ODataV4Adaptor in Syncfusion® EJ2 TypeScript Grid Control
7 May 202524 minutes to read
The ODataV4Adaptor in the Syncfusion® Grid Control allows seamless integration of the Grid with OData v4 services, enabling efficient data fetching and manipulation. This guide provides detailed instructions on binding data and performing CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) actions using the ODataV4Adaptor in your Syncfusion® Grid Control.
This section describes a step-by-step process for retrieving data using ODataV4Adaptor, then binding it to the EJ2 TypeScript Grid control to facilitate data and CRUD operations.
Creating an ODataV4 service
To configure a server with Syncfusion® Grid, you need to follow the below steps:
Step 1: Set Up Your Development Environment
Before you start, make sure you have the following installed:
- .NET Core SDK
- Node.js
- Visual Studio or any other preferred code editor
Step 2: Create a New ASP.NET Core Project
Open Visual Studio and create an ASP.NET Core Web API project named ODataV4Adaptor.
Step 3: Install NuGet Packages
Using the NuGet package manager in Visual Studio (Tools → NuGet Package Manager → Manage NuGet Packages for Solution), install the Microsoft.AspNetCore.OData NuGet package.
Step 4: Add the Microsoft.TypeScript.MSBuild NuGet package to the project:
Using the NuGet package manager in Visual Studio (Tools → NuGet Package Manager → Manage NuGet Packages for Solution), install the Microsoft.TypeScript.MSBuild NuGet package.
Step 5: Configure the server
In the Program.cs file of your project, configure the server to serve static files by adding the following code:
var app = builder.Build();
app.UseDefaultFiles();
app.UseStaticFiles();Comment out the below line in launchSettings.json:
"https": {
"commandName": "Project",
"dotnetRunMessages": true,
"launchBrowser": true,
// "launchUrl": "swagger",
"applicationUrl": "https://localhost:xxxx;http://localhost:xxxx",
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
},This configuration enables the server to locate and serve the index.html file.
Step 6: Model Class Creation
Create a model class named OrdersDetails.cs in the server-side Models folder to represent the order data.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace ODataV4Adaptor.Models
{
public class OrdersDetails
{
public static List<OrdersDetails> order = new List<OrdersDetails>();
public OrdersDetails()
{
}
public OrdersDetails(
int OrderID, string CustomerId, int EmployeeId, string ShipCountry)
{
this.OrderID = OrderID;
this.CustomerID = CustomerId;
this.EmployeeID = EmployeeId;
this.ShipCountry = ShipCountry;
}
public static List<OrdersDetails> GetAllRecords()
{
if (order.Count() == 0)
{
int code = 10000;
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
{
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 1, "ALFKI", i + 0, "Denmark"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 2, "ANATR", i + 2, "Brazil"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 3, "ANTON", i + 1, "Germany"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 4, "BLONP", i + 3, "Austria"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 5, "BOLID", i + 4, "Switzerland"));
code += 5;
}
}
return order;
}
[Key]
public int? OrderID { get; set; }
public string? CustomerID { get; set; }
public int? EmployeeID { get; set; }
public string? ShipCountry { get; set; }
}
}Step 7: Build the Entity Data Model
To construct the Entity Data Model for your ODataV4 service, utilize the ODataConventionModelBuilder to define the model’s structure. Start by creating an instance of the ODataConventionModelBuilder, then register the entity set Orders using the EntitySet<T> method, where OrdersDetails represents the CLR type containing order details.
[program.cs]
using Microsoft.OData.ModelBuilder;
// Create an ODataConventionModelBuilder to build the OData model
var modelBuilder = new ODataConventionModelBuilder();
// Register the "Orders" entity set with the OData model builder
modelBuilder.EntitySet<OrdersDetails>("Orders");Step 8: Register the ODataV4 Services
Once the Entity Data Model is built, you need to register the ODataV4 services in your ASP.NET Core application. Here’s how:
[program.cs]
// Add controllers with OData support to the service collection
builder.Services.AddControllers().AddOData(
options => options
.Count()
.AddRouteComponents("odata", modelBuilder.GetEdmModel()));Step 9: Add controllers
Finally, add controllers to expose the OData endpoints. Here’s an example:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.OData.Query;
using ODataV4Adaptor.Server.Models;
namespace ODataV4Adaptor.Controllers
{
[Route("[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class OrdersController : ControllerBase
{
/// <summary>
/// Retrieves all orders.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>The collection of orders.</returns>
[HttpGet]
[EnableQuery]
public IActionResult Get()
{
var data = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().AsQueryable();
return Ok(data);
}
}
}Step 10: Run the Application
Run the application in Visual Studio. It will be accessible on a URL like https://localhost:xxxx.
After running the application, you can verify that the server-side API controller is successfully returning the order data in the URL(https://localhost:xxxx/odata/Orders). Here xxxx denotes the port number.
Connecting syncfusion® grid to an odataV4 service
To integrate the Syncfusion® Grid control into your TypeScript and ASP.NET Core project using Visual Studio, follow these steps:
Step 1: Create a package.json file:
Run the following command in the project root to create a package.json file:
npm init -yStep 2: Install Webpack and Other Dependencies
npm i -D -E clean-webpack-plugin css-loader html-webpack-plugin mini-css-extract-plugin ts-loader typescript webpack webpack-cliStep 3: Configure package.json Scripts
Replace the scripts property of package.json file with the following code:
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack --mode=development --watch",
"release": "webpack --mode=production",
"publish": "npm run release && dotnet publish -c Release"
},Step 4: Create wwwroot Folder
Create a folder named wwwroot in the project root directory. This folder will contain static files served by the web server.
