutation should accept an OrderInput object containing the new order details.
[schema.graphql] input OrderInput { OrderID: Int! CustomerID: String Freight: Float ShipCity: String ShipCountry: String } type Mutation { createOrder(value: OrderInput): Order! } -
Implement the createOrder resolver function in your resolver file. This function should add the new order data to your data source and return the newly created order object.
[resolver.js] Mutation: { createOrder: (parent, { value }, context, info) => { const newOrder = value; OrderData.push(newOrder); return newOrder; }, } -
Configure the getMutation function in your
GraphQLAdaptorto return the appropriate GraphQL mutation query string based on the insert action. This query string should reference the createOrder mutation defined in your schema.[index.ts] // mutation for performing insert operation getMutation: function (action: string) { if (action === 'insert') { return `mutation CreateOrderMutation($value: OrderInput!){ createOrder(value: $value){ OrderID, CustomerID, Freight, ShipCity, ShipCountry }}`; } }
Update Operation
Updating an existing record in the database involves the following steps:
-
Define the updateOrder mutation in your GraphQL schema to handle updating an order. This mutation should accept three arguments:
- key: The unique identifier of the order to be updated.
- keyColumn: The name of the column containing the unique identifier.
- value: An OrderInput object containing the updated order details.
[schema.graphql] type Order { OrderID: Int! CustomerID: String Freight: Float ShipCity: String ShipCountry: String } input OrderInput { OrderID: Int! CustomerID: String Freight: Float ShipCity: String ShipCountry: String } type Mutation { updateOrder(key: Int!, keyColumn: String, value: OrderInput): Order } -
Implement the updateOrder resolver function in your resolver file. This function should find the order based on the provided key and keyColumn, update its properties with the values from the value argument, and return the updated order object.
[resolver.js] Mutation: { updateOrder: (parent, { key, keyColumn, value }, context, info) => { let updatedOrder = OrderData.find(order => order.OrderID === parseInt(key)); updatedOrder.CustomerID = value.CustomerID; updatedOrder.EmployeeID = value.EmployeeID; updatedOrder.Freight = value.Freight; updatedOrder.ShipCity = value.ShipCity; updatedOrder.ShipCountry = value.ShipCountry; return updatedOrder; // Make sure to return the updated order. }, } -
Configure the getMutation function in your GraphQLAdaptor to return the appropriate GraphQL mutation query string based on the update action. This query string should reference the updateOrder mutation defined in your schema.
[index.ts] // mutation for performing update operation getMutation: function (action: any): string { if (action === 'update') { return `mutation UpdateOrderMutation($key: Int!, $keyColumn: String,$value: OrderInput){ updateOrder(key: $key, keyColumn: $keyColumn, value: $value) { OrderID, CustomerID, Freight, ShipCity, ShipCountry }}`; } }
Delete Operation
Deleting a record from the database involves the following steps:
-
Define the deleteOrder mutation in your GraphQL schema to handle deleting an order. This mutation should accept three arguments similar to the updateOrder mutation.
[schema.graphql] type Order { OrderID: Int! CustomerID: String Freight: Float ShipCity: String ShipCountry: String } input OrderInput { OrderID: Int! CustomerID: String Freight: Float ShipCity: String ShipCountry: String } type Mutation { deleteOrder(key: Int!, keyColumn: String, value: OrderInput): Order! } -
Implement the deleteOrder resolver function in your resolver file. This function should find the order based on the provided key and keyColumn, remove it from your data source, and return the deleted order object.
[resolver.js] Mutation: { deleteOrder: (parent, { key, keyColumn, value }, context, info) => { const orderIndex = OrderData.findIndex(order => order.OrderID === parseInt(key)); if (orderIndex === -1) throw new Error("Order not found." + value); const deletedOrders = OrderData.splice(orderIndex, 1); return deletedOrders[0]; } } -
Configure the getMutation function in your GraphQL adaptor to return the appropriate GraphQL mutation query string based on the delete action. This query string should reference the deleteOrder mutation defined in your schema.
