How can I help you?
UrlAdaptor in Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid
18 Dec 202524 minutes to read
The UrlAdaptor serves as the base adaptor for facilitating communication between remote data services and an UI control. It enables seamless data binding and interaction with custom API services or any remote service through URLs. The UrlAdaptor is particularly useful for the scenarios where a custom API service with unique logic for handling data and CRUD operations is in place. This approach allows for custom handling of data and CRUD operations, and the resultant data returned in the result and count format for display in the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid.
This section describes a step-by-step process for retrieving data using UrlAdaptor, then binding it to the ASP.NET MVC Grid to facilitate data and CRUD operations.
Creating an API Service
To configure a server with Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid, follow the below steps:
1. Project Creation:
Open Visual Studio and create an ASP.NET MVC project named UrlAdaptor. To create an ASP.NET MVC application, follow the documentation link for detailed steps.
2. Model Class Creation:
Create a model class named Orders.cs inside the Models folder on the server-side. This model will represent the order data structure.
namespace UrlAdaptor_MVC.Models
{
public class Orders
{
public int OrderID { get; set; }
public string CustomerID { get; set; }
public int EmployeeID { get; set; }
public DateTime OrderDate { get; set; }
public string ShipCity { get; set; }
public decimal Freight { get; set; }
public static List<Orders> GetAllRecords()
{
return new List<Orders>()
{
new Orders() { OrderID = 10248, CustomerID = "VINET", EmployeeID = 5, OrderDate = DateTime.Now.AddDays(-10), ShipCity = "Reims", Freight = 32.38M },
new Orders() { OrderID = 10249, CustomerID = "TOMSP", EmployeeID = 6, OrderDate = DateTime.Now.AddDays(-8), ShipCity = "Münster", Freight = 11.61M },
new Orders() { OrderID = 10250, CustomerID = "HANAR", EmployeeID = 4, OrderDate = DateTime.Now.AddDays(-6), ShipCity = "Rio de Janeiro", Freight = 65.83M }
};
}
}
}3. API Controller Creation:
Create a file named GridController.cs under the Controllers folder. This controller will handle data retrieval and communication with the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid.
using System.Web.Mvc;
using Syncfusion.EJ2.Base;
using UrlAdaptor_MVC.Models;
namespace UrlAdaptor_MVC.Controllers
{
public class GridController : Controller
{
private static List<Orders> order = Orders.GetAllRecords();
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult UrlDatasource(DataManagerRequest dm)
{
// Retrieve data source and convert to queryable.
IEnumerable<Orders> DataSource = order;
DataOperations operation = new DataOperations();
// Get total record count.
int count = DataSource.Count();
// Return result and total record count.
return dm.RequiresCounts ? Json(new { result = DataSource, count }) : Json(DataSource);
}
}
}Connecting Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid to an API Service
To integrate the Syncfusion Grid into your ASP.NET MVC project using Visual Studio, follow these steps:
Step 1: Install the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Package:
To add ASP.NET MVC in the application, open the NuGet package manager in Visual Studio (Tools → NuGet Package Manager → Manage NuGet Packages for Solution), search for Syncfusion.EJ2.MVC5 and install it.
Alternatively, you can install it using the following Package Manager Console command:
Install-Package Syncfusion.EJ2.MVC5 -Version 32.2.3Step 2: Add Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC namespace
Add Syncfusion.EJ2 namespace reference in Web.config under Views folder.
<namespaces>
<add namespace="Syncfusion.EJ2"/>
</namespaces>Step 3: Add stylesheet and script resources
To include the required styles and scripts, add the following references inside the <head> of ~/Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file:
<head>
...
<!-- Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC control styles -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/bootstrap5.css" />
<!-- Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC control scripts -->
<script src="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/dist/ej2.min.js"></script>
<!-- Include the necessary CSS files to style the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC controls: -->
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-base/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-grids/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-buttons/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-popups/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-richtexteditor/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-navigations/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-dropdowns/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-lists/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-inputs/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-calendars/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-notifications/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/systemjs/0.19.38/system.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/syncfusion-helper.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</head>Step 4: Register Syncfusion Script Manager
To ensure proper script execution, register the Syncfusion Script Manager EJS().ScriptManager() at the end of <body> in the ~/Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file as follows.
<body>
...
<!-- Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Script Manager -->
@Html.EJS().ScriptManager()
</body>Step 5: Add the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid
Now, add the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid tag helper in ~/Views/Home/Index.cshtml file.
// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").DataSource(ds => ds.Url("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDatasource").Adaptor("UrlAdaptor")).Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("120").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).IsPrimaryKey(true).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer ID").Width("140").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("ShipCity").Width("140").Add();
}).Render()Step 7: Run the Project
Run the project in Visual Studio, and the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid will successfully fetch data from the API service.
- The Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid provides built-in support for handling various data operations such as searching, sorting, filtering, aggregate and paging on the server-side. These operations can be handled using methods such as
PerformSearching,PerformFiltering,PerformSorting,PerformTakeandPerformSkipavailable in the Syncfusion.EJ2.MVC5 package. Let’s explore how to manage these data operations using theUrlAdaptor.- In an API service project, add
Syncfusion.EJ2.MVC5by opening the NuGet package manager in Visual Studio (Tools → NuGet Package Manager → Manage NuGet Packages for Solution), search and install it.- To access
DataManagerRequest, import Syncfusion.EJ2.Base inGridController.csfile.
Handling Searching Operation
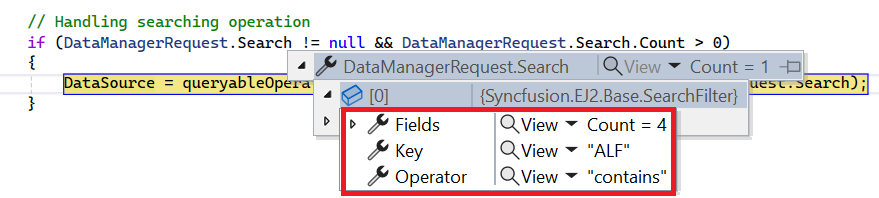
To enable search functionality, ensure that your API endpoint supports custom searching criteria. Implement the searching logic on the server-side using the PerformSearching. This allows the custom data source to undergo searching based on the criteria specified in the incoming DataManagerRequest object.
