How can I help you?
Connecting Microsoft SQL Server data in to Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid
16 Apr 202524 minutes to read
This section describes how to connect and retrieve data from a Microsoft SQL Server database using Microsoft.Data.SqlClient and bind it to the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid.
Microsoft SQL Server database can be bound to the Grid in different ways (i.e.) using DataSource property, custom adaptor feature and remote data binding using various adaptors. In this documentation, two approaches will be examined to connect a Microsoft SQL Server database to a Grid. Both the approaches have capability to handle data and CRUD operations with built-in methods as well as can be customized as per your own.
1. Using UrlAdaptor
The UrlAdaptor serves as the base adaptor for facilitating communication between remote data services and an UI component. It enables the remote binding of data to the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid by connecting to an existing pre-configured API service linked to the Microsoft SQL Server database. While the Grid supports various adaptors to fulfill this requirement, including Web API, ODataV4, UrlAdaptor, Web Method, and GraphQL, the UrlAdaptor is particularly useful for the scenarios where a custom API service with unique logic for handling data and CRUD operations is in place. This approach allows for custom handling of data and CRUD operations, and the resultant data returned in the result and count format for display in the Grid.
2. Using CustomAdaptor
The CustomAdaptor serves as a mediator between the UI component and the database for data binding. While the data source from the database can be directly bound to the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid locally using the DataSource property, the CustomAdaptor approach is preferred as it allows for customization of both data operations and CRUD operations according to specific requirements. In this approach, for every action in the Grid, a corresponding request with action details is sent to the CustomAdaptor. The Grid provides predefined methods to perform data operations such as searching, filtering, sorting, aggregation, paging and grouping. Alternatively, your own custom methods can be employed to execute operations and return the data in the result and count format for displaying in the Grid. Additionally, for CRUD operations, predefined methods can be overridden to provide custom functionality. Further details on this can be found in the latter part of the documentation.
Binding data from Microsoft SQL Server using an API service
This section describes step by step process how to retrieve data from a Microsoft SQL Server using an API service and bind it to the Grid.
Creating an API Service
To configure a server with Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid, follow the below steps:
1. Open Visual Studio and create an ASP.NET MVC project named Grid_MSSQL. To create an ASP.NET MVC application, follow the documentation link for detailed steps.
2. To connect a Microsoft SQL Server database using the Microsoft SQL driver in your application, you need to install the Microsoft.Data.SqlClient NuGet package. To add Microsoft.Data.SqlClient in the app, open the NuGet package manager in Visual Studio (Tools → NuGet Package Manager → Manage NuGet Packages for Solution), search and install it.
3. Create a MVC controller (aka, GridController.cs) file under Controllers folder that helps to establish data communication with the Grid.
4. In a MVC controller (aka, GridController), connect to Microsoft SQL Server. In the GetOrderData method SqlConnection helps to connect the Microsoft SQL Server database. Next, using SqlCommand and SqlDataAdapter you can process the desired SQL query string and retrieve data from the database. The Fill method of the DataAdapter is used to populate the SQL data into a DataTable as shown in the following code snippet.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using Microsoft.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using Syncfusion.EJ2.Base;
using Syncfusion.EJ2.Linq;
namespace Grid_MSSQL.Controllers
{
public class GridController : Controller
{
/// <summary>
/// Connection string for the database.
/// </summary>
private readonly string ConnectionString = @"<Enter a valid connection string>";
/// <summary>
/// Processes the DataManager request to perform searching, filtering, sorting, and paging operations.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="DataManagerRequest">Contains the details of the data operation requested.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON object with the filtered, sorted, and paginated data along with the total record count.</returns>
public JsonResult UrlDataSource(DataManagerRequest DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database).
IQueryable<Orders> dataSource = GetOrderData().AsQueryable();
// Get the total count of records.
int totalRecordsCount = dataSource.Count();
// Return data based on the request.
return Json(new { result = dataSource, count = totalRecordsCount }, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}
/// <summary>
/// Retrieves order data from the database.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Returns a list of orders fetched from the database.</returns>
private List<Orders> GetOrderData()
{
// SQL query to select all records from the orders table, sorted by OrderID.
string query = "SELECT * FROM dbo.Orders ORDER BY OrderID;";
// List to store the retrieved order data.
List<Orders> orders = new List<Orders>();
// Using block to ensure proper disposal of the SQL connection.
using (SqlCommand sqlConnection = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
// Open the database connection.
sqlConnection.Open();
// Using block to ensure proper disposal of the SQL command and data adapter.