Step 5: Create webpack.config.js
Create a file named webpack.config.js in the project root, with the following code to configure the Webpack compilation process:
const path = require("path");
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require("html-webpack-plugin");
const { CleanWebpackPlugin } = require("clean-webpack-plugin");
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require("mini-css-extract-plugin");
module.exports = {
entry: "./src/index.ts",
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, "wwwroot"),
filename: "[name].[chunkhash].js",
publicPath: "/",
},
resolve: {
extensions: [".js", ".ts"],
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.ts$/,
use: "ts-loader",
},
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader, "css-loader"],
},
],
},
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin(),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: "./src/index.html",
}),
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
filename: "css/[name].[chunkhash].css",
}),
],
};Step 6: Create a new directory named src in the project root for the client code.
Step 7: Install Syncfusion® Packages
Open your terminal in the project’s root folder and install the required Syncfusion® packages using npm:
npm install @syncfusion/ej2-grids --save
npm install @syncfusion/ej2-data --saveStep 8: Create src/index.html and add the following code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>EJ2 Grid</title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta name="description" content="Typescript Grid Control" />
<meta name="author" content="Syncfusion" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-base/styles/material.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-grids/styles/material.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-buttons/styles/material.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-popups/styles/material.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-richtexteditor/styles/material.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-navigations/styles/material.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-dropdowns/styles/material.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-lists/styles/material.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-inputs/styles/material.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-calendars/styles/material.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-notifications/styles/material.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/26.1.35/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/material.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/systemjs/0.19.38/system.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/syncfusion-helper.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id='container'>
