How can I help you?
Bind data to the Syncfusion® Controls using WebApiAdaptor
4 Dec 202417 minutes to read
In this topic, you can learn how to retrieve data from WebApi Controller, bind to Grid control using WebApiAdaptor of DataManger, and perform CRUD operations.
You can use the WebApiAdaptor of DataManager to interact with Web APIs created with OData endpoint. The WebApiAdaptor is extended from the ODataAdaptor. Hence, to use WebApiAdaptor, the endpoint should understand the OData formatted queries sent along with the request.
To enable the OData query option for Web API, refer to this documentation.
Prerequisite software
The following software are needed
- Visual Studio 2022 v17.0 or later.
- .NET SDK 6.0 or later.
Create the database
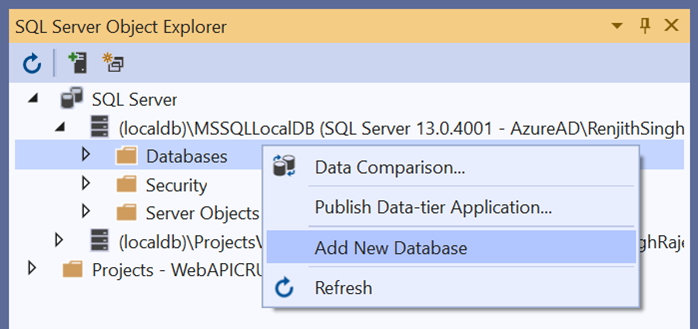
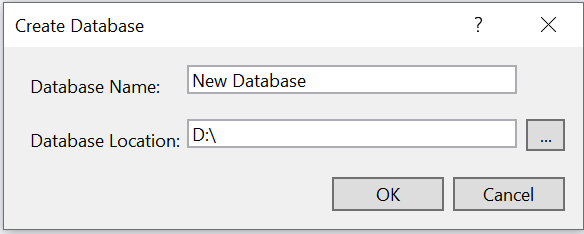
Open Visual Studio, select View -> SQL Server Object Explorer. Right-click on the Databases folder to create a new Database and name it as OrdersDetails.
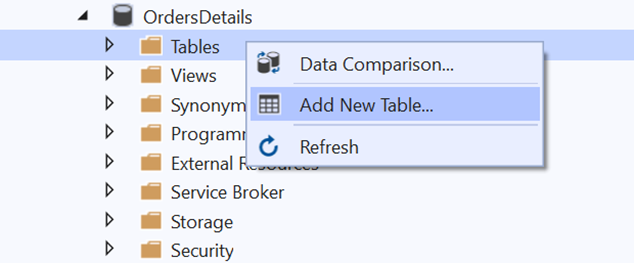
Right-click on the Tables folder of the created database and click Add New Table.
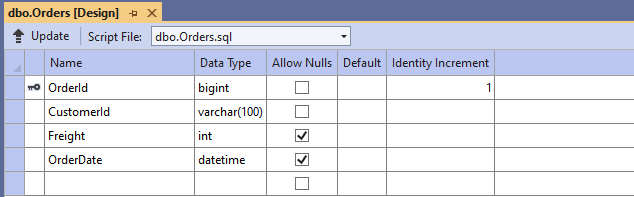
Use the following query to add a new table named Orders.