using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(query, sqlConnection))
using (SqlDataAdapter dataAdapter = new SqlDataAdapter(sqlCommand))
{
// DataTable to store the query result.
DataTable dataTable = new DataTable();
// Fill the DataTable with data from the database.
dataAdapter.Fill(dataTable);
// Convert DataTable rows into a list of orders objects.
orders = (from DataRow row in dataTable.Rows
select new Orders
{
OrderID = Convert.ToInt32(row["OrderID"]),
CustomerID = row["CustomerID"].ToString(),
EmployeeID = Convert.IsDBNull(row["EmployeeID"]) ? (int?)null : Convert.ToInt32(row["EmployeeID"]),
ShipCity = row["ShipCity"].ToString(),
Freight = Convert.ToDecimal(row["Freight"])
}).ToList();
}
}
// Return the list of orders.
return orders;
}
#region Models
/// <summary>
/// Represents the orders model mapped to the database table.
/// </summary>
public class Orders
{
public int? OrderID { get; set; }
public string CustomerID { get; set; }
public int? EmployeeID { get; set; }
public decimal? Freight { get; set; }
public string ShipCity { get; set; }
}
#endregion
}
}5. Run the application and it will be hosted within the URL https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDataSource.
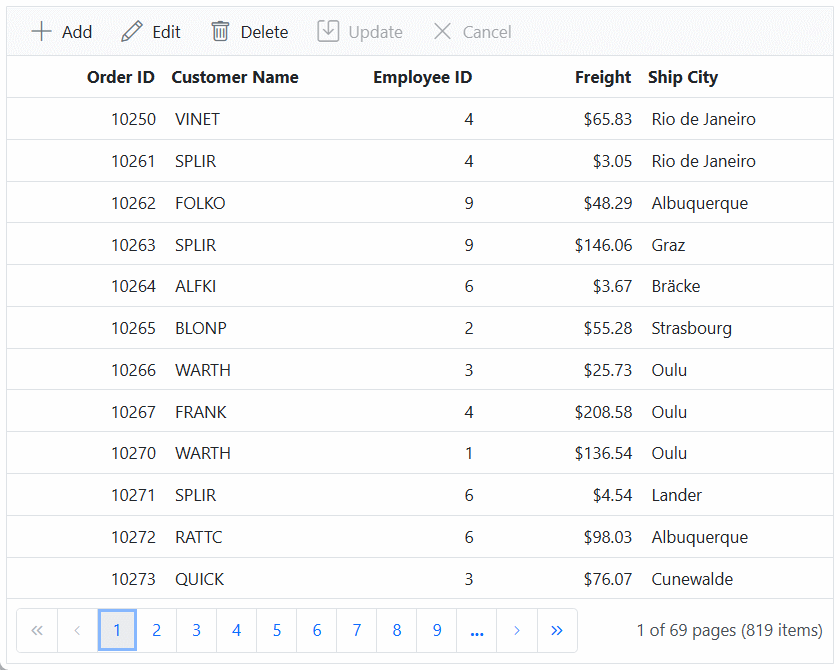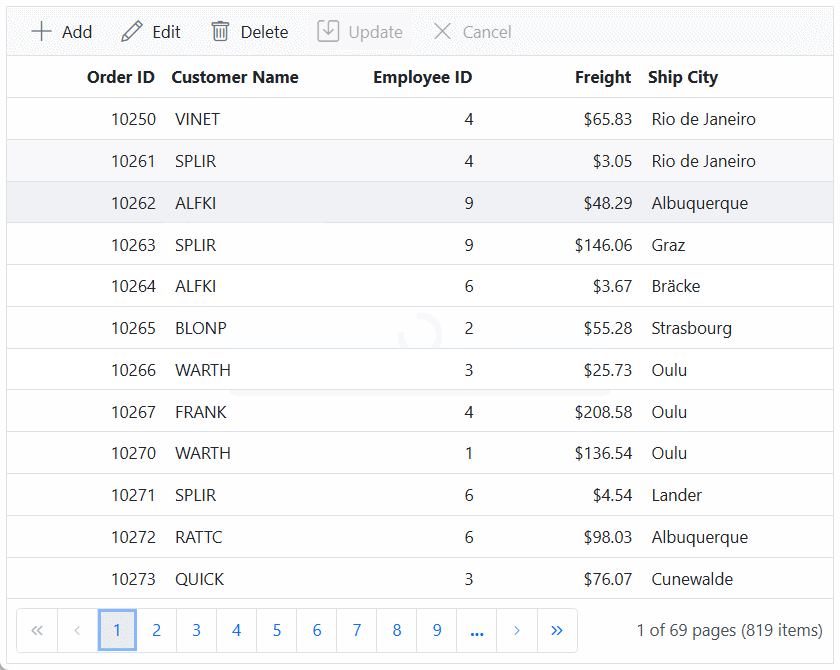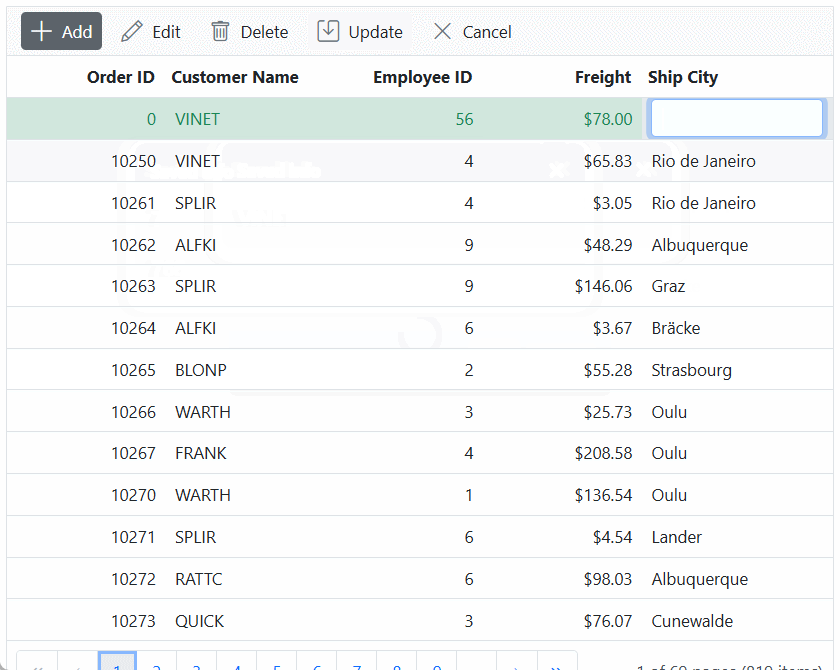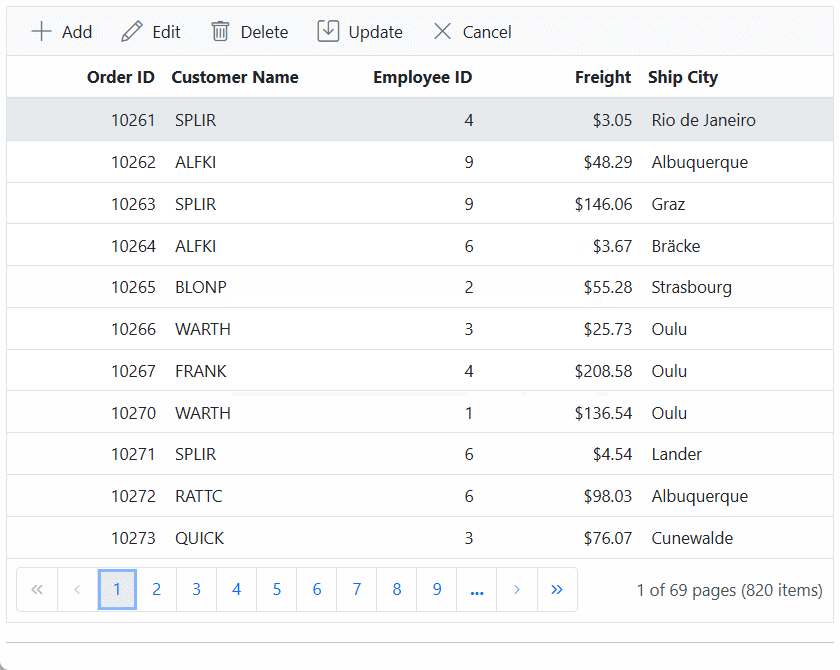
6. Finally, the retrieved data from Microsoft SQL Server database which is in the form of list can be found in an MVC controller available in the URL link https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDataSource, as shown in the browser page below.
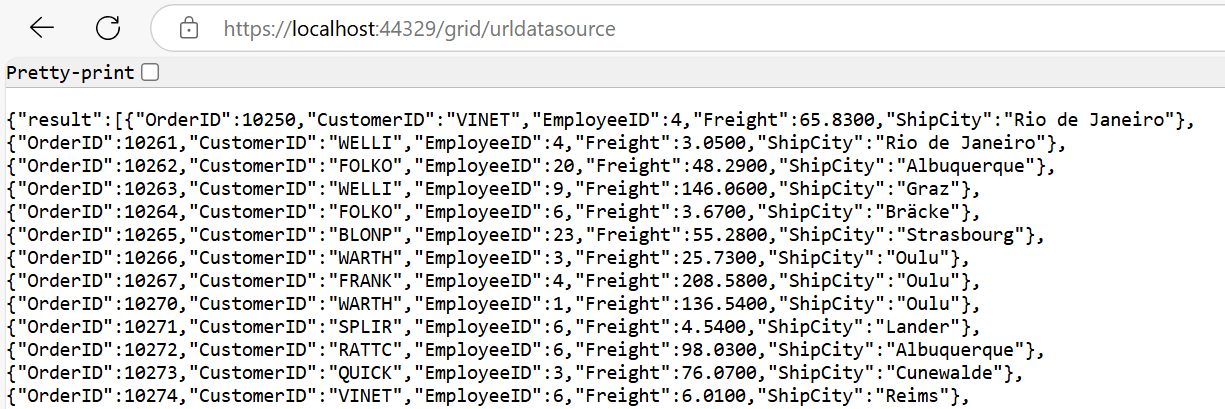
Connecting Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid to an API Service
To integrate the Syncfusion Grid into your ASP.NET MVC project using Visual Studio, follow these steps:
Step 1: Install the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Package:
To add ASP.NET MVC in the application, open the NuGet package manager in Visual Studio (Tools → NuGet Package Manager → Manage NuGet Packages for Solution), search for Syncfusion.EJ2.MVC5 and install it.
Alternatively, you can install it using the following Package Manager Console command:
Install-Package Syncfusion.EJ2.MVC5 -Version 32.2.3Step 2: Add Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC namespace
Add Syncfusion.EJ2 namespace reference in Web.config under Views folder.
<namespaces>
<add namespace="Syncfusion.EJ2"/>
</namespaces>Step 3: Add stylesheet and script resources
To include the required styles and scripts, add the following references inside the <head> of ~/Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file:
<head>
...
<!-- Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC control styles -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/bootstrap5.css" />
<!-- Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC control scripts -->
<script src="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/dist/ej2.min.js"></script>
<!-- Include the necessary CSS files to style the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC controls: -->
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-base/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-grids/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-buttons/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-popups/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-richtexteditor/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-navigations/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-dropdowns/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-lists/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-inputs/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-calendars/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-notifications/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/systemjs/0.19.38/system.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/syncfusion-helper.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</head>Step 4: Register Syncfusion Script Manager
To ensure proper script execution, register the Syncfusion Script Manager EJS().ScriptManager() at the end of <body> in the ~/Pages/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file as follows.
<body>
...
<!-- Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Script Manager -->
@Html.EJS().ScriptManager()
</body>Step 5: Add the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid
Now, add the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid tag helper in ~/Views/Home/Index.cshtml file. This allows the Grid to be rendered and interact with data dynamically from a remote database.
-
Create a
DataManagerinstance specifying the URL of your API endpoint(https:localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDataSource) using theurlproperty and set theadaptorUrlAdaptor. -
The
DataManageroffers multiple adaptor options to connect with remote database based on an API service. Below is an example of theUrlAdaptorconfiguration where an API service are set up to return the resulting data in theresultandcountformat. -
The
UrlAdaptoracts as the base adaptor for interacting with remote data service. Most of the built-in adaptors are derived from theUrlAdaptor.
// Replace `xxxx` with your actual port number
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").DataSource(ds => ds.Url("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDataSource").Adaptor("UrlAdaptor")).Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer Name").Width("100").Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("Freight").HeaderText("Freight").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Format("C2").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("Ship City").Width("120").Add();
}).Render()public class GridController : Controller
{
/// <summary>
/// Connection string for the database.