<div id='Grid'></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Step 9: Create src/index.ts and add the following code:
import { Grid } from '@syncfusion/ej2-grids';
import { DataManager, ODataV4Adaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
let data: DataManager = new DataManager({
url: 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/orders',
adaptor: new ODataV4Adaptor()
});
let grid: Grid = new Grid({
dataSource: data,
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, isPrimaryKey: true, type: 'number' },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'EmployeeID', headerText: 'Employee ID', width: 140 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'ShipCountry', width: 140 }
]
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');Step 10: Create src/tsconfig.json in the project and add the following content:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"noImplicitAny": true,
"noEmitOnError": true,
"removeComments": false,
"sourceMap": true,
"target": "es5"
},
"exclude": [
"node_modules",
"wwwroot"
]
}Step 11: Install additional packages and build the project
npm i @types/node
npm run buildStep 12: Run the project
Run the project in Visual Studio.
The wwwroot/index.html file is served at https://localhost:xxxx.
With these steps, you have integrated the Syncfusion® Grid control with your ASP.NET Core project and set up the necessary client-side configuration using Webpack and TypeScript. This will allow the Syncfusion® Grid to fetch data from your API and display it accordingly.
Handling searching operation
To enable search operations in your web application using OData, you first need to configure the OData support in your service collection. This involves adding the Filter method within the OData setup, allowing you to filter data based on specified criteria. Once enabled, clients can utilize the $filter query option in their requests to search for specific data entries.
// Create a new instance of the web application builder
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Create an ODataConventionModelBuilder to build the OData model
var modelBuilder = new ODataConventionModelBuilder();
// Register the "Orders" entity set with the OData model builder
modelBuilder.EntitySet<OrdersDetails>("Orders");
// Add services to the container.
// Add controllers with OData support to the service collection
builder.Services.AddControllers().AddOData(
options => options
.Count()
.Filter() //searching