Create Table Orders(
OrderId BigInt Identity(1,1) Primary Key Not Null,
CustomerId Varchar(100) Not Null,
Freight int Null,
OrderDate datetime null
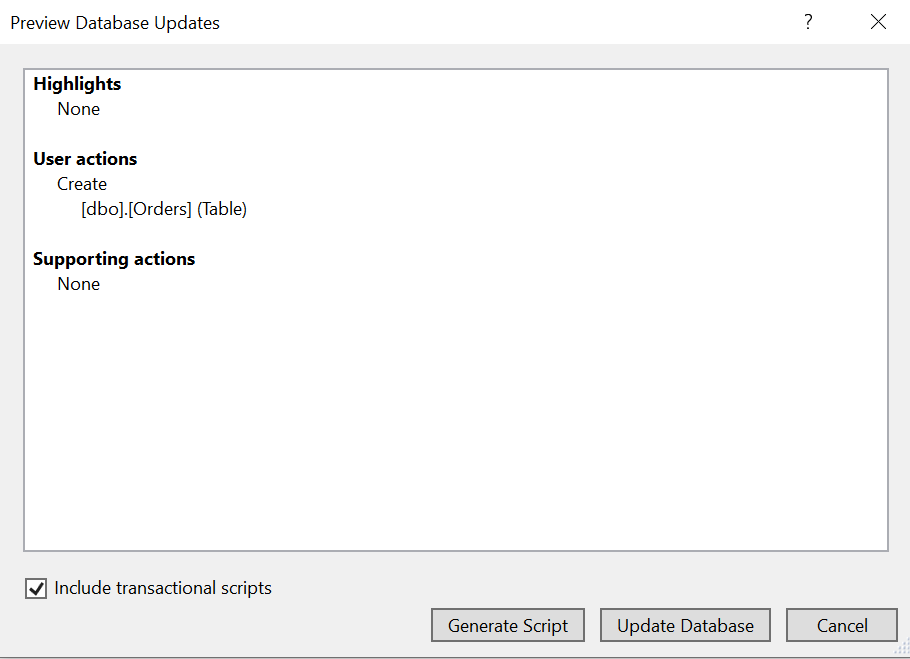
)Now, the Orders table design will look like below. Click on the Update button.
Now, click on Update Database.
Create ASP.NET Core Application
Open Visual Studio and follow the steps in the below documentation to create the Application.
Generate DbContext and model class from the database
Now, DbContext and model classes are going to be scaffolded from the existing OrdersDetails database. To perform scaffolding and work with the SQL Server database in the application, you need to install the following NuGet packages.
Run the following commands in the Package Manager Console.
- Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools -Version 6.0.2: This package creates database context and model classes from the database.
- Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -Version 6.0.2: The database provider allows Entity Framework Core to work with SQL Server.
Once the above packages are installed, you can scaffold DbContext and Model classes. Run the following command in the Package Manager Console.