/// </summary>
private readonly string ConnectionString = @"<Enter a valid connection string>";
/// <summary>
/// Processes the DataManager request to perform searching, filtering, sorting, and paging operations.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="DataManagerRequest">Contains the details of the data operation requested.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON object with the filtered, sorted, and paginated data along with the total record count.</returns>
public JsonResult UrlDataSource(DataManagerRequest DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database).
IQueryable<Orders> dataSource = GetOrderData().AsQueryable();
// Get the total count of records.
int totalRecordsCount = dataSource.Count();
// Return data based on the request.
return Json(new { result = dataSource, count = totalRecordsCount }, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}
/// <summary>
/// Retrieves order data from the database.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Returns a list of orders fetched from the database.</returns>
private List<Orders> GetOrderData()
{
// SQL query to select all records from the orders table, sorted by OrderID.
string query = "SELECT * FROM dbo.Orders ORDER BY OrderID;";
// List to store the retrieved order data.
List<Orders> orders = new List<Orders>();
// Using block to ensure proper disposal of the SQL connection.
using (SqlCommand sqlConnection = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
// Open the database connection.
sqlConnection.Open();
// Using block to ensure proper disposal of the SQL command and data adapter.
using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(query, sqlConnection))
using (SqlDataAdapter dataAdapter = new SqlDataAdapter(sqlCommand))
{
// DataTable to store the query result.
DataTable dataTable = new DataTable();
// Fill the DataTable with data from the database.
dataAdapter.Fill(dataTable);
// Convert DataTable rows into a list of orders objects.
orders = (from DataRow row in dataTable.Rows
select new Orders
{
OrderID = Convert.ToInt32(row["OrderID"]),
CustomerID = row["CustomerID"].ToString(),
EmployeeID = Convert.IsDBNull(row["EmployeeID"]) ? (int?)null : Convert.ToInt32(row["EmployeeID"]),
ShipCity = row["ShipCity"].ToString(),
Freight = Convert.ToDecimal(row["Freight"])
}).ToList();
}
}
// Return the list of orders.
return orders;
}
#region Models
/// <summary>
/// Represents the orders model mapped to the database table.
/// </summary>
public class Orders
{
public int? OrderID { get; set; }
public string CustomerID { get; set; }
public int? EmployeeID { get; set; }
public decimal? Freight { get; set; }
public string ShipCity { get; set; }
}
#endregion
}Step 6: Run the Project
Run the project in Visual Studio, and the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid will successfully fetch data from the API service.
- The Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid provides built-in support for handling various data operations such as searching, sorting, filtering, aggregate and paging on the server-side. These operations can be handled using methods such as
PerformSearching,PerformFiltering,PerformSorting,PerformTakeandPerformSkipavailable in the Syncfusion.EJ2.MVC5 package. Let’s explore how to manage these data operations using theUrlAdaptor.- In an API service project, add
Syncfusion.EJ2.MVC5by opening the NuGet package manager in Visual Studio (Tools → NuGet Package Manager → Manage NuGet Packages for Solution), search and install it.- To access
DataManagerRequest, import Syncfusion.EJ2.Base inGridController.csfile.
Handling searching operation
To handle searching operation, ensure that your API endpoint supports custom searching criteria. Implement the searching logic on the server-side using the PerformSearching method from the QueryableOperation class. This allows the custom data source to undergo searching based on the criteria specified in the incoming DataManagerRequest object.
/// <summary>
/// Processes the DataManager request to perform searching operation.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="DataManagerRequest">Contains the details of the data operation requested.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON object with the searched data along with the total record count.</returns>
public JsonResult UrlDataSource(DataManagerRequest DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database).
IQueryable<Orders> dataSource = GetOrderData().AsQueryable();
// Initialize QueryableOperation instance.
QueryableOperation queryableOperation = new QueryableOperation();
// Handling searching operation.
if (DataManagerRequest.Search?.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = queryableOperation.PerformSearching(dataSource, DataManagerRequest.Search);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method.
}
// Get the total count of records.
int totalRecordsCount = DataSource.Count();
// Return data based on the request.
return Json(new { result = dataSource, count = totalRecordsCount }, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").DataSource(ds => ds.Url("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDatasource").Adaptor("UrlAdaptor")).Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer Name").Width("100").Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("Freight").HeaderText("Freight").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Format("C2").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("Ship City").Width("120").Add();
}).Toolbar(new List<string>() { "Search" }).Render()Handling filtering operation
To handle filtering operation, ensure that your API endpoint supports custom filtering criteria. Implement the filtering logic on the server-side using the PerformFiltering method from the QueryableOperation class. This allows the custom data source to undergo filtering based on the criteria specified in the incoming DataManagerRequest object.
/// <summary>
/// Processes the DataManager request to perform filtering operation.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="DataManagerRequest">Contains the details of the data operation requested.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON object with the filtered data along with the total record count.</returns>
public JsonResult UrlDataSource(DataManagerRequest DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database).
IQueryable<Orders> dataSource = GetOrderData().AsQueryable();
// Initialize QueryableOperation instance.
QueryableOperation queryableOperation = new QueryableOperation();
// Handling filtering operation.
if (DataManagerRequest.Where?.Count > 0)
{
foreach (WhereFilter condition in DataManagerRequest.Where)
{
foreach (WhereFilter predicate in condition.predicates)
{
dataSource = queryableOperation.PerformFiltering(dataSource, DataManagerRequest.Where, predicate.Operator);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method.
}
}
}
// Get the total count of records.
int totalRecordsCount = DataSource.Count();
// Return data based on the request.
return Json(new { result = dataSource, count = totalRecordsCount }, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").DataSource(ds => ds.Url("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDatasource").Adaptor("UrlAdaptor")).Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer Name").Width("100").Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("Freight").HeaderText("Freight").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Format("C2").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("Ship City").Width("120").Add();
}).AllowFiltering().Render()Handling sorting operation
To handle sorting operation, ensure that your API endpoint supports custom sorting criteria. Implement the sorting logic on the server-side using the PerformSorting method from the QueryableOperation class. This allows the custom data source to undergo sorting based on the criteria specified in the incoming DataManagerRequest object.
/// <summary>
/// Processes the DataManager request to perform sorting operation.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="DataManagerRequest">Contains the details of the data operation requested.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON object with the sorted data along with the total record count.</returns>
public JsonResult UrlDataSource(DataManagerRequest DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database).
IQueryable<Orders> dataSource = GetOrderData().AsQueryable();
// Initialize QueryableOperation instance.
QueryableOperation queryableOperation = new QueryableOperation();
// Handling sorting operation.
if (DataManagerRequest.Sorted?.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = queryableOperation.PerformSorting(dataSource, DataManagerRequest.Sorted);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method.
}
// Get the total count of records.
int totalRecordsCount = DataSource.Count();
// Return data based on the request.
return Json(new { result = dataSource, count = totalRecordsCount }, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").DataSource(ds => ds.Url("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDatasource").Adaptor("UrlAdaptor")).Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer Name").Width("100").Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("Freight").HeaderText("Freight").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Format("C2").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("Ship City").Width("120").Add();
}).AllowSorting().Render()Handling paging operation
To handle paging operation, ensure that your API endpoint supports custom paging criteria. Implement the paging logic on the server-side using the PerformTake and PerformSkip method from the QueryableOperation class. This allows the custom data source to undergo paging based on the criteria specified in the incoming DataManagerRequest object.
/// <summary>
/// Processes the DataManager request to perform paging operation.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="DataManagerRequest">Contains the details of the data operation requested.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON object with the paginated data along with the total record count.</returns>
public JsonResult UrlDataSource(DataManagerRequest DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database).
IQueryable<Orders> dataSource = GetOrderData().AsQueryable();
// Initialize QueryableOperation instance.
QueryableOperation queryableOperation = new QueryableOperation();
// Get the total count of records.
int totalRecordsCount = dataSource.Count();
// Handling paging operation.
if (DataManagerRequest.Skip > 0)
{
dataSource = queryableOperation.PerformSkip(dataSource, DataManagerRequest.Skip);
}
if (DataManagerRequest.Take > 0)
{
dataSource = queryableOperation.PerformTake(dataSource, DataManagerRequest.Take);
}
// Return data based on the request.
return Json(new { result = dataSource, count = totalRecordsCount }, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").DataSource(ds => ds.Url("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDatasource").Adaptor("UrlAdaptor")).Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer Name").Width("100").Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("Freight").HeaderText("Freight").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Format("C2").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("Ship City").Width("120").Add();
}).AllowPaging().Render()Handling CRUD operations
The Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid seamlessly integrates CRUD (Create, Read, Update, and Delete) operations with server-side controller actions through specific properties: InsertUrl, RemoveUrl, UpdateUrl and BatchUrl. These properties enable the Grid to communicate with the data service for every Grid action, facilitating server-side operations.