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult UrlDatasource(DataManagerRequest DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database).
IEnumerable<Orders> DataSource = order;
DataOperations operation = new DataOperations(); // Initialize DataOperations instance.
// Handling Searching.
if (DataManagerRequest.Search != null && DataManagerRequest.Search.Count > 0)
{
DataSource = operation.PerformSearching(DataSource, DataManagerRequest.Search);
}
// Get the total records count.
int count = DataSource.Count();
// Return data based on the request.
return DataManagerRequest.RequiresCounts ? Json(new { result = DataSource, count }) : Json(DataSource);
}// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").DataSource(ds => ds.Url("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDatasource").Adaptor("UrlAdaptor")).Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("120").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).IsPrimaryKey(true).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer ID").Width("140").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("ShipCity").Width("140").Add();
}).Toolbar(new List<string>() { "Search" }).Render()Handling Filtering Operation
To handle filtering operation, configure your API endpoint to support filter criteria. Implement the filtering logic on the server-side using the PerformFiltering. This allows the custom data source to undergo filtering based on the criteria specified in the incoming DataManagerRequest object.
Single column filtering

Multi column filtering

[HttpPost]
public ActionResult UrlDatasource(DataManagerRequest DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database).
IEnumerable<Orders> DataSource = order;
DataOperations operation = new DataOperations(); // Initialize DataOperations instance.
// Handling filtering operation.
if (DataManagerRequest.Where != null && DataManagerRequest.Where.Count > 0)
{
DataSource = operation.PerformFiltering(DataSource, DataManagerRequest.Where, DataManagerRequest.Where[0].Operator);
}
// Get the total records count.
int count = DataSource.Count();
// Return data based on the request.
return DataManagerRequest.RequiresCounts ? Json(new { result = DataSource, count }) : Json(DataSource);
}// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").DataSource(ds => ds.Url("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDatasource").Adaptor("UrlAdaptor")).Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("120").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).IsPrimaryKey(true).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer ID").Width("140").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("ShipCity").Width("140").Add();
}).AllowFiltering().Render()Handling Sorting Operation
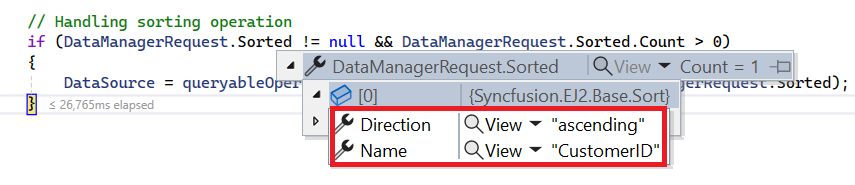
To handle sorting operation, configure your API to support custom sorting criteria. Implement the sorting logic on the server-side using the PerformSorting. This allows the custom data source to undergo sorting based on the criteria specified in the incoming DataManagerRequest object.
Single column sorting
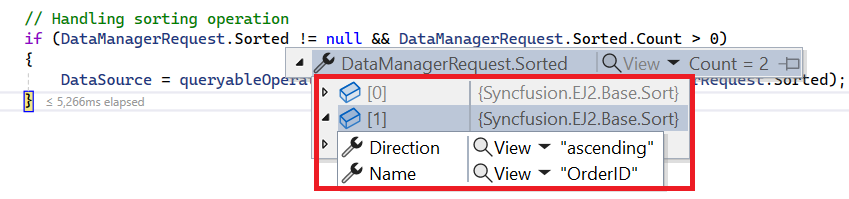
Multi column sorting
public ActionResult UrlDatasource(DataManagerRequest DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database).
IEnumerable<Orders> DataSource = order;
DataOperations operation = new DataOperations(); // Initialize DataOperations instance.
// Handling Sorting operation.
if (DataManagerRequest.Sorted != null && DataManagerRequest.Sorted.Count > 0)
{
DataSource = operation.PerformSorting(DataSource, DataManagerRequest.Sorted);
}
// Get the total count of records.
int count = DataSource.Count();
return DataManagerRequest.RequiresCounts ? Json(new { result = DataSource, count }) : Json(DataSource);
}// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").DataSource(ds => ds.Url("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDatasource").Adaptor("UrlAdaptor")).Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("120").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).IsPrimaryKey(true).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer ID").Width("140").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("ShipCity").Width("140").Add();
}).AllowSorting().Render()Handling Paging Operation
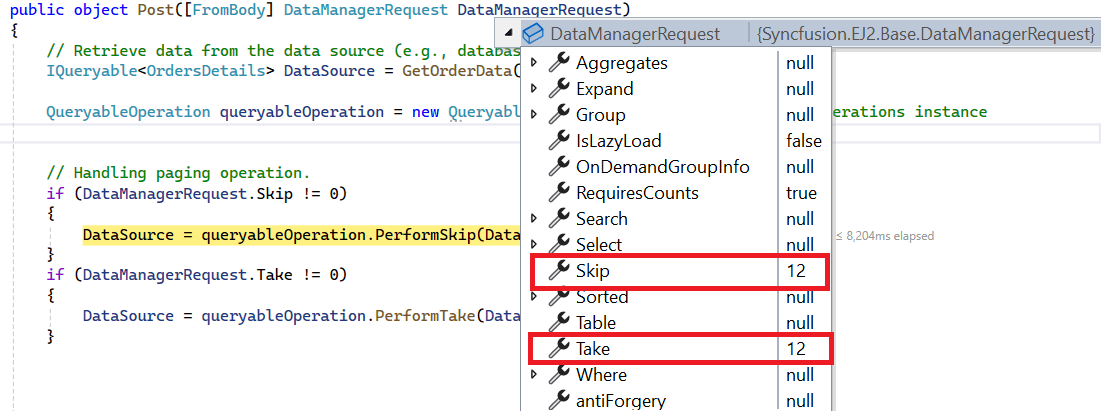
To handle paging operation, ensure that your API endpoint supports custom paging criteria. Implement the paging logic on the server-side using the PerformTake and PerformSkip. This allows the custom data source to undergo paging based on the criteria specified in the incoming DataManagerRequest object.
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult UrlDatasource(DataManagerRequest DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database).