.AddRouteComponents("odata", modelBuilder.GetEdmModel()));import { Grid, Toolbar } from '@syncfusion/ej2-grids';
import { DataManager, ODataV4Adaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
let data: DataManager = new DataManager({
url: 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/Orders', Here xxxx represents the port number
adaptor: new ODataV4Adaptor()
});
Grid.Inject(Toolbar);
let grid: Grid = new Grid({
dataSource: data,
toolbar:['Search'],
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, isPrimaryKey: true, type: 'number' },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'EmployeeID', headerText: 'Employee ID', width: 140 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'ShipCountry', width: 140 }
]
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');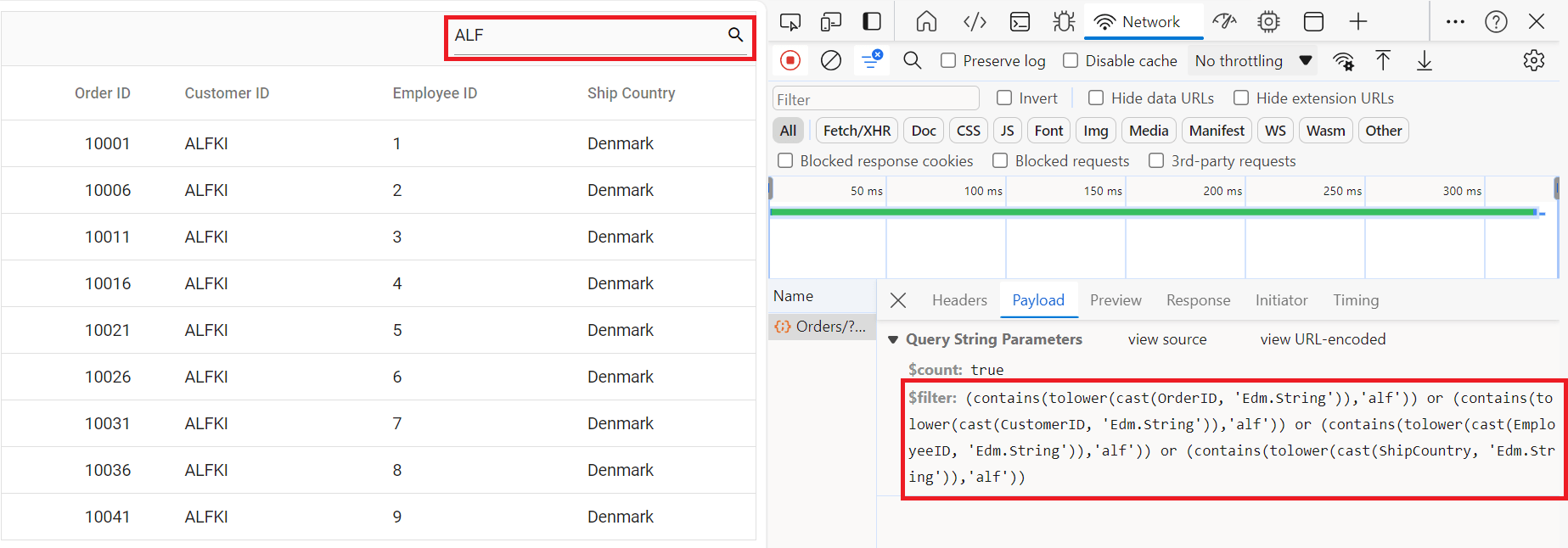
Handling filtering operation
To enable filter operations in your web application using OData, you first need to configure the OData support in your service collection. This involves adding the Filter method within the OData setup, allowing you to filter data based on specified criteria. Once enabled, clients can utilize the $filter query option in your requests to filter for specific data entries.
// Create a new instance of the web application builder
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Create an ODataConventionModelBuilder to build the OData model
var modelBuilder = new ODataConventionModelBuilder();
// Register the "Orders" entity set with the OData model builder
modelBuilder.EntitySet<OrdersDetails>("Orders");
// Add services to the container.
// Add controllers with OData support to the service collection
builder.Services.AddControllers().AddOData(
options => options
.Count()
.Filter() // filtering
.AddRouteComponents("odata", modelBuilder.GetEdmModel()));import { Grid, Filter } from '@syncfusion/ej2-grids';
import { DataManager, ODataV4Adaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
let data: DataManager = new DataManager({
url: 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/Orders',
adaptor: new ODataV4Adaptor()
});
Grid.Inject(Filter);
let grid: Grid = new Grid({
dataSource: data,
allowFiltering: true,
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, isPrimaryKey: true, type: 'number' },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'EmployeeID', headerText: 'Employee ID', width: 140 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'ShipCountry', width: 140 }
]
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');Single column filtering
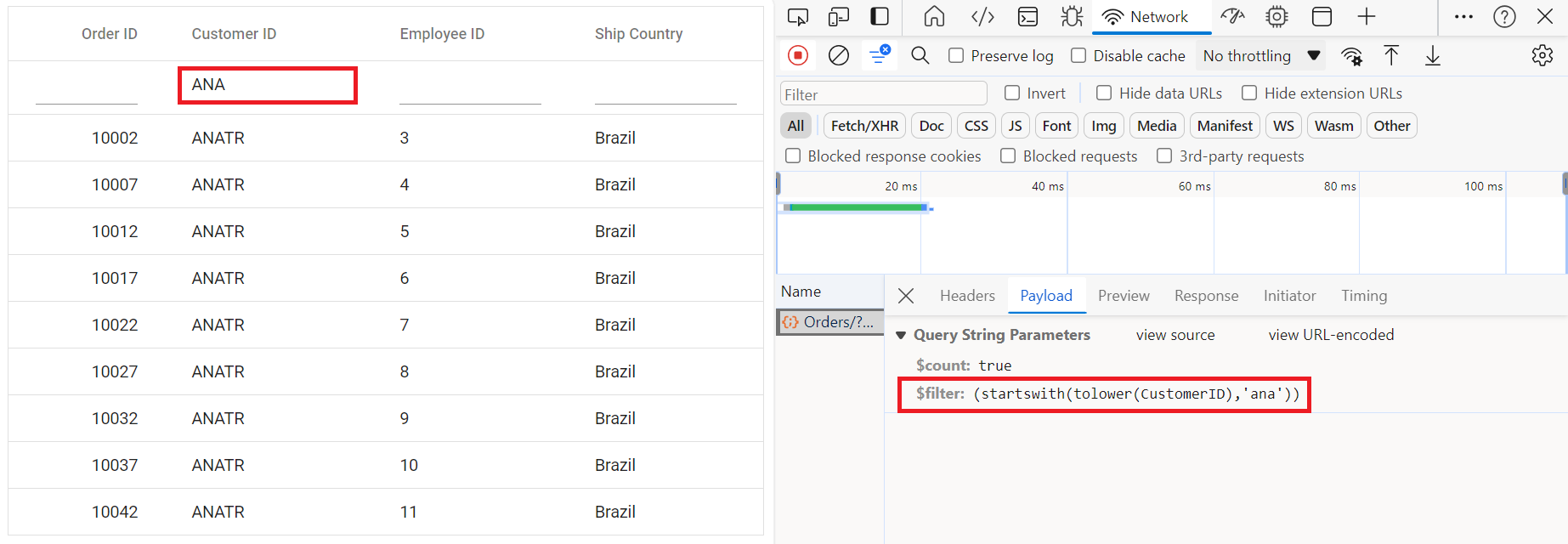
Multi column filtering