CRUD operations mapping
CRUD operations within the Grid can be mapped to server-side controller actions using specific properties:
- InsertUrl: Specifies the URL for inserting new data.
- RemoveUrl: Specifies the URL for removing existing data.
- UpdateUrl: Specifies the URL for updating existing data.
- BatchUrl: Specifies the URL for batch editing.
To enable editing in ASP.NET MVC Grid, refer to the editing documentation. In the below example, the inline edit Mode is enabled and Toolbar property is configured to display toolbar items for editing purposes.
// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").DataSource(ds => ds.Url("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDatasource")
.UpdateUrl("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Update")
.InsertUrl("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Insert")
.RemoveUrl("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Remove").Adaptor("UrlAdaptor")).Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).IsPrimaryKey(true).IsIdentity(true).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer Name").Width("100").ValidationRules(new { required = "true" }).Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).ValidationRules(new { required = "true", number = true}).Add();
col.Field("Freight").HeaderText("Freight").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Format("C2").ValidationRules(new { required = "true", min=1, max=1000 }).Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("Ship City").Width("120").ValidationRules(new { required = "true" }).Add();
}).EditSettings(edit => { edit.AllowAdding(true).AllowEditing(true).AllowDeleting(true).Mode(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.EditMode.Normal); }).Toolbar(new List<string>() { "Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Update", "Cancel" }).Render()
- Normal/Inline editing is the default edit
Modefor the Grid. To enable CRUD operations, ensure that the IsPrimaryKey property is set to true for a specific Grid column, ensuring that its value is unique.- If database has an auto generated column, ensure to define IsIdentity property of Grid column to disable them during adding or editing operations.
Insert operation:
To insert a new row, simply click the Add toolbar button. The new record edit form will be displayed as shown below. Upon clicking the Update toolbar button, record will inserted into the Orders table by calling the following POST method of an API.
/// <summary>
/// Inserts a new order record into the database using parameterized queries.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="model">Contains the details of the order to be inserted.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON result indicating success.</returns>
public JsonResult Insert(CRUDModel<Orders> model)
{
using (SqlCommand sqlConnection = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
// Define the SQL query to insert a new order record using parameters.
string query = "INSERT INTO Orders (CustomerID, Freight, ShipCity, EmployeeID) VALUES (@CustomerID, @Freight, @ShipCity, @EmployeeID)";
using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(query, sqlConnection))
{
// Add parameters to prevent SQL injection and handle null values.
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@CustomerID", model.value.CustomerID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Freight", model.value.Freight ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@ShipCity", model.value.ShipCity ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@EmployeeID", model.value.EmployeeID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
// Open the database connection and execute the command.
sqlConnection.Open();
sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
// Return a JSON response indicating success.
return Json(new { success = true });
}
public class CRUDModel<T> where T : class
{
public string action { get; set; }
public string keyColumn { get; set; }
public object key { get; set; }
public T value { get; set; }
public List<T> added { get; set; }
public List<T> changed { get; set; }
public List<T> deleted { get; set; }
public IDictionary<string, object> @params { get; set; }
}Update operation:
To edit a row, first select desired row and click the Edit toolbar button. The edit form will be displayed and proceed to modify any column value as per your requirement. Clicking the Update toolbar button will update the edit record in the Orders table by involving the following Post method of an API.
/// <summary>
/// Update a existing data item from the data collection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="model">It contains the updated record detail which is need to be updated.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON result indicating success.</returns>
public JsonResult Update(CRUDModel<Orders> model)
{
using (SqlCommand sqlConnection = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
// Define the SQL query to update the order details based on OrderID.
string query = "UPDATE Orders SET CustomerID=@CustomerID, Freight=@Freight, EmployeeID=@EmployeeID, ShipCity=@ShipCity WHERE OrderID=@OrderID";
using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(query, sqlConnection))
{
// Add parameters to ensure data integrity and prevent SQL injection.
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@CustomerID", model.value.CustomerID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Freight", model.value.Freight ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@ShipCity", model.value.ShipCity ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@EmployeeID", model.value.EmployeeID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@OrderID", model.value.OrderID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
// Open the database connection and execute the update command.
sqlConnection.Open();
sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
// Return a JSON response indicating success.
return Json(new { success = true });
}
public class CRUDModel<T> where T : class
{
public string action { get; set; }
public string keyColumn { get; set; }
public object key { get; set; }
public T value { get; set; }
public List<T> added { get; set; }
public List<T> changed { get; set; }
public List<T> deleted { get; set; }
public IDictionary<string, object> @params { get; set; }
}Delete operation
To delete a row, simply select the desired row and click the Delete toolbar button. This action will trigger a DELETE request to an API, containing the primary key value of the selected record. As a result corresponding record will be removed from the Orders table.
/// <summary>
/// Remove a specific data item from the data collection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value">It contains the specific record detail which is need to be removed.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON result indicating success.</returns>
public JsonResult Remove(CRUDModel<Orders> model)
{
using (SqlCommand sqlConnection = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
// Define the SQL query to delete the order based on OrderID.
string query = "DELETE FROM Orders WHERE OrderID=@OrderID";
using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(query, sqlConnection))
{
// Add parameter to ensure data integrity and prevent SQL injection.
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@OrderID", model.key ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
// Open the database connection and execute the delete command.
sqlConnection.Open();
sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
// Return a JSON response indicating success.
return Json(new { success = true });
}
public class CRUDModel<T> where T : class
{
public string action { get; set; }
public string keyColumn { get; set; }
public object key { get; set; }
public T value { get; set; }
public List<T> added { get; set; }
public List<T> changed { get; set; }
public List<T> deleted { get; set; }
public IDictionary<string, object> @params { get; set; }
}Batch operation
To perform batch operation, define the edit Mode as Batch and specify the BatchUrl property in the DataManager. Use the Add toolbar button to insert new row in batch editing mode. To edit a cell, double-click the desired cell and update the value as required. To delete a record, simply select the record and press the Delete toolbar button. Now, all CRUD operations will be executed in single request. Clicking the Update toolbar button will update the newly added, edited, or deleted records from the Orders table using a single API POST request.
/// <summary>
/// Batch update (Insert, Update, and Delete) a collection of data items from the data collection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value">The set of information along with details about the CRUD actions to be executed from the database.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON response with success or error message.</returns>
public JsonResult BatchUpdate(CRUDModel<Orders> value)
{
// Establish SQL connection.
using (SqlCommand sqlConnection = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
sqlConnection.Open();
// Begin a database transaction to ensure atomicity.
using (SqlTransaction transaction = sqlConnection.BeginTransaction())
{
// Process updated records.
if (value.changed != null && value.changed.Count > 0)
{
// SQL query for updating records in the database.
string updateQuery = "UPDATE Orders SET CustomerID=@CustomerID, Freight=@Freight, EmployeeID=@EmployeeID, ShipCity=@ShipCity WHERE OrderID=@OrderID.";
foreach (Orders record in value.changed)
{
using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(updateQuery, sqlConnection, transaction))
{
// Add parameters to avoid SQL injection.
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@CustomerID", record.CustomerID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Freight", record.Freight ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@EmployeeID", record.EmployeeID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@ShipCity", record.ShipCity ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@OrderID", record.OrderID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
// Execute the update query.
sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
// Process newly inserted records.
if (value.added != null && value.added.Count > 0)
{
// SQL query for inserting new records into the database.
string insertQuery = "INSERT INTO Orders (CustomerID, Freight, ShipCity, EmployeeID) VALUES (@CustomerID, @Freight, @ShipCity, @EmployeeID).";
foreach (Orders record in value.added)
{
using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(insertQuery, sqlConnection, transaction))
{
// Add parameters to avoid SQL injection.
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@CustomerID", record.CustomerID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Freight", record.Freight ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@ShipCity", record.ShipCity ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@EmployeeID", record.EmployeeID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
// Execute the insert query.
sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
// Process deleted records.
if (value.deleted != null && value.deleted.Count > 0)
{
// SQL query for deleting records from the database.
string deleteQuery = "DELETE FROM Orders WHERE OrderID=@OrderID.";
foreach (Orders record in value.deleted)
{
using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(deleteQuery, sqlConnection, transaction))
{
// Add parameter to avoid SQL injection.