IEnumerable<Orders> DataSource = order;
DataOperations operation = new DataOperations(); // Initialize DataOperations instance.
// Get the total records count.
int count = DataSource.Count();
// Handling paging operation.
if (DataManagerRequest.Skip != 0)
{
DataSource = operation.PerformSkip(DataSource, DataManagerRequest.Skip);
}
if (DataManagerRequest.Take != 0)
{
DataSource = operation.PerformTake(DataSource, DataManagerRequest.Take);
}
// Return data based on the request.
return DataManagerRequest.RequiresCounts ? Json(new { result = DataSource, count }) : Json(DataSource);
}// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").DataSource(ds => ds.Url("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDatasource").Adaptor("UrlAdaptor")).Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("120").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).IsPrimaryKey(true).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer ID").Width("140").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("ShipCity").Width("140").Add();
}).AllowPaging().Render()Handling CRUD Operations
The Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid seamlessly integrates CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations with server-side controller actions through specific properties: InsertUrl, RemoveUrl, UpdateUrl,CrudUrl, and BatchUrl. These properties enable the Grid to communicate with the data service for every Grid action, facilitating server-side operations.
CRUD Operations Mapping:
The following properties enable the Grid to interact with API endpoints for different CRUD actions:
- InsertUrl: Specifies the URL for inserting new data.
- RemoveUrl: Specifies the URL for removing existing data.
- UpdateUrl: Specifies the URL for updating existing data.
- CrudUrl: Specifies a single URL for all CRUD operations.
- BatchUrl: Specifies the URL for batch editing.
To enable editing in ASP.NET MVC Grid, refer to the editing Documentation. In the below example, the inline edit Mode is enabled and Toolbar property is configured to display toolbar items for editing purposes.
// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").DataSource(ds => ds.Url("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDatasource")
.UpdateUrl("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Update")
.InsertUrl("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Insert")
.RemoveUrl("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Remove").Adaptor("UrlAdaptor")).Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("120").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).IsPrimaryKey(true).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer ID").Width("140").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("ShipCity").Width("140").Add();
}).EditSettings(edit => { edit.AllowAdding(true).AllowEditing(true).AllowDeleting(true).Mode(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.EditMode.Normal); }).Toolbar(new List<string>() { "Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Update", "Cancel" }).Render()Normal/Inline editing is the default edit
Modefor the Grid. To enable CRUD operations, ensure that theisPrimaryKeyproperty is set to true for a specific Grid column, ensuring that its value is unique.
The below class is used to structure data sent during CRUD operations.
public class CRUDModel<T>
{
public string action { get; set; }
public string keyColumn { get; set; }
public object key { get; set; }
public T value { get; set; }
public List<T> Added { get; set; }
public List<T> Changed { get; set; }
public List<T> Deleted { get; set; }
public IDictionary<string, object> @params { get; set; }
}Insert Operation:
To insert a new record, utilize the InsertUrl property to specify the controller action mapping URL for the insert operation.
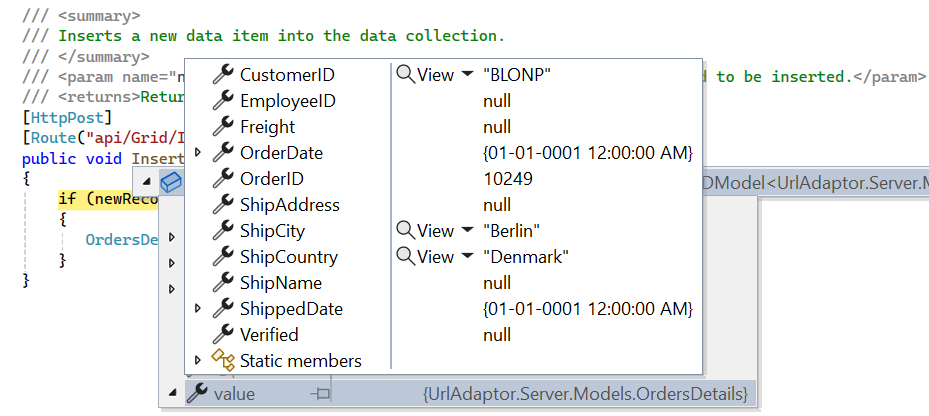
/// <summary>
/// Inserts a new data item into the data collection.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Returns void.</returns>
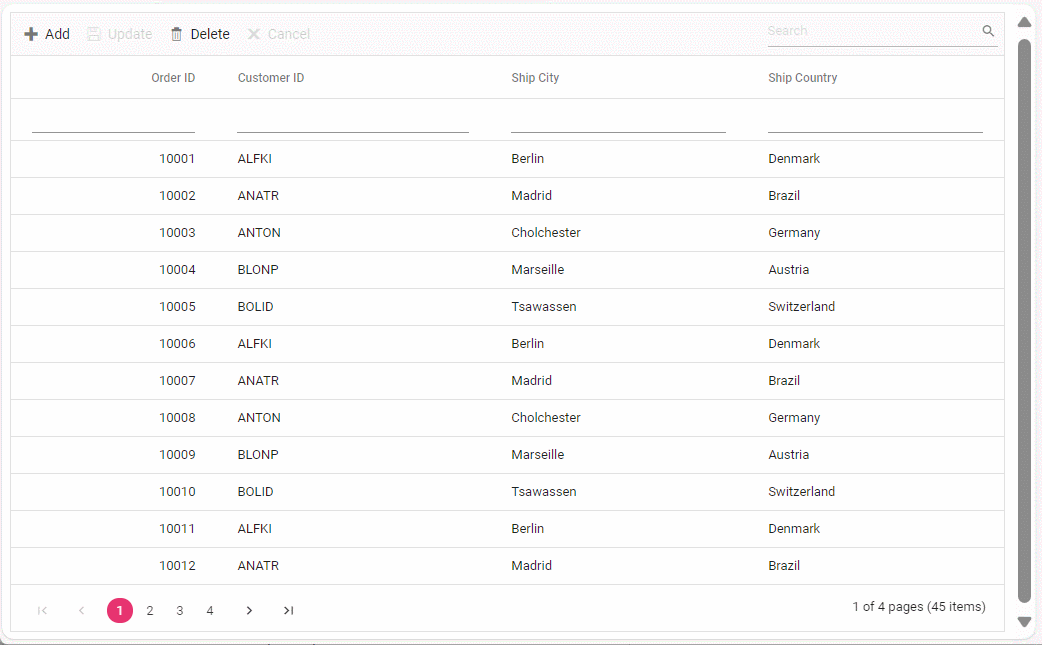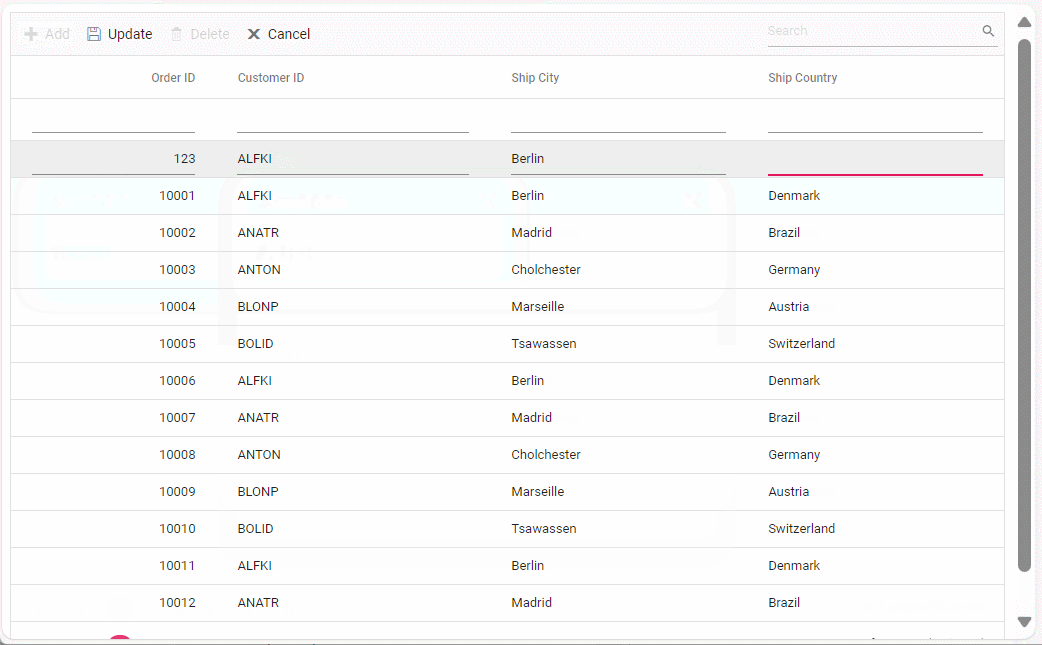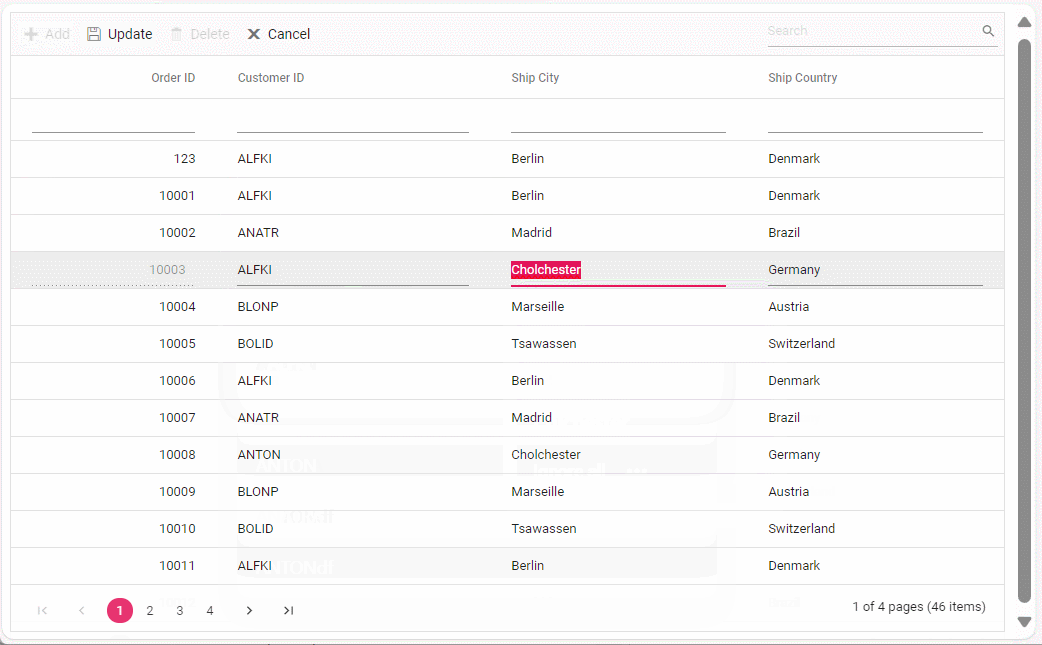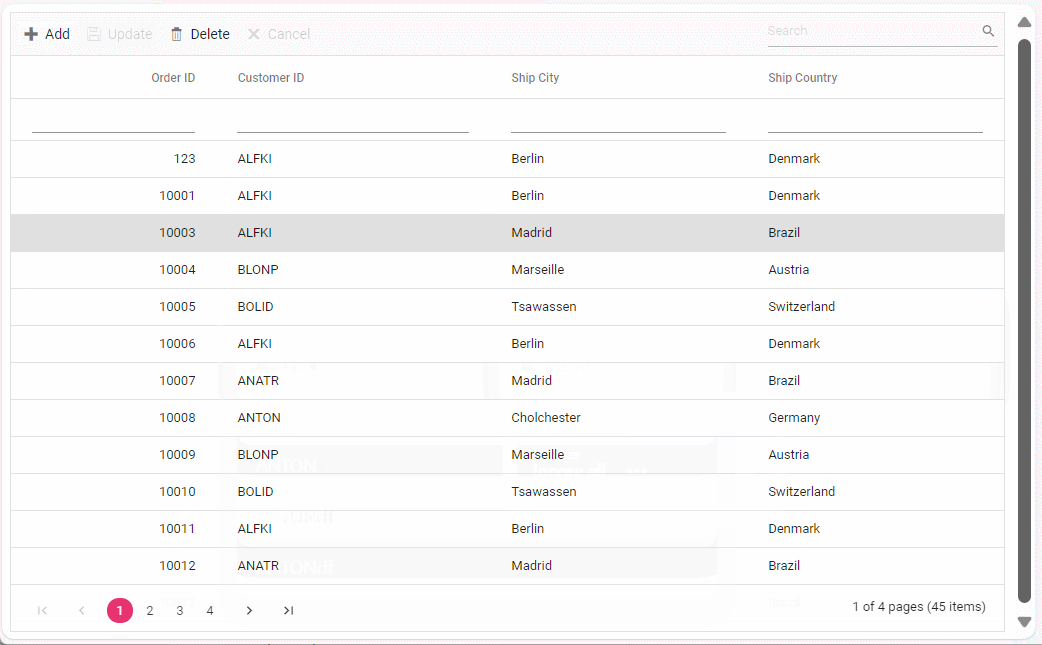
public ActionResult Insert(Orders value)
{
if (value != null)
{
// Assign a new OrderID if missing.