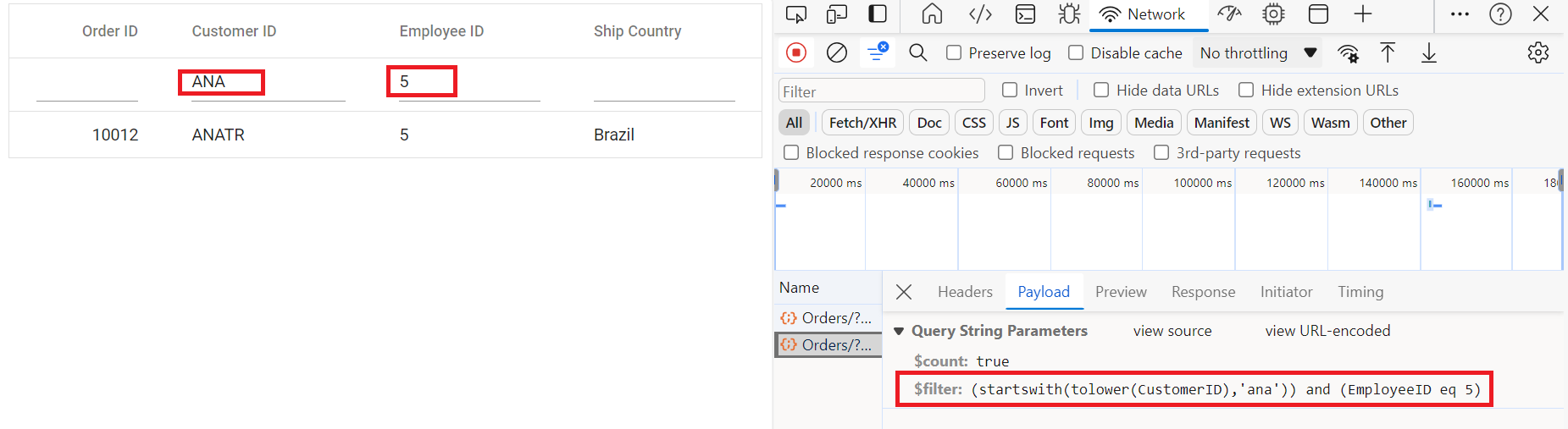
Handling sorting operation
To enable sorting operations in your web application using OData, you first need to configure the OData support in your service collection. This involves adding the OrderBy method within the OData setup, allowing you to sort data based on specified criteria. Once enabled, clients can utilize the $orderby query option in their requests to sort data entries according to desired attributes.
// Create a new instance of the web application builder
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Create an ODataConventionModelBuilder to build the OData model
var modelBuilder = new ODataConventionModelBuilder();
// Register the "Orders" entity set with the OData model builder
modelBuilder.EntitySet<OrdersDetails>("Orders");
// Add services to the container.
// Add controllers with OData support to the service collection
builder.Services.AddControllers().AddOData(
options => options
.Count()
.OrderBy() // sorting
.AddRouteComponents("odata", modelBuilder.GetEdmModel()));import { Grid, Sort} from '@syncfusion/ej2-grids';
import { DataManager, ODataV4Adaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
let data: DataManager = new DataManager({
url: 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/Orders',
adaptor: new ODataV4Adaptor()
});
Grid.Inject(Sort);
let grid: Grid = new Grid({
dataSource: data,
allowSorting: true,
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, isPrimaryKey: true, type: 'number' },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'EmployeeID', headerText: 'Employee ID', width: 140 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'ShipCountry', width: 140 }
]
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');Single column sorting
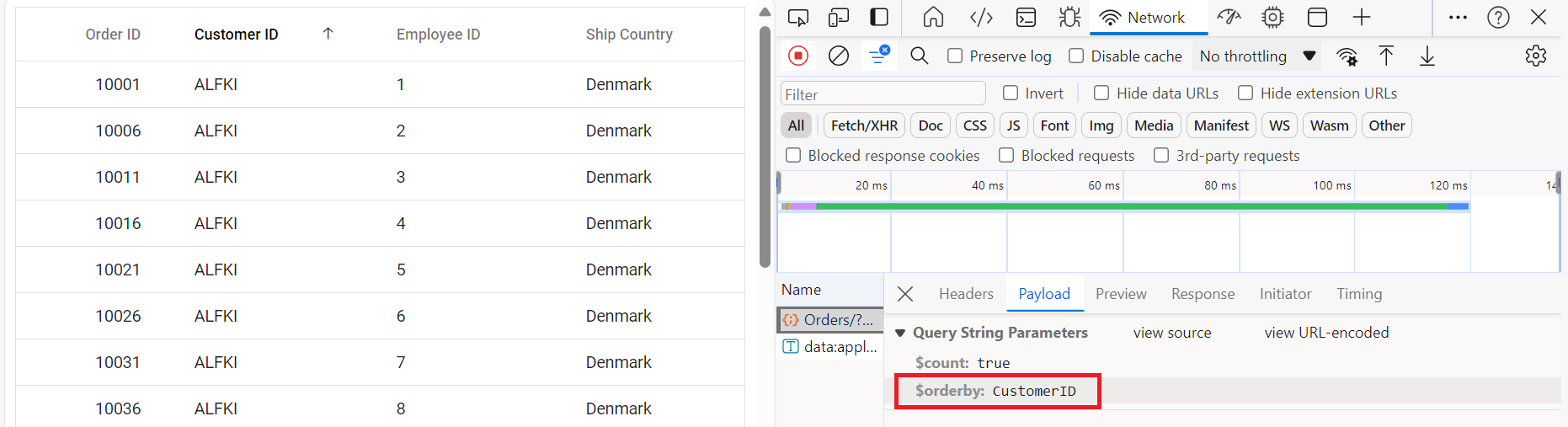
Multi column sorting
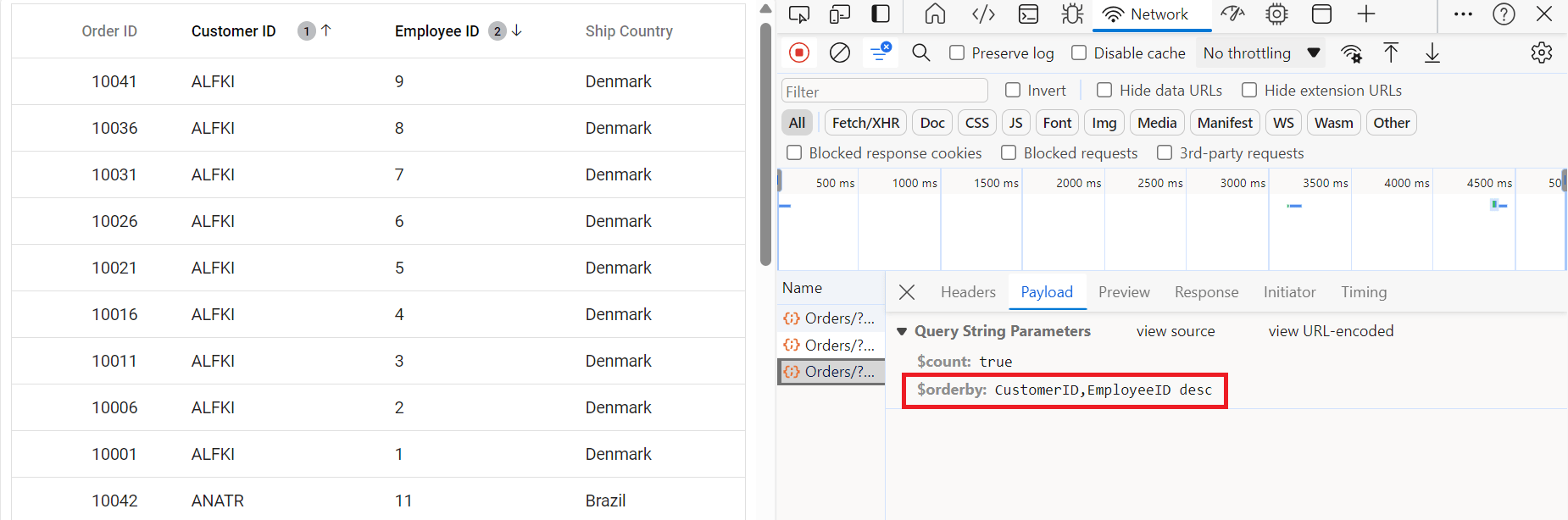
Handling paging operation
To implement paging operations in your web application using OData, you can utilize the SetMaxTop method within your OData setup to limit the maximum number of records that can be returned per request. While you configure the maximum limit, clients can utilize the $skip and $top query options in their requests to specify the number of records to skip and the number of records to take, respectively.
// Create a new instance of the web application builder
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Create an ODataConventionModelBuilder to build the OData model
var modelBuilder = new ODataConventionModelBuilder();
// Register the "Orders" entity set with the OData model builder
modelBuilder.EntitySet<OrdersDetails>("Orders");
// Add services to the container.