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@OrderID", record.OrderID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
// Execute the delete query.
sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
// Commit the transaction if all operations succeed.
transaction.Commit();
}
}
// Return success response.
return Json(new { success = true });
}// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").DataSource(ds => ds.Url("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDatasource").BatchUrl("https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/BatchUpdate").Adaptor("UrlAdaptor")).Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).IsPrimaryKey(true).IsIdentity(true).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer Name").Width("100").ValidationRules(new { required = "true" }).Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).ValidationRules(new { required = "true", number = true}).Add();
col.Field("Freight").HeaderText("Freight").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Format("C2").ValidationRules(new { required = "true", min=1, max=1000 }).Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("Ship City").Width("120").ValidationRules(new { required = "true" }).Add();
}).AllowPaging().EditSettings(edit => { edit.AllowAdding(true).AllowEditing(true).AllowDeleting(true).Mode(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.EditMode.Batch); }).Toolbar(new List<string>() { "Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Update", "Cancel" }).Render()When you run the application, the resultant Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid will look like this
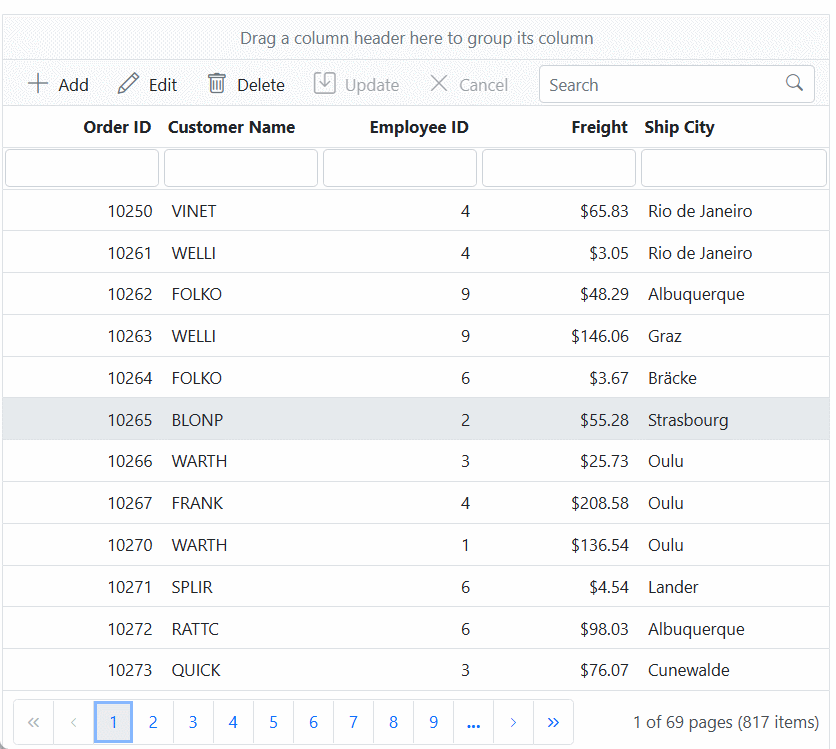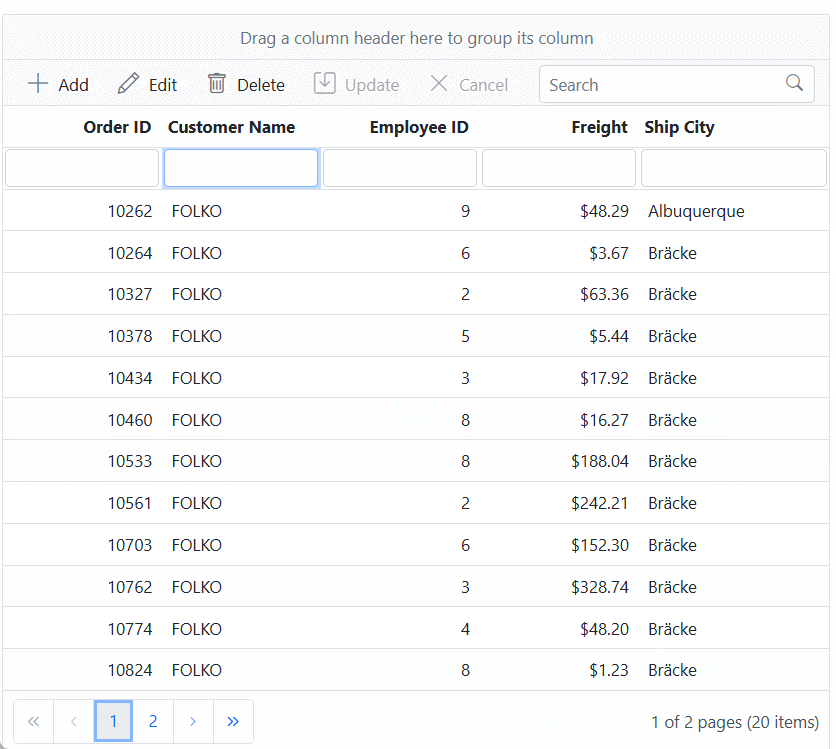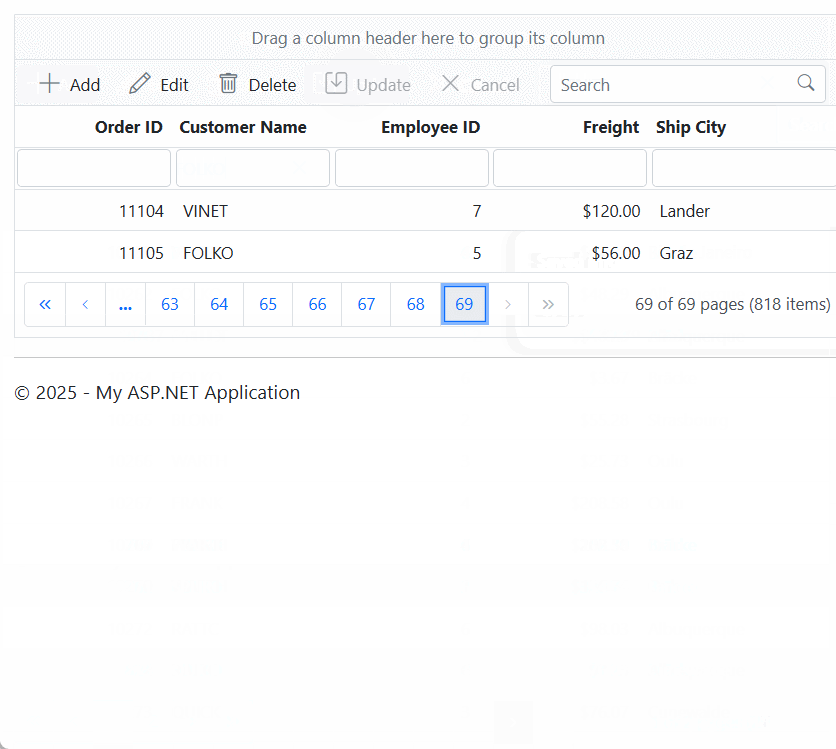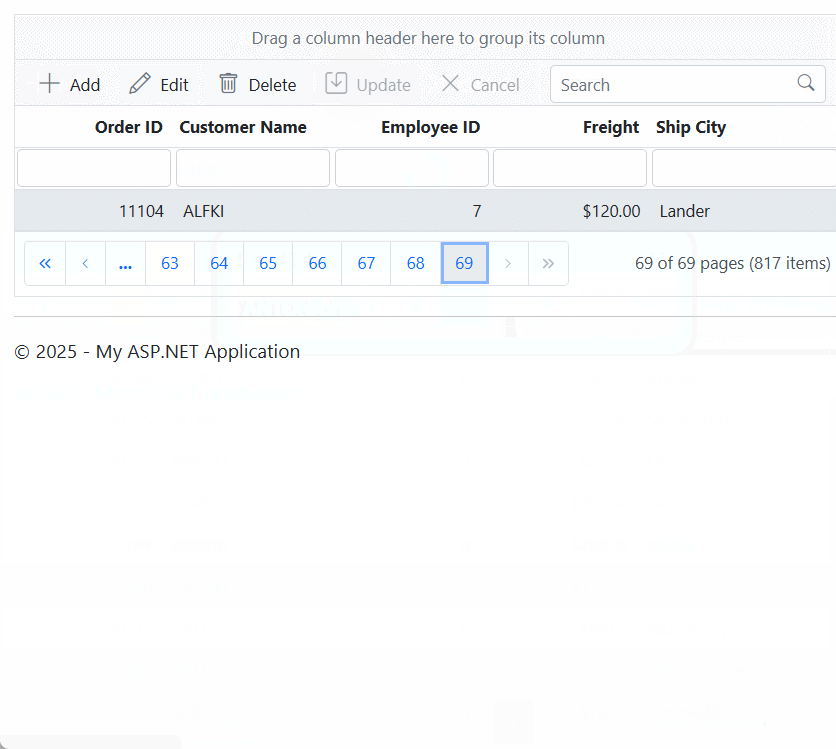
Binding data from Microsoft SQL Server using CustomAdaptor
This section describes step by step process how to retrieve data from a Microsoft SQL Server using CustomAdaptor and bind it to the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid.