value.OrderID = order.Count > 0 ? order.Max(o => o.OrderID) + 1 : 1;
order.Insert(0, value);
}
// Ensure returning the expected format.
return Json(new { result = value, count = order.Count });
}Update Operation:
For updating existing records, utilize the UpdateUrl property to specify the controller action mapping URL for the update operation.
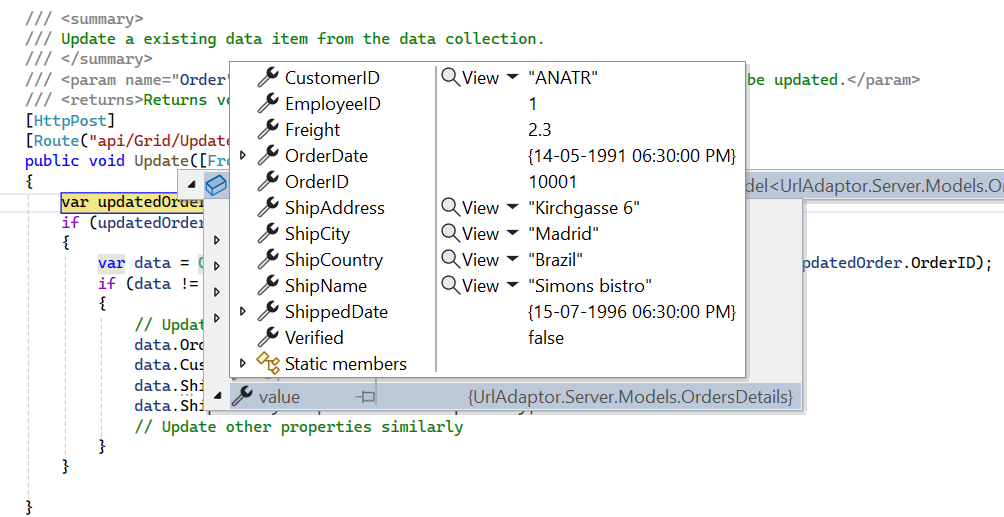
/// <summary>
/// Update a existing data item from the data collection.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Returns void.</returns>
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Update(Orders value)
{
// Find existing record.
var data = order.FirstOrDefault(or => or.OrderID == value.OrderID);
if (data != null)
{
// Update existing record.
data.CustomerID = value.CustomerID;
data.ShipCountry = value.ShipCountry;
data.ShipCity = value.ShipCity;
// Update other properties similarly.
}
return Json(value);
}Delete Operation
To delete existing records, use the RemoveUrl property to specify the controller action mapping URL for the delete operation.
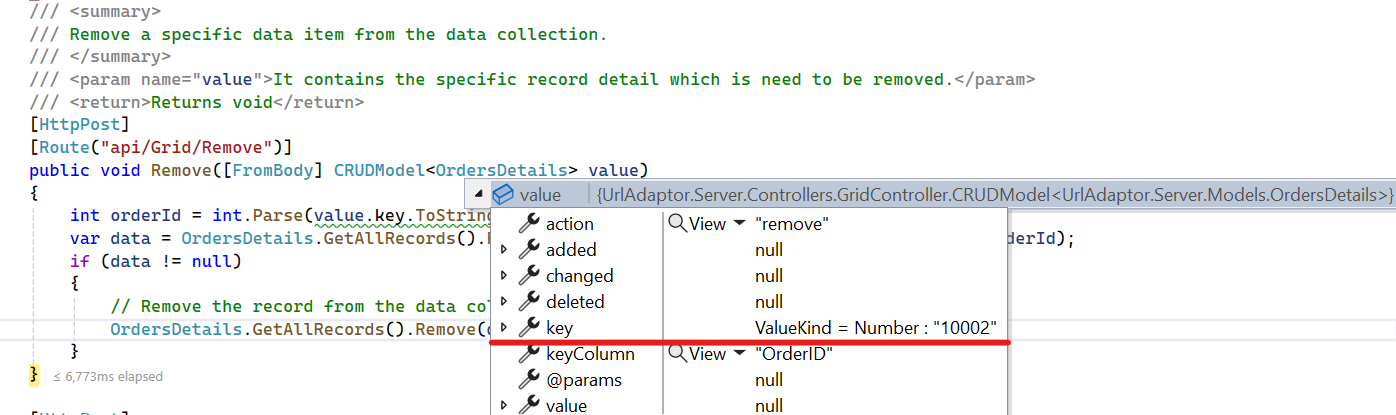
/// <summary>
/// Remove a specific data item from the data collection.
/// </summary>
/// <return>Returns void.</return>
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Remove(CRUDModel<Orders> value)
{
var data = order.FirstOrDefault(or => or.OrderID == int.Parse(value.key.ToString())); // Get key value from the deletedRecord.
if (data != null)
{
// Remove the record from the data collection.
order.Remove(data);
}
return Json(value);
}
Single method for performing all CRUD Operations:
Using the CrudUrl property, the controller action mapping URL can be specified to perform all the CRUD operation at server-side using a single method instead of specifying separate controller action method for CRUD (insert, update and delete) operations.