// Add controllers with OData support to the service collection
var recordCount= OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Count;
builder.Services.AddControllers().AddOData(
options => options
.Count()
.SetMaxTop(recordCount)
.AddRouteComponents(
"odata",
modelBuilder.GetEdmModel()));import { Grid, Page} from '@syncfusion/ej2-grids';
import { DataManager, ODataV4Adaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
let data: DataManager = new DataManager({
url: 'https://localhost:7199/odata/Orders',
adaptor: new ODataV4Adaptor()
});
Grid.Inject(Page);
let grid: Grid = new Grid({
dataSource: data,
allowPaging: true,
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, isPrimaryKey: true, type: 'number' },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'EmployeeID', headerText: 'Employee ID', width: 140 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'ShipCountry', width: 140 }
]
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');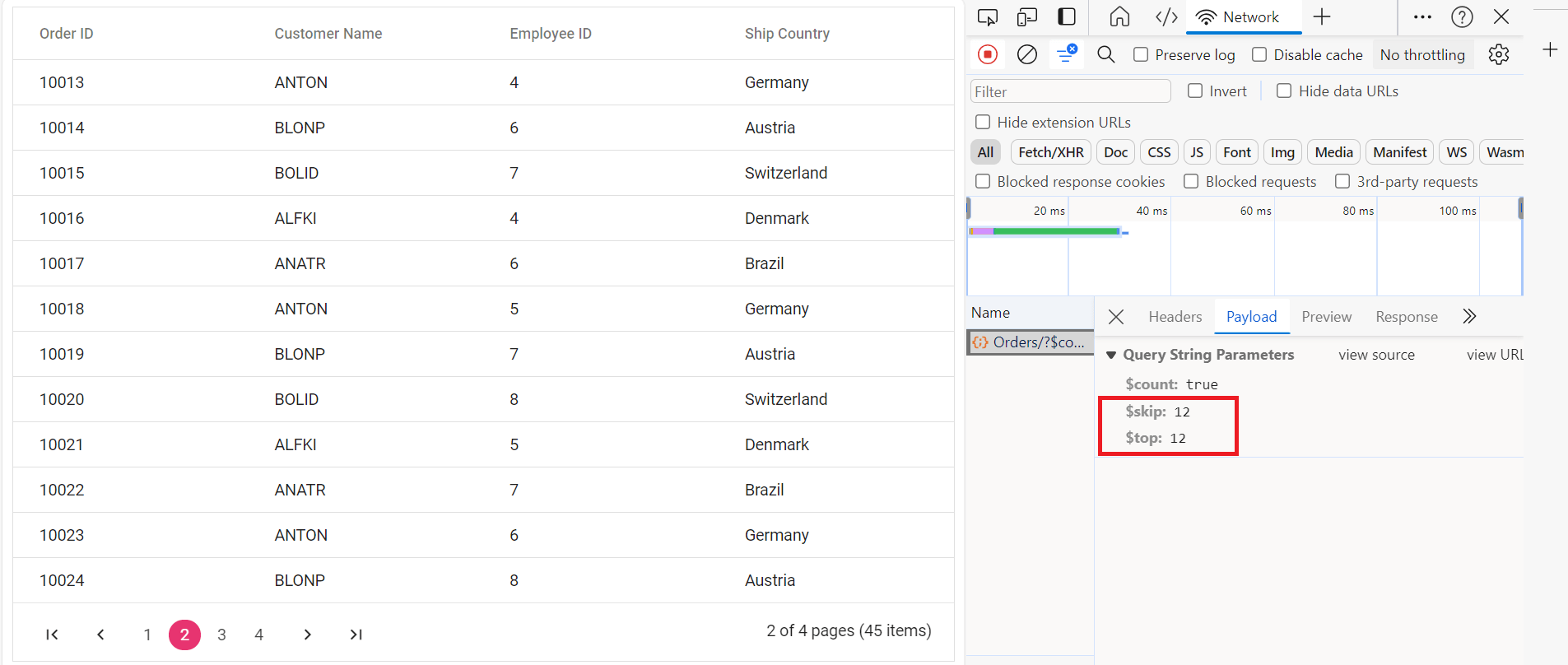
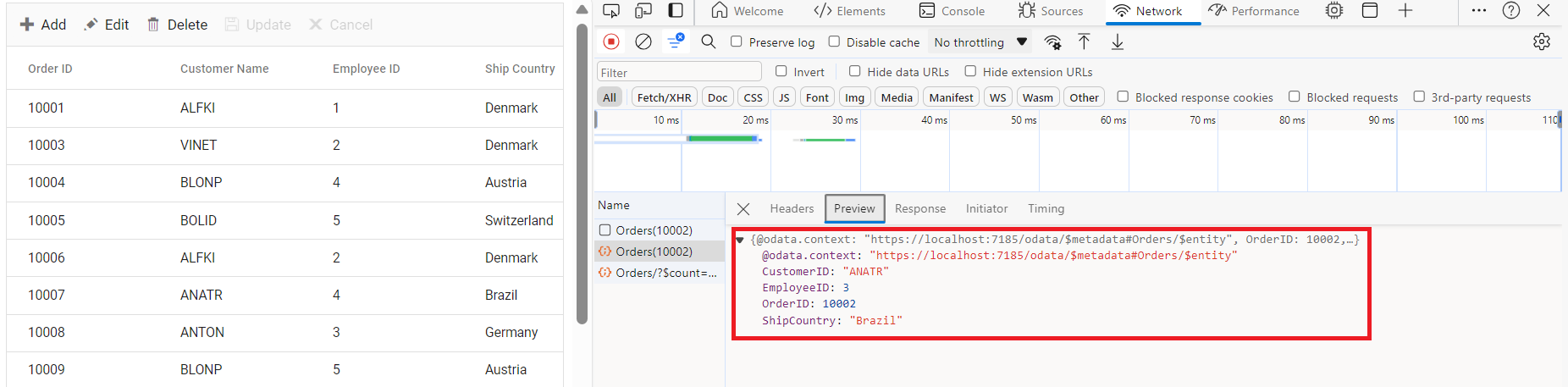
Handling CRUD operations
To manage CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations using the ODataV4Adaptor, follow the provided guide for configuring the Syncfusion® Grid for editing and utilize the sample implementation of the OrdersController in your server application. This controller handles HTTP requests for CRUD operations such as GET, POST, PATCH, and DELETE.