.[index.ts] // mutation for performing delete operation getMutation: function (action: string) { if (action === 'delete') { return `mutation RemoveOrderMutation($key: Int!, $keyColumn: String, $value: OrderInput){ deleteOrder(key: $key, keyColumn: $keyColumn, value: $value) { OrderID, CustomerID, Freight, ShipCity, ShipCountry }}`; } }
Normal/Inline editing is the default edit mode for the Grid control. To enable CRUD operations, ensure that the isPrimaryKey property is set to true for a specific grid column, ensuring that its value is unique.
import { OrderData } from "./db";
import { DataUtil } from "@syncfusion/ej2-data";
const resolvers = {
Query: {
getOrders: (parent, { datamanager }, context, info) => {
var ret = DataUtil.processData(datamanager, OrderData);
return ret;
}
},
Mutation: {
createOrder: (parent, { value }, context, info) => {
const newOrder = value;
OrderData.push(newOrder);
return newOrder;
},
updateOrder: (parent, { key, keyColumn, value }, context, info) => {
let updatedOrder = OrderData.find(order => order.OrderID === parseInt(key));
updatedOrder.CustomerID = value.CustomerID;
updatedOrder.EmployeeID = value.EmployeeID;
updatedOrder.Freight = value.Freight;
updatedOrder.ShipCity = value.ShipCity;
updatedOrder.ShipCountry = value.ShipCountry;
return updatedOrder; // Make sure to return the updated order.
},
deleteOrder: (parent, { key, keyColumn, value }, context, info) => {
const orderIndex = OrderData.findIndex(order => order.OrderID === parseInt(key));
if (orderIndex === -1) throw new Error("Order not found." + value);