The following code example describes the above behavior.
[HttpPost]
public JsonResult CrudUpdate(CRUDModel<Orders> request)
{
// Perform update operation.
if (request.action == "update")
{
var existingRecord = order.FirstOrDefault(o => o.OrderID == request.value.OrderID);
if (existingRecord != null)
{
existingRecord.CustomerID = request.value.CustomerID;
existingRecord.ShipCity = request.value.ShipCity;
existingRecord.Freight = request.value.Freight;
}
}
// Perform insert operation.
else if (request.action == "insert")
{
var newId = order.Any() ? order.Max(o => o.OrderID) + 1 : 1;
request.value.OrderID = newId;
order.Add(request.value);
}
// Perform remove operation.
else if (request.action == "remove")
{
var key = int.Parse(request.key.ToString());
var recordToRemove = order.FirstOrDefault(o => o.OrderID == key);
if (recordToRemove != null)
{
order.Remove(recordToRemove);
}
}
return Json(order);
}// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").DataSource(ds => ds.Url("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDatasource")
.CrudUrl("/Grid/CrudUpdate").Adaptor("UrlAdaptor")).AllowSorting().Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("120").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).IsPrimaryKey(true).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer ID").Width("140").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("ShipCity").Width("140").Add();
}).AllowPaging().EditSettings(edit => { edit.AllowAdding(true).AllowEditing(true).AllowDeleting(true).Mode(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.EditMode.Normal); }).Toolbar(new List<string>() { "Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Update", "Cancel" }).Render()Batch Operation:
To perform batch operation, define the edit Mode as Batch and specify the BatchUrl property in the DataManager. Use the Add toolbar button to insert new row in batch editing mode. To edit a cell, double-click the desired cell and update the value as required. To delete a record, simply select the record and press the Delete toolbar button. Now, all CRUD operations will be executed in single request. Clicking the Update toolbar button will update the newly added, edited, or deleted records from the Orders table using a single API POST request.