1. To create a simple Grid, the procedure is explained in the above-mentioned topic on Connecting Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid to an API service
2. To connect a Microsoft SQL Server database using the Microsoft SQL driver in your application, you need to install the Microsoft.Data.SqlClient NuGet package. To add Microsoft.Data.SqlClient in the app, open the NuGet package manager in Visual Studio (Tools → NuGet Package Manager → Manage NuGet Packages for Solution), search and install it.
3. If you intend to inject your own service into the CustomAdaptor and utilize it, you can achieve this as follows:
- Create a
CustomAdaptorthat extends theUrlAdaptorclass. - Override the
processResponsemethod to process server responses.
4. Within the processResponse method of CustomAdaptor, fetch data by calling the GetOrderData method.
-
In this GetOrderData method, fetch data from the Microsoft SQL Server database using the SqlDataAdapter class.
-
Employ the
Fillmethod of theDataAdapterto populate a DataSet with the results of theSelectcommand of theDataAdapter, followed by conversion of the DataSet into a List. -
Finally, return the response as a result and count pair object in the
Postmethod to bind the data to the Grid.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer Name").Width("100").Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("Freight").HeaderText("Freight").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Format("C2").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("Ship City").Width("120").Add();
}).Render()
<script>
class CustomAdaptor extends ej.data.UrlAdaptor {
processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes) {
var original = super.processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes);
return original;
}
}
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
let grid = document.getElementById("Grid").ej2_instances[0];
if (grid) {
let dataManager = new ejs.data.DataManager({
url: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDataSource", // Replace `xxxx` with your actual port number.
adaptor: new CustomAdaptor(),
});
grid.dataSource = dataManager;
}
});
</script>using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using Microsoft.Data.SqlClient
using System.Linq;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using Syncfusion.EJ2.Base;
using Syncfusion.EJ2.Linq;
namespace Grid_MSSQL.Controllers
{
public class GridController : Controller
{
/// <summary>
/// Connection string for the database.
/// </summary>
private readonly string ConnectionString = @"<Enter a valid connection string>";
/// <summary>
/// Processes the DataManager request to perform searching, filtering, sorting, and paging operations.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="DataManagerRequest">Contains the details of the data operation requested.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON object with the filtered, sorted, and paginated data along with the total record count.</returns>
public JsonResult UrlDataSource(DataManagerRequest DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database).
IQueryable<Orders> DataSource = GetOrderData().AsQueryable();
// Get the total count of records.
int totalRecordsCount = dataSource.Count();
// Return data based on the request.
return Json(new { result = dataSource, count = totalRecordsCount }, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}
/// <summary>
/// Retrieves order data from the database.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Returns a list of orders fetched from the database.</returns>
private List<Orders> GetOrderData()
{
string query = "SELECT * FROM dbo.Orders ORDER BY OrderID;";
List<Orders> orders = new List<Orders>();
using (SqlCommand sqlConnection = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
sqlConnection.Open();
using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(query, sqlConnection))
using (SqlDataAdapter dataAdapter= new SqlDataAdapter(sqlCommand))
{
DataTable dataTable = new DataTable();
dataAdapter.Fill(dataTable);
orders = (from DataRow row in dataTable.Rows select new Orders
{
OrderID = Convert.ToInt32(row["OrderID"]),
CustomerID = row["CustomerID"].ToString(),
EmployeeID = Convert.IsDBNull(row["EmployeeID"]) ? (int?)null : Convert.ToInt32(row["EmployeeID"]),
ShipCity = row["ShipCity"].ToString(),
Freight = Convert.ToDecimal(row["Freight"])
}).ToList();
}
}
return orders;
}
#region Models
/// <summary>
/// Represents the orders model mapped to the database table.
/// </summary>
public class Orders
{
public int? OrderID { get; set; }
public string CustomerID { get; set; }
public int? EmployeeID { get; set; }
public decimal? Freight { get; set; }
public string ShipCity { get; set; }
}
#endregion
}
}
- The
DataManagerRequestencompasses details about the Grid actions such as searching, filtering, sorting, aggregate, paging and grouping.
Handling searching operation
When utilizing the CustomAdaptor in ASP.NET MVC, managing the searching operation involves overriding the processResponse method of the UrlAdaptor class.
In the code example below, searching a custom data source can be accomplished by employing the built-in PerformSearching method of the QueryableOperation class. Alternatively, you can implement your own method for searching operation and bind the resultant data to the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid.
/// <summary>
/// Processes the DataManager request to perform searching operation.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="DataManagerRequest">Contains the details of the data operation requested.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON object with the searched data along with the total record count.</returns>
public JsonResult UrlDataSource(DataManagerRequest DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database).
IQueryable<Orders> dataSource = GetOrderData().AsQueryable();
// Initialize QueryableOperation instance.
QueryableOperation queryableOperation = new QueryableOperation();
// Handling searching operation.
if (DataManagerRequest.Search?.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = queryableOperation.PerformSearching(dataSource, DataManagerRequest.Search);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method.
}
// Get the total count of records.
int totalRecordsCount = DataSource.Count();
// Return data based on the request.
return Json(new { result = dataSource, count = totalRecordsCount }, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer Name").Width("100").Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("Freight").HeaderText("Freight").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Format("C2").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("Ship City").Width("120").Add();
}).Toolbar(new List<string>() { "Search" }).Render()
<script>
class CustomAdaptor extends ej.data.UrlAdaptor {
processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes) {
var original = super.processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes);
return original;
}
}
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
let grid = document.getElementById("Grid").ej2_instances[0];
if (grid) {
let dataManager = new ejs.data.DataManager({
url: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDataSource", // Replace `xxxx` with your actual port number.
adaptor: new CustomAdaptor(),
});
grid.dataSource = dataManager;
}
});
</script>Handling filtering operation
When utilizing the CustomAdaptor in ASP.NET MVC, managing the filtering operation involves overriding the processResponse method of the UrlAdaptor class.
In the code example below, filtering a custom data source can be achieved by utilizing the built-in PerformFiltering method of the QueryableOperation class. Alternatively, you can implement your own method for filtering operation and bind the resulting data to the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid.
/// <summary>
/// Processes the DataManager request to perform filtering operation.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="DataManagerRequest">Contains the details of the data operation requested.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON object with the filtered data along with the total record count.</returns>
public JsonResult UrlDataSource(DataManagerRequest DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database).
IQueryable<Orders> DataSource = GetOrderData().AsQueryable();
// Initialize QueryableOperation instance.
QueryableOperation queryableOperation = new QueryableOperation();
// Handling filtering operation.
if (DataManagerRequest.Where?.Count > 0)
{
foreach(WhereFilter condition in DataManagerRequest.Where)
{
foreach(WhereFilter predicate in condition.predicates)
{
dataSource = queryableOperation.PerformFiltering(dataSource, DataManagerRequest.Where, predicate.Operator);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method.
}
}
}
// Get the total count of records.
int totalRecordsCount = DataSource.Count();
// Return data based on the request.
return Json(new { result = dataSource, count = totalRecordsCount }, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer Name").Width("100").Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("Freight").HeaderText("Freight").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Format("C2").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("Ship City").Width("120").Add();
}).AllowFiltering().Render()
<script>
class CustomAdaptor extends ej.data.UrlAdaptor {
processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes) {
var original = super.processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes);
return original;
}
}
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
let grid = document.getElementById("Grid").ej2_instances[0];
if (grid) {
let dataManager = new ejs.data.DataManager({
url: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDataSource", // Replace `xxxx` with your actual port number.
adaptor: new CustomAdaptor(),
});
grid.dataSource = dataManager;
}
});
</script>Handling sorting operation
When utilizing the CustomAdaptor in ASP.NET MVC, managing the sorting operation involves overriding the processResponse method of the UrlAdaptor class.