const deletedOrders = OrderData.splice(orderIndex, 1);
return deletedOrders[0];
}
}
};
export default resolvers;#Grid Sort direction
input Sort {
name: String
direction: String
}
#Grid aggregates type
input Aggregate {
field: String!
type: String!
}
#Syncfusion DataManager query params
input DataManager {
skip: Int
take: Int
sorted: [Sort]
group: [String]
table: String
select: [String]
where: String
search: String
requiresCounts: Boolean,
aggregates: [Aggregate],
params: String
}
#Grid field names
input OrderInput {
OrderID: Int!
CustomerID: String
ShipCity: String
ShipCountry: String
}
type Order {
OrderID: Int!
CustomerID: String
ShipCity: String
ShipCountry: String
}
#need to return type as 'result (i.e, current pager data)' and count (i.e., total number of records in your database)
type ReturnType {
result: [Order]
count: Int
aggregates: String
}
type Query {
getOrders(datamanager: DataManager): ReturnType
}
type Mutation {
createOrder(value: OrderInput): Order!
updateOrder(key: Int!, keyColumn: String, value: OrderInput): Order
deleteOrder(key: Int!, keyColumn: String, value: OrderInput): Order!
}import { Grid, Edit, Toolbar } from '@syncfusion/ej2-grids';
import { DataManager, GraphQLAdaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
let data: DataManager = new DataManager({
url: "http://localhost:xxxx", adaptor: new GraphQLAdaptor({
response: {
result: 'getOrders.result',
count: 'getOrders.count'
},
query: `query getOrders($datamanager: DataManager) {
getOrders(datamanager: $datamanager) {