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult BatchUpdate(CRUDModel<Orders> batchModel)
{
if (batchModel.Added != null)
{
foreach (var item in batchModel.Added)
{
item.OrderID = order.Count > 0 ? order.Max(o => o.OrderID) + 1 : 1;
order.Insert(0, item);
}
}
if (batchModel.Changed != null)
{
foreach (var item in batchModel.Changed)
{
var data = order.FirstOrDefault(or => or.OrderID == item.OrderID);
if (data != null)
{
data.CustomerID = item.CustomerID;
data.ShipCity = item.ShipCity;
// Update other properties as needed.
}
}
}
if (batchModel.Deleted != null)
{
foreach (var item in batchModel.Deleted)
{
var data = order.FirstOrDefault(or => or.OrderID == item.OrderID);
if (data != null)
{
order.Remove(data);
}
}
}
return Json(order);
}// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").DataSource(ds => ds.Url("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDatasource").BatchUrl("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/BatchUpdate").Adaptor("UrlAdaptor")).AllowSorting().Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("120").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).IsPrimaryKey(true).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer ID").Width("140").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("ShipCity").Width("140").Add();
}).AllowPaging().EditSettings(edit => { edit.AllowAdding(true).AllowEditing(true).AllowDeleting(true).Mode(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.EditMode.Batch); }).Toolbar(new List<string>() { "Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Update", "Cancel" }).Render()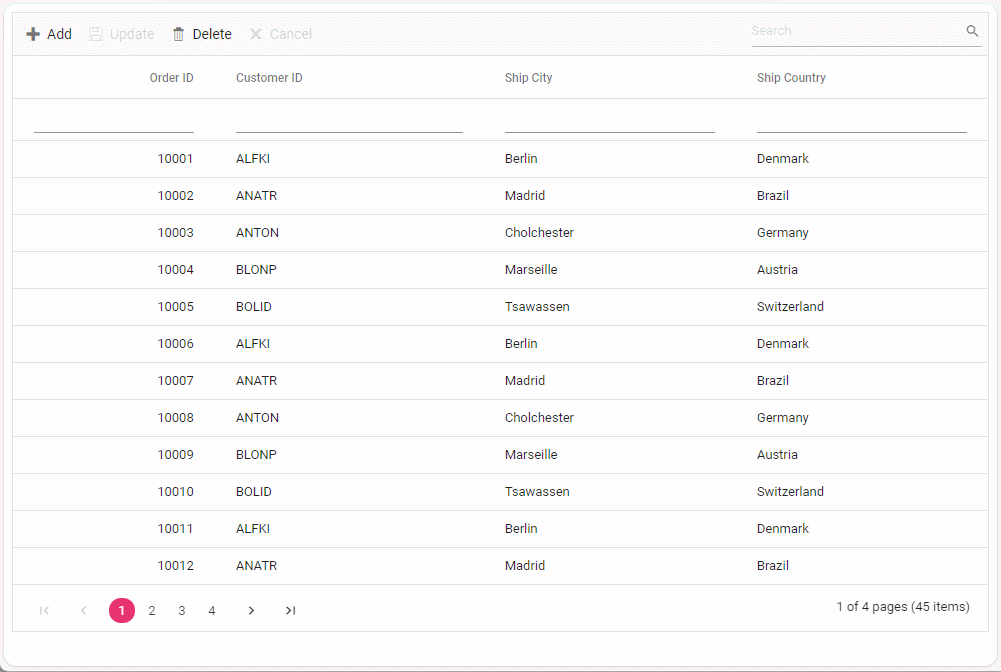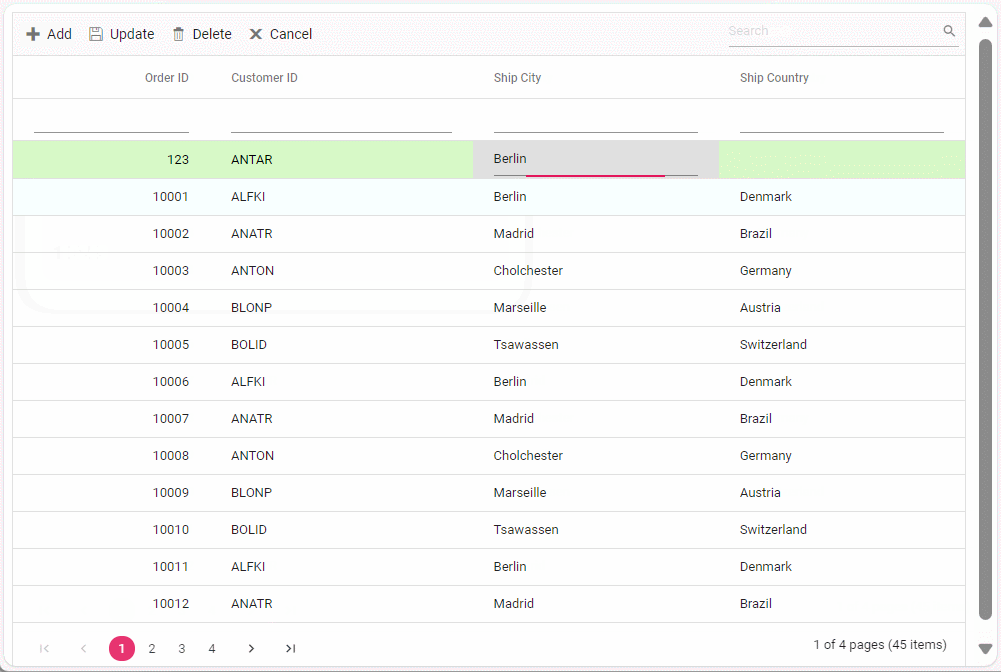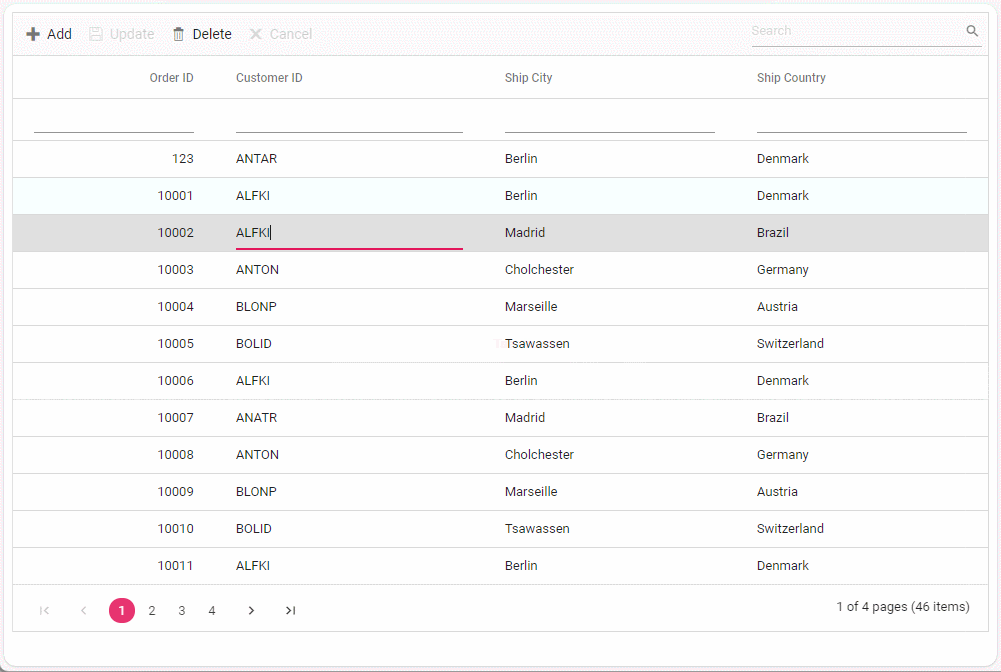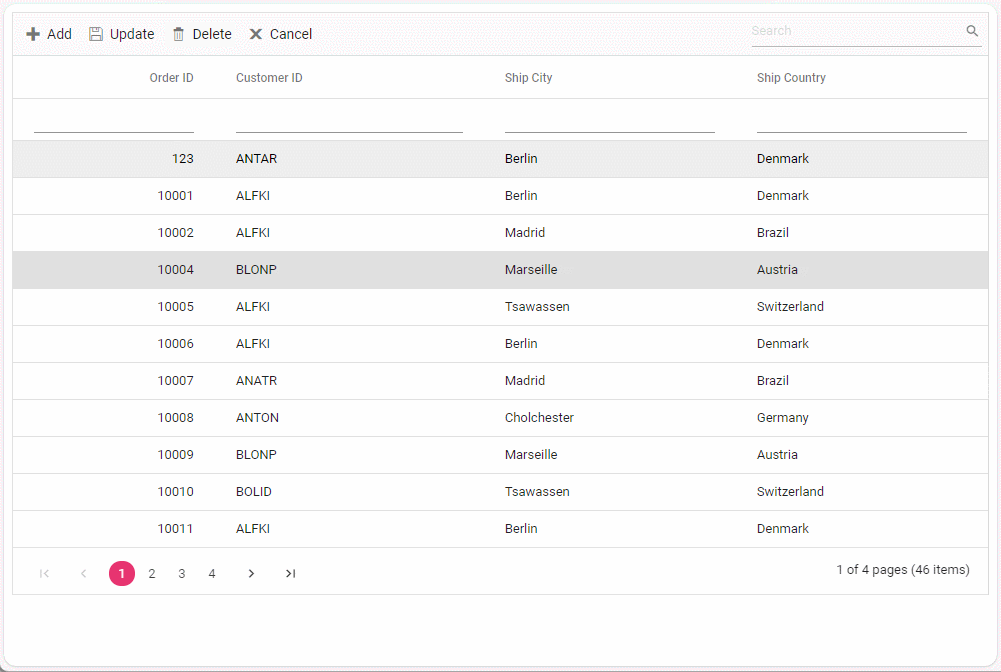
Foreign key column with UrlAdaptor
Configuration of foreign key column with remote data using UrlAdaptor requires assigning the DataManager instance with the endpoint URL to the particular column data source along with foreign key field and foreign key value properties. When both grid and foreign key column uses a UrlAdaptor, the grid data and the foreign key data are fetched separately from their respective remote endpoints. During operations such as filtering or sorting, the grid sends requests to the server based on the foreign key field and its corresponding value.
// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("grid").DataSource(dataManger => { dataManger.Url("http://localhost:xxxx/api/Grid").Adaptor("UrlAdaptor"); }).Height("315px").AllowFiltering(true).AllowSorting(true).Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").IsPrimaryKey(true).Width("120").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").ForeignKeyField("CustomerID").ForeignKeyValue("CustomerName").DataSource(dataManger => { dataManger.Url("http://localhost:xxxx/api/Customers").Adaptor("UrlAdaptor"); }).HeaderText("Customer Name").Width("140").Add();
col.Field("Freight").HeaderText("Freight").Width("120").Format("C2").EditType("numericedit").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("ShipName").HeaderText("Ship Name").Width("160").Add();
}).Render()Handling filter and search operation
Filtering a foreign-key column automatically shows the related text value via foreignKeyValue property, while the actual filtering is performed using the foreignKeyField property. This ensures that the filter request sent to the server uses the actual “CustomerID” field value, allowing the main data source to be filtered accurately.
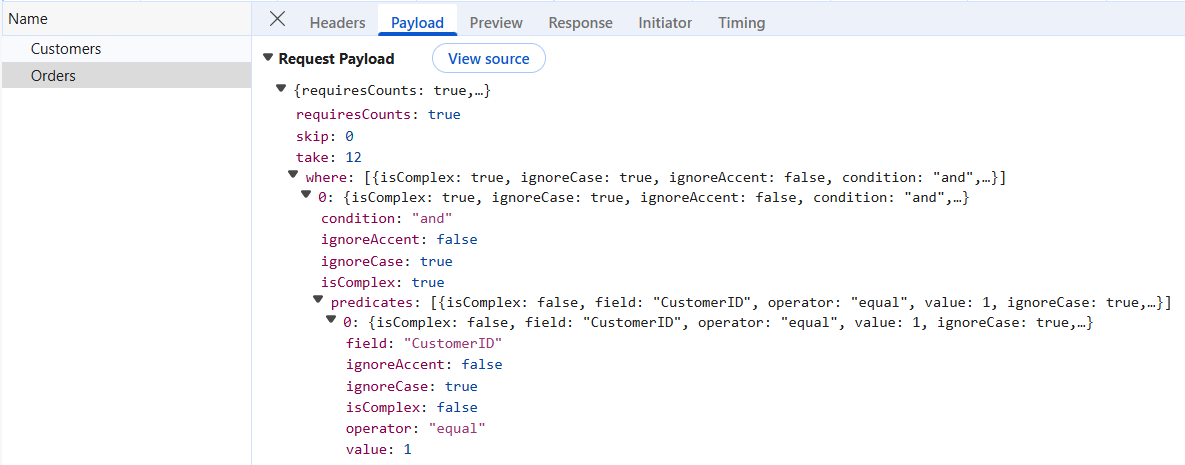
[HttpPost]
public object Post([FromBody] DataManagerRequest DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source.
IQueryable<OrdersDetails> DataSource = GetOrderData().AsQueryable();
QueryableOperation queryableOperation = new QueryableOperation(); // Initialize QueryableOperation instance.
// Handling filtering operation
if (DataManagerRequest.Where != null && DataManagerRequest.Where.Count > 0)
{
DataSource = operation.PerformFiltering(DataSource, DataManagerRequest.Where, DataManagerRequest.Where[0].Operator);
}
// Get the total count of records.
int totalRecordsCount = DataSource.Count();
// Return data based on the request.
return new { result = DataSource, count = totalRecordsCount };
}Search process in a grid with foreign key columns creates a filter query for each column using the provided search term. For foreign key columns specifically, the grid first queries the associated foreign key data source to retrieve the underlying field value that matches the search term. It then constructs a filter query using that value and the column’s field, applying it to the main dataset.
Handling sort operation
Sort operation on a foreign key column orders records based on the underlying “CustomerID” field value. The sorting query sent to the server includes the corresponding foreign key value. To sort by the foreign key value, supply the foreign key’s data source to the sorted query within the PerformSorting method.
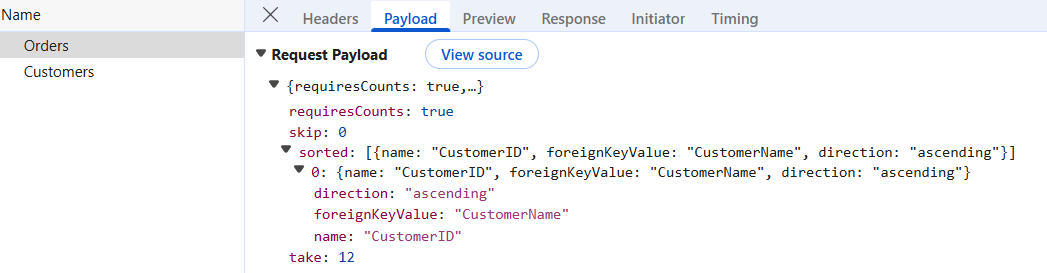
[HttpPost]
public object Post([FromBody] DataManagerRequest DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database).
IQueryable<OrdersDetails> DataSource = GetOrderData().AsQueryable();
QueryableOperation queryableOperation = new QueryableOperation(); // Initialize QueryableOperation instance.
if (DataManagerRequest.Sorted != null && DataManagerRequest.Sorted.Count > 0) //Sorting
{
for (int i = 0; i < DataManagerRequest.Sorted.Count; i++)
{
if (DataManagerRequest.Sorted[i].ForeignKeyValue == "CustomerName")
{
DataManagerRequest.Sorted[i].ForeignKeyDataSource = GetCustomerData().AsQueryable();
}
}
DataSource = operation.PerformSorting(DataSource, DataManagerRequest.Sorted);
}
// Get the total count of records.
int totalRecordsCount = DataSource.Count();
// Return data based on the request.
return new { result = DataSource, count = totalRecordsCount };
}Sort operation for a foreign key column based on its foreign key value mandates including the foreign key data source in the sorted query of the
DataManagerrequest on the server. If the foreign key data source is not passed, the sorting operation will be performed based on the column field.