In the code example below, sorting a custom data source can be accomplished by employing the built-in PerformSorting method of the QueryableOperation class. Alternatively, you can implement your own method for sorting operation and bind the resulting data to the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid.
/// <summary>
/// Processes the DataManager request to perform sorting operation.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="DataManagerRequest">Contains the details of the data operation requested.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON object with the sorted data along with the total record count.</returns>
public JsonResult UrlDataSource(DataManagerRequest DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database).
IQueryable<Orders> dataSource = GetOrderData().AsQueryable();
// Initialize QueryableOperation instance.
QueryableOperation queryableOperation = new QueryableOperation();
// Handling sorting operation.
if (DataManagerRequest.Sorted?.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = queryableOperation.PerformSorting(dataSource, DataManagerRequest.Sorted);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method.
}
// Get the total count of records.
int totalRecordsCount = DataSource.Count();
// Return data based on the request.
return Json(new { result = dataSource, count = totalRecordsCount }, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer Name").Width("100").Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("Freight").HeaderText("Freight").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Format("C2").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("Ship City").Width("120").Add();
}).AllowSorting().Render()
<script>
class CustomAdaptor extends ej.data.UrlAdaptor {
processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes) {
var original = super.processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes);
return original;
}
}
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
let grid = document.getElementById("Grid").ej2_instances[0];
if (grid) {
let dataManager = new ejs.data.DataManager({
url: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDataSource", // Replace `xxxx` with your actual port number.
adaptor: new CustomAdaptor(),
});
grid.dataSource = dataManager;
}
});
</script>Handling paging operation
When utilizing the CustomAdaptor in ASP.NET MVC, managing the paging operation involves overriding the processResponse method of the UrlAdaptor class.
In the code example below, paging a custom data source can be achieved by utilizing the built-in PerformTake and PerformSkip method of the QueryableOperation class. Alternatively, you can use your own method for paging operation and bind the resulting data to the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid.
/// <summary>
/// Processes the DataManager request to perform paging operation.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="DataManagerRequest">Contains the details of the data operation requested.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON object with the paginated data along with the total record count.</returns>
public JsonResult UrlDataSource(DataManagerRequest DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database).
IQueryable<Orders> dataSource = GetOrderData().AsQueryable();
// Initialize QueryableOperation instance.
QueryableOperation queryableOperation = new QueryableOperation();
// Get the total count of records.
int totalRecordsCount = dataSource.Count();
// Handling paging operation.
if (DataManagerRequest.Skip > 0)
{
dataSource = queryableOperation.PerformSkip(dataSource, DataManagerRequest.Skip);
}
if (DataManagerRequest.Take > 0)
{
dataSource = queryableOperation.PerformTake(dataSource, DataManagerRequest.Take);
}
// Return data based on the request.
return Json(new { result = dataSource, count = totalRecordsCount }, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer Name").Width("100").Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Add();
col.Field("Freight").HeaderText("Freight").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Format("C2").Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("Ship City").Width("120").Add();
}).AllowPaging().Render()
<script>
class CustomAdaptor extends ej.data.UrlAdaptor {
processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes) {
var original = super.processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes);
return original;
}
}
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
let grid = document.getElementById("Grid").ej2_instances[0];
if (grid) {
let dataManager = new ejs.data.DataManager({
url: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDataSource", // Replace `xxxx` with your actual port number.
adaptor: new CustomAdaptor(),
});
grid.dataSource = dataManager;
}
});
</script>Handling CRUD operations
To enable editing in the Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid, utilize the GridEditSettings property. The Grid offers multiple edit modes including the Inline/Normal, Dialog and Batch editing. For more details, refer to the Grid editing documentation.
In this scenario, the inline edit Mode and Toolbar property configured to display toolbar items for editing purpose.
// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).IsPrimaryKey(true).IsIdentity(true).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer Name").Width("100").ValidationRules(new { required = "true" }).Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).ValidationRules(new { required = "true", number = true}).Add();
col.Field("Freight").HeaderText("Freight").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Format("C2").ValidationRules(new { required = "true", min=1, max=1000 }).Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("Ship City").Width("120").ValidationRules(new { required = "true" }).Add();
}).EditSettings(edit => { edit.AllowAdding(true).AllowEditing(true).AllowDeleting(true).Mode(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.EditMode.Normal); }).Toolbar(new List<string>() { "Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Update", "Cancel" }).Render()
<script>
class CustomAdaptor extends ej.data.UrlAdaptor {
processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes) {
var original = super.processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes);
return original;
}
}
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
let grid = document.getElementById("Grid").ej2_instances[0];
if (grid) {
let dataManager = new ejs.data.DataManager({
url: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDataSource", // Replace `xxxx` with your actual port number.
adaptor: new CustomAdaptor(),
insertUrl: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Insert",
updateUrl: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Update",
removeUrl: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Remove",
// Enable batch URL when batch editing is enabled.
//batchUrl: 'https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/BatchUpdate',
});
grid.dataSource = dataManager;
}
});
</script>
- Normal/Inline editing is the default edit
Modefor the Grid. To enable CRUD operations, ensure that the IsPrimaryKey property is set to true for a specific Grid column, ensuring that its value is unique.- If database has an auto generated column, ensure to define IsIdentity property of Grid column to disable them during adding or editing operations.
The CRUD operations can be performed and customized on our own by overriding the following CRUD methods of the UrlAdaptor
- insert
- remove
- update
- batchRequest
Let’s see how to perform CRUD operation using Microsoft SQL Server data with Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid.
Insert operation:
To execute the insert operation, you will need to override the insert method of the CustomAdaptor. Then, integrate the following code snippet into the CustomAdaptor class. The below code snippet demonstrated how to handle the insertion of new records within the insert method of CustomAdaptor. Modify the logic within this method according to the requirements of your application.
/// <summary>
/// Inserts a new data item into the data collection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="model">It contains the new record detail which is need to be inserted.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON result indicating success.</returns>
public JsonResult Insert(CRUDModel<Orders> model)
{
using (SqlCommand sqlConnection = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
// Define the SQL query to insert a new order record using parameters.
string query = "INSERT INTO Orders (CustomerID, Freight, ShipCity, EmployeeID) VALUES (@CustomerID, @Freight, @ShipCity, @EmployeeID)";
using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(query, sqlConnection))
{
// Add parameters to prevent SQL injection and handle null values.
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@CustomerID", model.value.CustomerID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Freight", model.value.Freight ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@ShipCity", model.value.ShipCity ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@EmployeeID", model.value.EmployeeID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
// Open the database connection and execute the command.
sqlConnection.Open();
sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
// Return a JSON response indicating success.
return Json(new { success = true });
}
public class CRUDModel<T> where T : class
{
public string? action { get; set; }
public string? keyColumn { get; set; }
public object? key { get; set; }
public T? value { get; set; }
public List<T>? added { get; set; }
public List<T>? changed { get; set; }
public List<T>? deleted { get; set; }
public IDictionary<string, object>? @params { get; set; }
}<script>
class CustomAdaptor extends ej.data.UrlAdaptor {
processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes) {
var original = super.processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes);
return original;
}
insert(dm, data) {
return {
url: dm.dataSource.insertUrl || dm.dataSource.url,
data: JSON.stringify({
__RequestVerificationToken: "Syncfusion",
value: data,
action: 'insert'
}),
type: 'POST'
};
}
}
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
let grid = document.getElementById("Grid").ej2_instances[0];
if (grid) {
let dataManager = new ejs.data.DataManager({
url: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDataSource",
adaptor: new CustomAdaptor(),
insertUrl: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Insert",
updateUrl: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Update",
removeUrl: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Remove",
});
grid.dataSource = dataManager;
}
});
</script>Update operation:
To execute the update operation, override the update method of the CustomAdaptor. Then, integrate the following code snippet into the CustomAdaptor class. The below code snippet demonstrated how to handle the updating of existing records within the update method of the CustomAdaptor. Modify the logic within this method according to the requirements of your application.
/// <summary>
/// Update a existing data item from the data collection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value">It contains the updated record detail which is need to be updated.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON result indicating success.</returns>
public JsonResult Update(CRUDModel<Orders> model)
{
using (SqlCommand sqlConnection = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
// Define the SQL query to update the order details based on OrderID.
string query = "UPDATE Orders SET CustomerID=@CustomerID, Freight=@Freight, EmployeeID=@EmployeeID, ShipCity=@ShipCity WHERE OrderID=@OrderID";
using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(query, sqlConnection))
{
// Add parameters to ensure data integrity and prevent SQL injection.