To enable CRUD operations in the Syncfusion® Grid control, follow the below steps:
import { Grid, Edit, Toolbar } from '@syncfusion/ej2-grids';
import { DataManager, ODataV4Adaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
let data: DataManager = new DataManager({
url: 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/Orders',
adaptor: new ODataV4Adaptor()
});
Grid.Inject(Edit, Toolbar);
let grid: Grid = new Grid({
dataSource: data,
toolbar:['Add','Edit','Update','Delete','Cancel'],
editSettings: { allowAdding: true, allowDeleting: true, allowEditing: true },
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, isPrimaryKey: true, type: 'number' },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'EmployeeID', headerText: 'Employee ID', width: 140 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'ShipCountry', width: 140 }
]
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');Normal/Inline editing is the default edit mode for the Grid control. To enable CRUD operations, ensure that the isPrimaryKey property is set to true for a specific Grid column, ensuring that its value is unique.
Insert Record
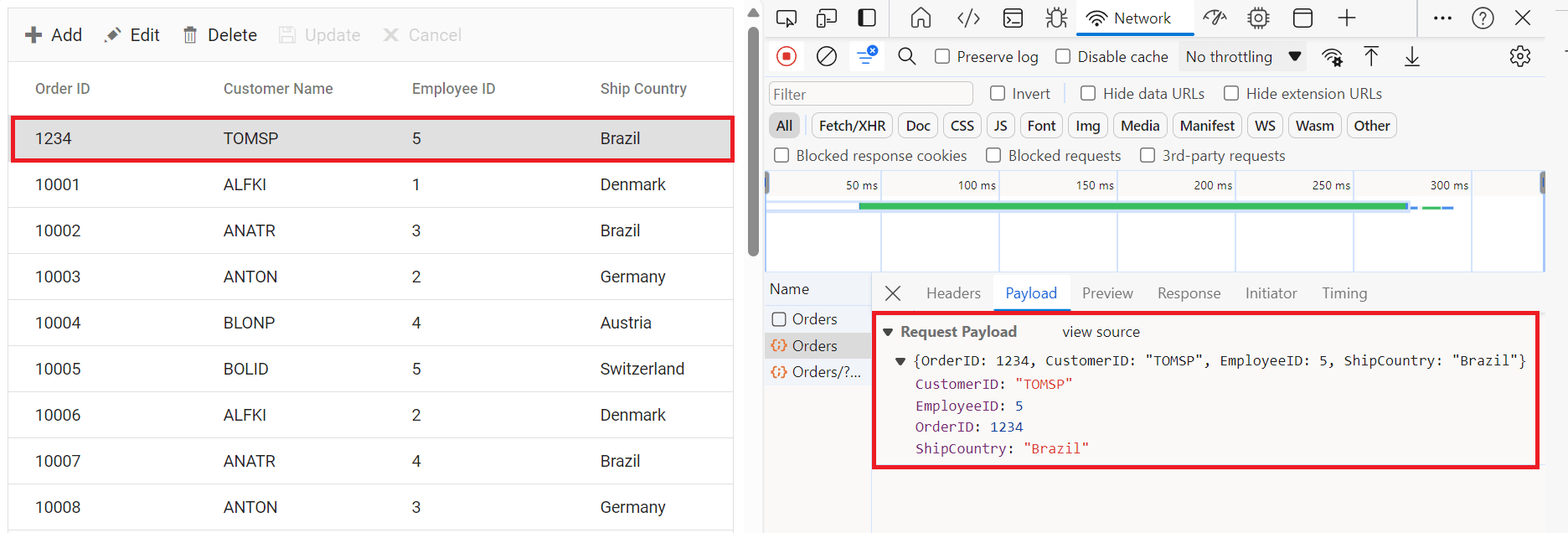
To insert a new record into your Syncfusion® Grid, you can utilize the HttpPost method in your server application. Below is a sample implementation of inserting a record using the OrdersController:
/// <summary>
/// Inserts a new order to the collection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="addRecord">The order to be inserted.</param>
/// <returns>It returns the newly inserted record detail.</returns>
[HttpPost]
[EnableQuery]
public IActionResult Post([FromBody] OrdersDetails addRecord)
{
if (addRecord == null)
{
return BadRequest("Null order");
}
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Insert(0, addRecord);
return Json(addRecord);
}
Update Record
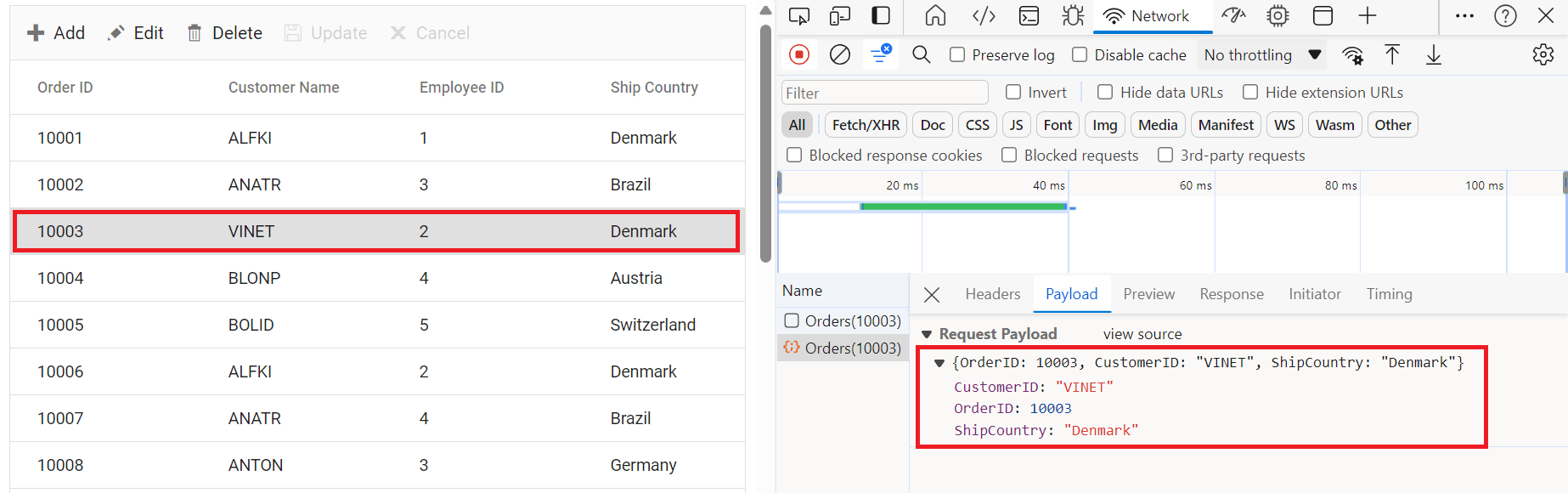
Updating a record in the Syncfusion® Grid can be achieved by utilizing the HttpPatch method in your controller. Here’s a sample implementation of updating a record:
/// <summary>
/// Updates an existing order.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">The ID of the order to update.</param>
/// <param name="updateRecord">The updated order details.</param>
/// <returns>It returns the updated order details.</returns>
[HttpPatch("{key}")]
public IActionResult Patch(int key, [FromBody] OrdersDetails updateRecord)
{
if (updateRecord == null)
{
return BadRequest("No records");
}
var existingOrder = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().FirstOrDefault(order => order.OrderID == key);
if (existingOrder != null)
{
// If the order exists, update its properties
existingOrder.CustomerID = updateRecord.CustomerID ?? existingOrder.CustomerID;
existingOrder.EmployeeID = updateRecord.EmployeeID ?? existingOrder.EmployeeID;
existingOrder.ShipCountry = updateRecord.ShipCountry ?? existingOrder.ShipCountry;
}
return Json(updateRecord);
}
Delete Record
To delete a record from your Syncfusion® Grid, you can utilize the HttpDelete method in your controller. Below is a sample implementation:
/// <summary>
/// Deletes an order.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">The ID of the order to delete.</param>
/// <returns>It returns the deleted record detail</returns>
[HttpDelete("{key}")]
public IActionResult Delete(int key)
{
var deleteRecord = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().FirstOrDefault(order => order.OrderID == key);