Scaffold-DbContext “Data Source=(localdb)\MSSQLLocalDB;Initial Catalog=OrdersDetails;Integrated Security=True;Connect Timeout=30;Encrypt=False;TrustServerCertificate=False;ApplicationIntent=ReadWrite;MultiSubnetFailover=False” Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -OutputDir ModelsThe above scaffolding command contains the following details for creating DbContext and model classes for the existing database and its tables.
- Connection string: Data Source=(localdb)\MSSQLLocalDB;Initial Catalog=OrdersDetails;Integrated Security=True;Connect Timeout=30;Encrypt=False;TrustServerCertificate=False;ApplicationIntent=ReadWrite;MultiSubnetFailover=False
- Data provider: Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
- Output directory: -OutputDir Models
After running the above command, OrdersDetailsContext.cs and Order.cs files will be created under the WEBAPICRUD.Models folder as follows.
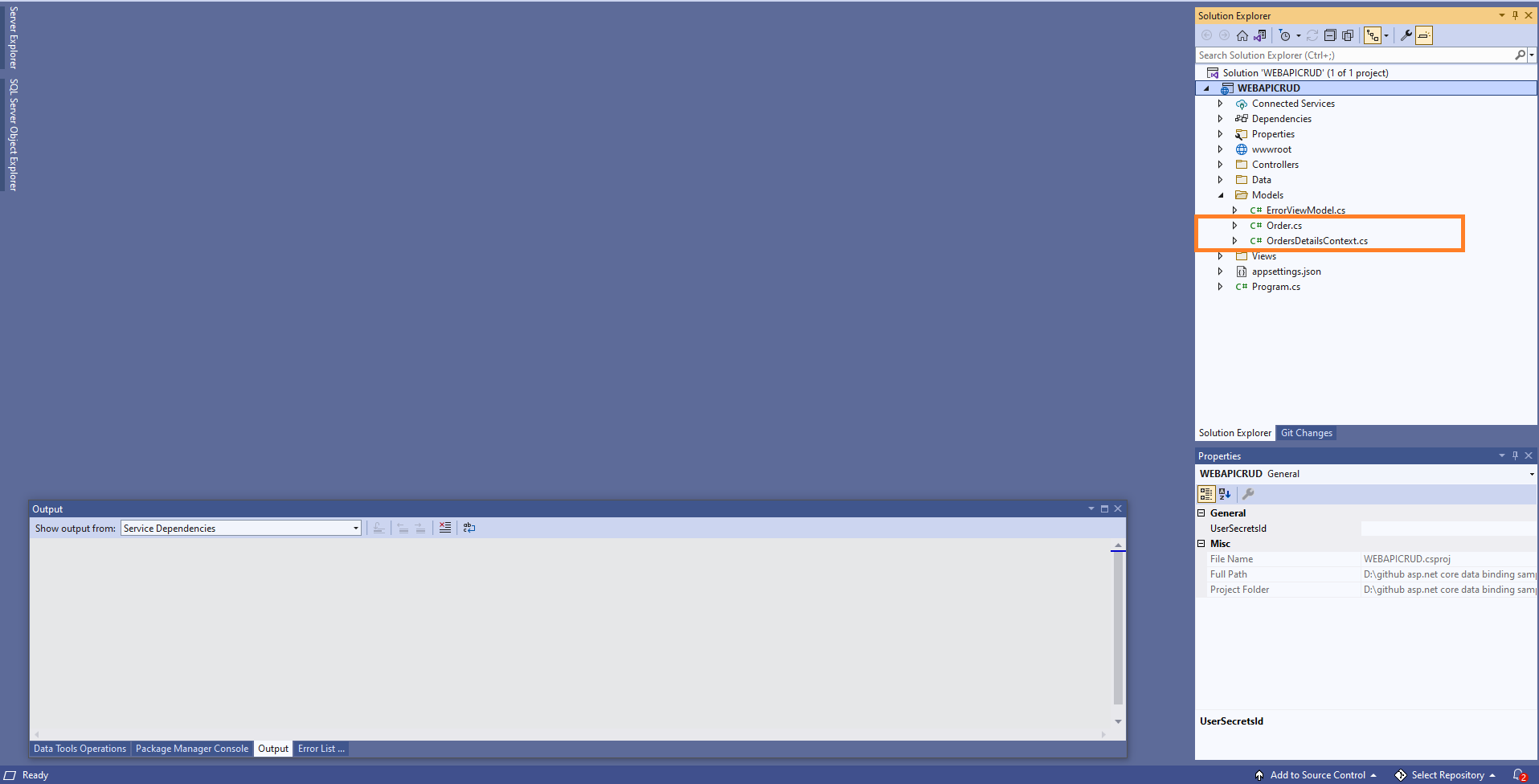
OrdersDetailsContext.cs file contains the connection string details in the OnConfiguring method.
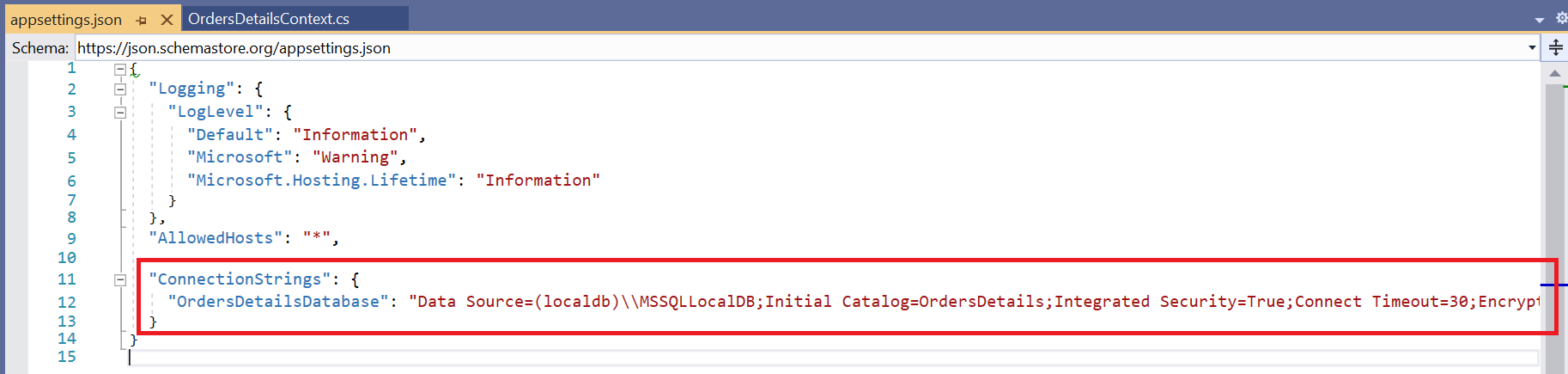
It is not recommended to have a connection string with sensitive information in the OrdersDetailsContext.cs file, so the connection string is moved to the appsettings.json file.