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@CustomerID", model.value.CustomerID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Freight", model.value.Freight ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@ShipCity", model.value.ShipCity ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@EmployeeID", model.value.EmployeeID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@OrderID", model.value.OrderID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
// Open the database connection and execute the update command.
sqlConnection.Open();
sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
// Return a JSON response indicating success.
return Json(new { success = true });
}
public class CRUDModel<T> where T : class
{
public string? action { get; set; }
public string? keyColumn { get; set; }
public object? key { get; set; }
public T? value { get; set; }
public List<T>? added { get; set; }
public List<T>? changed { get; set; }
public List<T>? deleted { get; set; }
public IDictionary<string, object>? @params { get; set; }
}<script>
class CustomAdaptor extends ej.data.UrlAdaptor {
processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes) {
var original = super.processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes);
return original;
}
update(dm, keyField, value) {
return {
url: dm.dataSource.updateUrl || dm.dataSource.url,
data: JSON.stringify({
__RequestVerificationToken: "Syncfusion",
value: value,
action: 'update',
}),
type: 'POST',
};
}
}
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
let grid = document.getElementById("Grid").ej2_instances[0];
if (grid) {
let dataManager = new ejs.data.DataManager({
url: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDataSource",
adaptor: new CustomAdaptor(),
insertUrl: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Insert",
updateUrl: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Update",
removeUrl: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Remove",
});
grid.dataSource = dataManager;
}
});
</script>Delete operation
To perform the delete operation, you need to override the remove method of the CustomAdaptor. Below is the code snippet that you can add to CustomAdaptor class. The below code snippet demonstrated how to handle the deletion of existing records within the remove method of CustomAdaptor. Modify the logic within this method according to the requirements of your application.
/// <summary>
/// Remove a specific data item from the data collection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="model">It contains the specific record detail which is need to be removed.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON result indicating success.</returns>
public JsonResult Remove(CRUDModel<Orders> model)
{
using (SqlCommand sqlConnection = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
// Define the SQL query to delete the order based on OrderID.
string query = "DELETE FROM Orders WHERE OrderID=@OrderID";
using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(query, sqlConnection))
{
// Add parameter to ensure data integrity and prevent SQL injection.
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@OrderID", model.key ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
// Open the database connection and execute the delete command.
sqlConnection.Open();
sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
// Return a JSON response indicating success.
return Json(new { success = true });
}
public class CRUDModel<T> where T : class
{
public string? action { get; set; }
public string? keyColumn { get; set; }
public object? key { get; set; }
public T? value { get; set; }
public List<T>? added { get; set; }
public List<T>? changed { get; set; }
public List<T>? deleted { get; set; }
public IDictionary<string, object>? @params { get; set; }
}<script>
class CustomAdaptor extends ej.data.UrlAdaptor {
processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes) {
var original = super.processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes);
return original;
}
remove(dm, keyField, value) {
return {
url: dm.dataSource.removeUrl || dm.dataSource.url,
data: JSON.stringify({
__RequestVerificationToken: "Syncfusion",
key: value,
keyColumn: keyField,
action: 'remove',
}),
type: 'POST',
};
}
}
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
let grid = document.getElementById("Grid").ej2_instances[0];
if (grid) {
let dataManager = new ejs.data.DataManager({
url: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDataSource",
adaptor: new CustomAdaptor(),
insertUrl: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Insert",
updateUrl: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Update",
removeUrl: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/Remove",
});
grid.dataSource = dataManager;
}
});
</script>Batch operation
To perform the batch operation, override the batchRequest method of the CustomAdaptor and add the following code in the CustomAdaptor. The below code snippet demonstrated how to handle the batch update request within the batchRequest method of CustomAdaptor. Modify the logic within this method according to the requirements of your application.
/// <summary>
/// Batch update (Insert, Update, and Delete) a collection of data items from the data collection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value">The set of information along with details about the CRUD actions to be executed from the database.</param>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON response with success or error message.</returns>
public JsonResult BatchUpdate(CRUDModel<Orders> value)
{
// Establish SQL connection.
using (SqlCommand sqlConnection = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
sqlConnection.Open();
// Begin a database transaction to ensure atomicity.
using (SqlTransaction transaction = sqlConnection.BeginTransaction())
{
// Process updated records.
if (value.changed != null && value.changed.Count > 0)
{
// SQL query for updating records in the database.
string updateQuery = "UPDATE Orders SET CustomerID=@CustomerID, Freight=@Freight, EmployeeID=@EmployeeID, ShipCity=@ShipCity WHERE OrderID=@OrderID.";
foreach (Orders record in value.changed)
{
using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(updateQuery, sqlConnection, transaction))
{
// Add parameters to avoid SQL injection.
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@CustomerID", record.CustomerID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Freight", record.Freight ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@EmployeeID", record.EmployeeID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@ShipCity", record.ShipCity ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@OrderID", record.OrderID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
// Execute the update query.
sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
// Process newly inserted records.
if (value.added != null && value.added.Count > 0)
{
// SQL query for inserting new records into the database.
string insertQuery = "INSERT INTO Orders (CustomerID, Freight, ShipCity, EmployeeID) VALUES (@CustomerID, @Freight, @ShipCity, @EmployeeID).";
foreach (Orders record in value.added)
{
using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(insertQuery, sqlConnection, transaction))
{
// Add parameters to avoid SQL injection.
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@CustomerID", record.CustomerID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Freight", record.Freight ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@ShipCity", record.ShipCity ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@EmployeeID", record.EmployeeID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
// Execute the insert query.
sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
// Process deleted records.
if (value.deleted != null && value.deleted.Count > 0)
{
// SQL query for deleting records from the database.
string deleteQuery = "DELETE FROM Orders WHERE OrderID=@OrderID.";
foreach (Orders record in value.deleted)
{
using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(deleteQuery, sqlConnection, transaction))
{
// Add parameter to avoid SQL injection.
sqlCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@OrderID", record.OrderID ?? (object)DBNull.Value);
// Execute the delete query.
sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
}
// Commit the transaction if all operations succeed.
transaction.Commit();
}
}
// Return success response.
return Json(new { success = true });
}
public class CRUDModel<T> where T : class
{
public string? action { get; set; }
public string? keyColumn { get; set; }
public object? key { get; set; }
public T? value { get; set; }
public List<T>? added { get; set; }
public List<T>? changed { get; set; }
public List<T>? deleted { get; set; }
public IDictionary<string, object>? @params { get; set; }
}// Replace `xxxx` with your actual localhost port number.
@Html.EJS().Grid("Grid").Columns(col =>
{
col.Field("OrderID").HeaderText("Order ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).IsPrimaryKey(true).IsIdentity(true).Add();
col.Field("CustomerID").HeaderText("Customer Name").Width("100").ValidationRules(new { required = "true" }).Add();
col.Field("EmployeeID").HeaderText("Employee ID").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).ValidationRules(new { required = "true", number = true}).Add();
col.Field("Freight").HeaderText("Freight").Width("100").TextAlign(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.TextAlign.Right).Format("C2").ValidationRules(new { required = "true", min=1, max=1000 }).Add();
col.Field("ShipCity").HeaderText("Ship City").Width("120").ValidationRules(new { required = "true" }).Add();
}).AllowPaging().EditSettings(edit => { edit.AllowAdding(true).AllowEditing(true).AllowDeleting(true).Mode(Syncfusion.EJ2.Grids.EditMode.Batch); }).Toolbar(new List<string>() { "Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Update", "Cancel" }).Render()
<script>
class CustomAdaptor extends ej.data.UrlAdaptor {
processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes) {
var original = super.processResponse(data, ds, query, xhr, request, changes);
return original;
}
batchRequest(dm, changes, e) {
return {
url: dm.dataSource.batchUrl || dm.dataSource.url,
data: JSON.stringify({
__RequestVerificationToken: "Syncfusion",
added: changes.addedRecords,
changed: changes.changedRecords,
deleted: changes.deletedRecords,
key: e.key,
action: 'batch',
}),
type: 'POST',
};
}
}
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
let grid = document.getElementById("Grid").ej2_instances[0];
if (grid) {
let dataManager = new ejs.data.DataManager({
url: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/UrlDataSource",
adaptor: new CustomAdaptor(),
batchUrl: "https://localhost:xxxx/Grid/BatchUpdate",
});
grid.dataSource = dataManager;
}
});
</script>When you run the application, the resultant Syncfusion ASP.NET MVC Grid will look like this