if (deleteRecord != null)
{
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Remove(deleteRecord);
}
return Json(deleteRecord);
}
You can find the complete sample for the ODataV4Adaptor in GitHub link.
Odata with custom url
The Syncfusion® ODataV4 adaptor extends support for calling customized URLs to accommodate data retrieval and CRUD actions as per your application’s requirements. However, when utilizing a custom URL with the ODataV4 adaptor, it’s Essential® to modify the routing configurations in your application’s route configuration file to align with your custom URL. You can invoke the custom URL by the following methods in the Datamanager
Configuring Custom URLs
To work with custom URLs for CRUD operations in the Syncfusion® Grid, you can use the following properties:
- insertUrl: Specifies the custom URL for inserting new records.
- removeUrl: Specifies the custom URL for deleting records.
- updateUrl: Specifies the custom URL for updating records.
- batchUrl: Specifies the custom URL for batch editing operations.
Ensure that the routing configurations on the server-side are properly updated to handle these custom URLs.
The following code example describes the above behavior.
import { Grid, Edit, Toolbar } from '@syncfusion/ej2-grids';
import { DataManager, ODataV4Adaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
let data: DataManager = new DataManager({
url: 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/Orders', // xxxx denotes port number
updateUrl: 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/Orders/Update', // custom URL to update the record
insertUrl: 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/Orders/Insert', // custom URL to insert new record
removeUrl: 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/Orders/Delete', // custom URL to delete the record
adaptor: new ODataV4Adaptor()
});
Grid.Inject(Edit, Toolbar);
let grid: Grid = new Grid({
dataSource: data,
toolbar:['Add','Edit','Update','Delete','Cancel'],
editSettings: { allowAdding: true, allowDeleting: true, allowEditing: true },
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, isPrimaryKey: true, type: 'number' },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'EmployeeID', headerText: 'Employee ID', width: 140 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'ShipCountry', width: 140 }
]
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');For batch editing, you can specify a custom batch URL as follows:
import { Grid, Edit, Toolbar } from '@syncfusion/ej2-grids';
import { DataManager, ODataV4Adaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
let data: DataManager = new DataManager({
url: 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/orders', // xxxx denotes port number
batchUrl: 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/orders/BatchUpdate', // custom URL for batch update
adaptor: new ODataV4Adaptor()
});
Grid.Inject(Edit, Toolbar);
let grid: Grid = new Grid({
dataSource: data,
toolbar:['Add','Edit','Update','Delete','Cancel'],
editSettings: { allowAdding: true, allowDeleting: true, allowEditing: true, mode: 'Batch' },
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, isPrimaryKey: true, type: 'number' },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'EmployeeID', headerText: 'Employee ID', width: 140 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'ShipCountry', width: 140 }
]
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');