Now, the DbContext must be configured using connection string and registered as scoped service using the AddDbContext method in Program.cs.
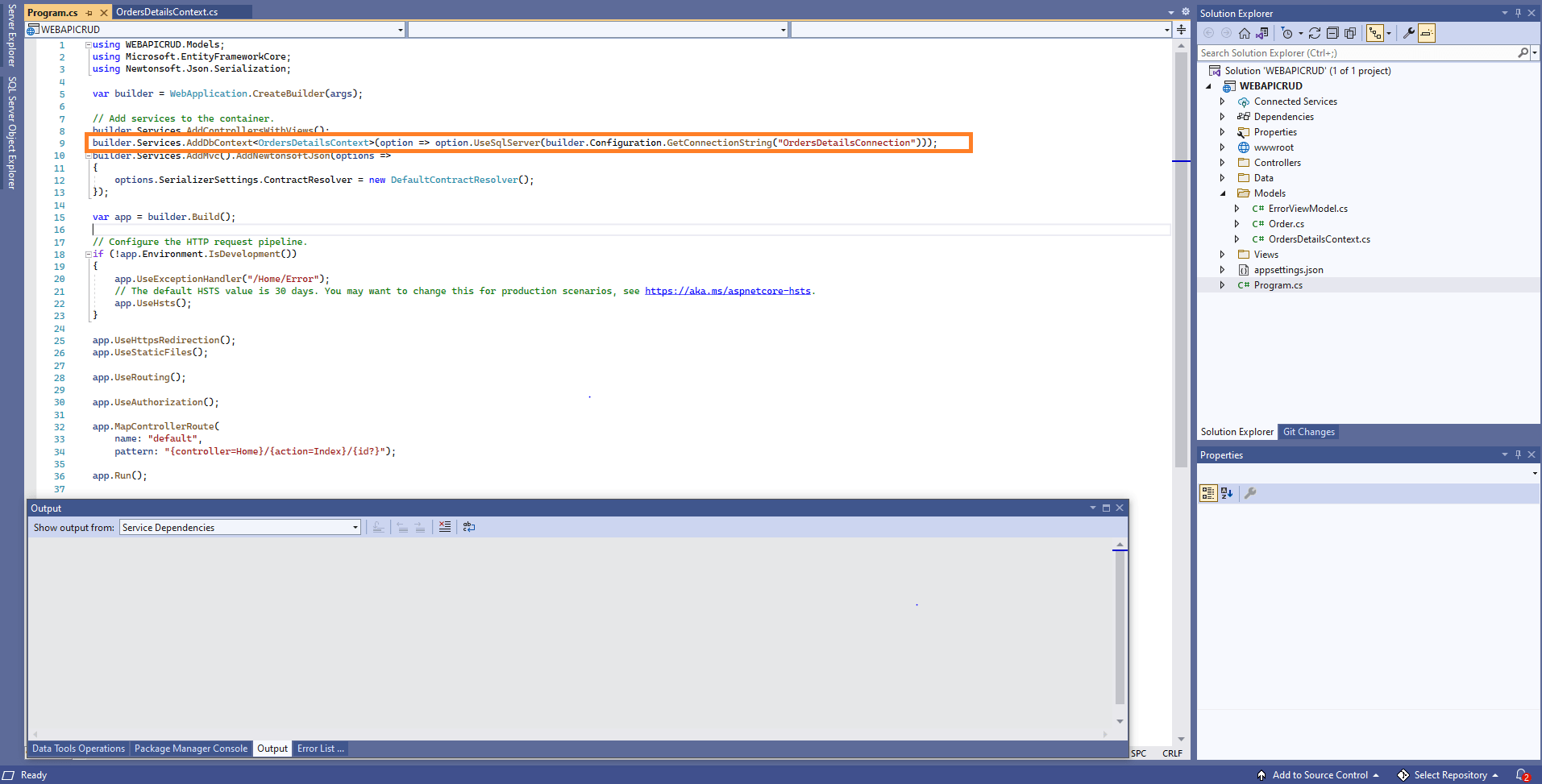
Creating API Controller
The application is now configured to connect with the OrdersDetails database using Entity Framework. Now, it’s time to consume data from the OrdersDetails database. To do so, a Web API controller is required to serve data from the DbContext to the ASP.NET Core application.