count,
result{
OrderID, CustomerID, ShipCity, ShipCountry}
}
}`,
// mutation for performing CRUD
getMutation: function (action: any): string {
if (action === 'insert') {
return `mutation CreateOrderMutation($value: OrderInput!){
createOrder(value: $value){
OrderID, CustomerID, ShipCity, ShipCountry
}}`;
}
if (action === 'update') {
return `mutation UpdateOrderMutation($key: Int!, $keyColumn: String,$value: OrderInput){
updateOrder(key: $key, keyColumn: $keyColumn, value: $value) {
OrderID, CustomerID, ShipCity, ShipCountry
}
}`;
} else {
return `mutation RemoveOrderMutation($key: Int!, $keyColumn: String, $value: OrderInput){
deleteOrder(key: $key, keyColumn: $keyColumn, value: $value) {
OrderID, CustomerID, ShipCity, ShipCountry
}
}`;
}
}
}),
});
Grid.Inject(Group, Filter, Page, Sort, Edit, Toolbar);
let grid: Grid = new Grid({
dataSource: data,
toolbar: ['Add', 'Edit', 'Update', 'Delete', 'Search'],
editSettings: { allowAdding: true, allowDeleting: true, allowEditing: true },
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, type: 'number', isPrimaryKey: true },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'ShipCity', headerText: 'Ship City', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'Ship Country', width: 140 }
],
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');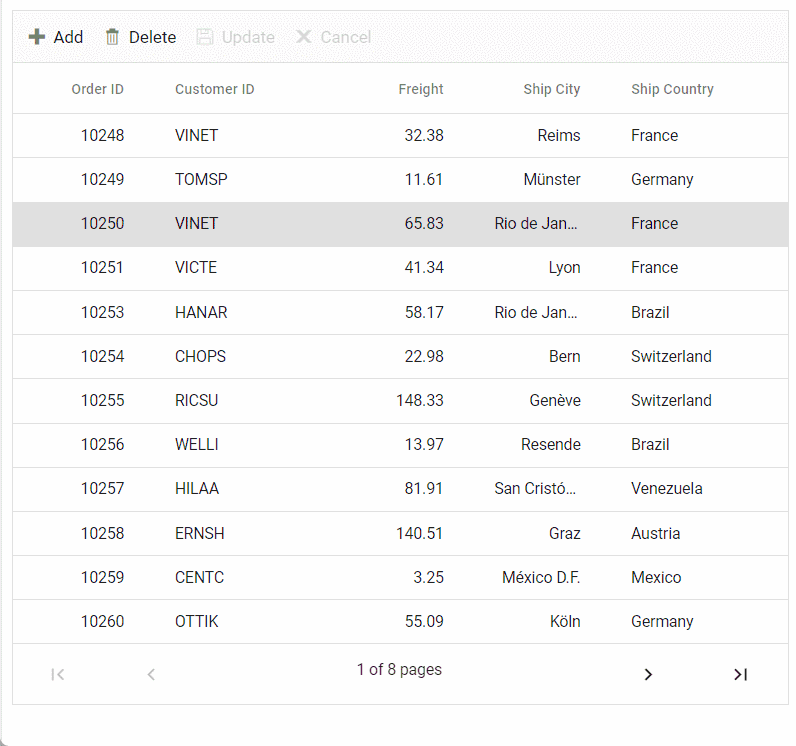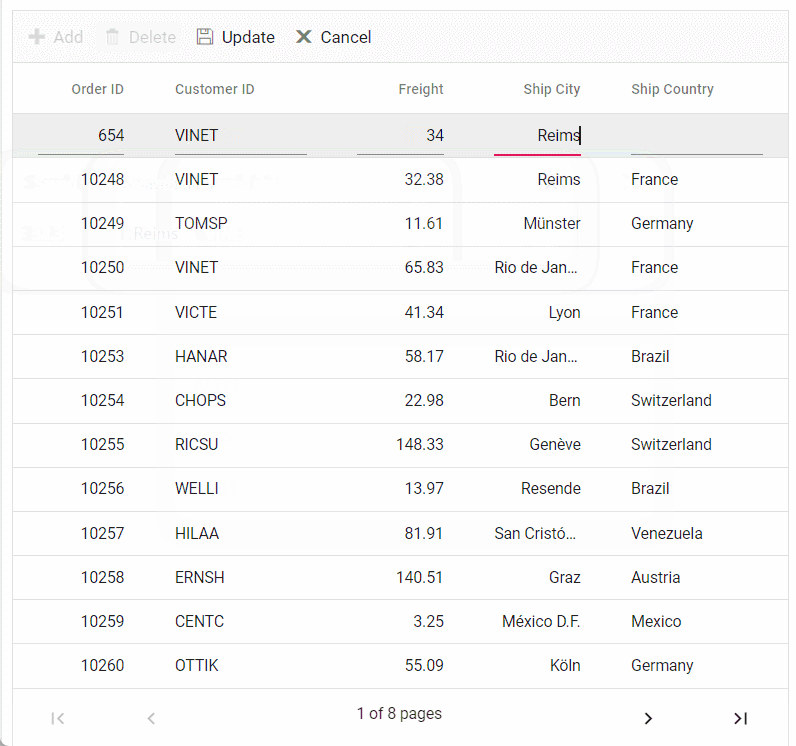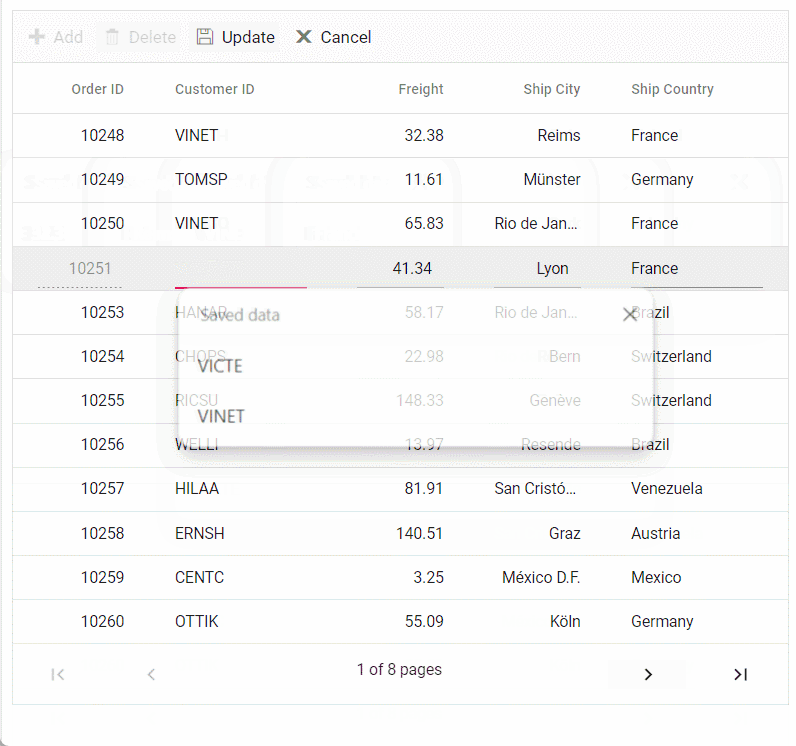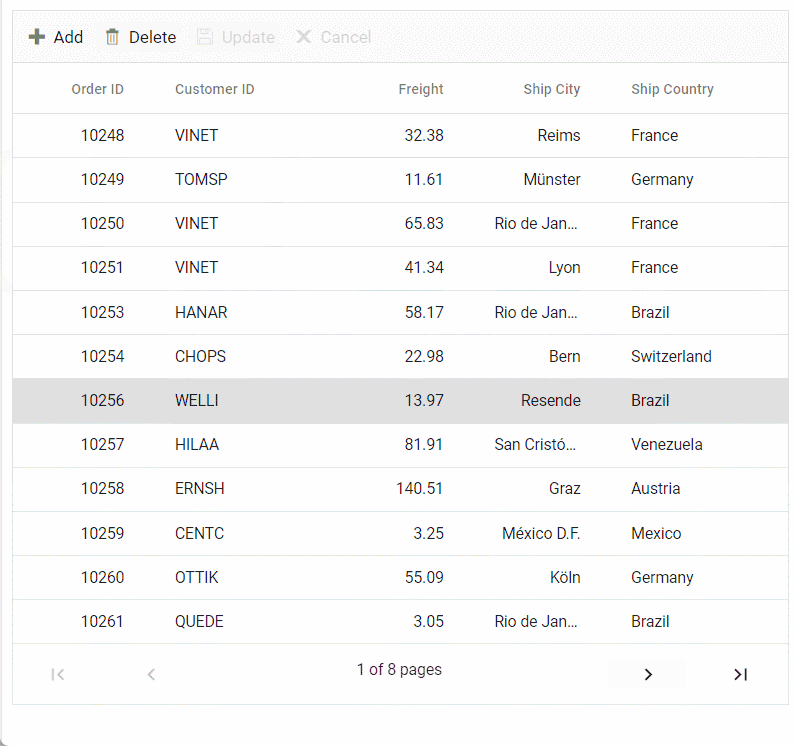
You can find the complete sample for the GraphQLAdaptor in GitHub link.