To create a Web API controller, right-click the Controller folder in the Server project and select Add -> New Item -> API controller with read/write actions to create a new Web API controller. This controller is named as OrdersController as it returns Orders table records.
Now, replace the Web API controller with the following code which contains code to handle CRUD operations in the Orders table.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using WEBAPICRUD.Models;
// For more information on enabling Web API for empty projects, visit https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=397860
namespace WEBAPICRUD.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class OrdersController : ControllerBase
{
private OrdersDetailsContext _context;
public OrdersController(OrdersDetailsContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
// GET: api/<OrdersController>
[HttpGet]
public object Get()
{
return new { Items = _context.Orders.ToList(), Count = _context.Orders.Count() };
}
// GET api/<OrdersController>/5
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public string Get(int id)
{
return "value";
}
// POST api/<OrdersController>
[HttpPost]
public void Post([FromBody] Order book)
{
_context.Orders.Add(book);
_context.SaveChanges();
}
// PUT api/<OrdersController>
[HttpPut]
public void Put(long id, [FromBody] Order book)
{
Order _book = _context.Orders.Where(x => x.OrderId.Equals(book.OrderId)).FirstOrDefault();
_book.CustomerId = book.CustomerId;
_book.Freight = book.Freight;
_book.OrderDate = book.OrderDate;
_context.SaveChanges();
}
// DELETE api/<OrdersController>/5
[HttpDelete("{id}")]
public void Delete(int id)
{
Order _book = _context.Orders.Where(x => x.OrderId.Equals(id)).FirstOrDefault();
_context.Orders.Remove(_book);
_context.SaveChanges();
}
}
}Install ASP.NET Core package in the application
Syncfusion® ASP.NET Core controls are available in nuget.org. Refer to NuGet packages topic to learn more about installing NuGet packages in various OS environments. To add ASP.NET Core controls in the application, open the NuGet package manager in Visual Studio (Tools → NuGet Package Manager → Manage NuGet Packages for Solution), search for Syncfusion.EJ2.AspNet.Core and then install it.
NOTE
The Syncfusion.EJ2.AspNet.Core NuGet package has dependencies, Newtonsoft.Json for JSON serialization and Syncfusion.Licensing for validating Syncfusion® license key.
Add Syncfusion® ASP.NET Core Tag Helper
Open ~/Views/_ViewImports.cshtml file and import the Syncfusion.EJ2 TagHelper.
@addTagHelper *, Syncfusion.EJ2Add Style Sheet
Checkout the Themes topic to learn different ways (CDN, NPM package, and CRG) to refer styles in ASP.NET Core application, and to have the expected appearance for Syncfusion® ASP.NET Core controls. Here, the theme is referred using CDN inside the <head> of ~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file as follows,
<head>
...
<!-- Syncfusion ASP.NET Core controls styles -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/material.css" />
</head>Add Script Reference
In this getting started walk-through, the required scripts are referred using CDN inside the <head> of ~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml file as follows,
<head>
...
<!-- Syncfusion ASP.NET Core controls scripts -->
<script src="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/dist/ej2.min.js"></script>
</head>Register Syncfusion® Script Manager
Open ~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml page and register the script manager
<body>
...
<!-- Syncfusion Script Manager -->
<ejs-scripts></ejs-scripts>
</body>Add Syncfusion® Grid control to an application
In previous steps, the Syncfusion® ASP.NET Core package is successfully configured in the application. Now, add the grid control to your Index.cshtml view page which is present under Views/Home folder.
<ejs-grid id="Grid"></ejs-grid>Binding data to Grid control using WebApiAdaptor
To consume data from the WebApi Controller, add the DataManager with WebApiAdaptor.
<ejs-grid id="Grid">
<e-data-manager url="/api/Orders" adaptor="WebApiAdaptor" crossdomain="true"></e-data-manager>
</ejs-grid>Grid columns can be defined by using the GridColumn component.
<ejs-grid id="Grid">
<e-data-manager url="/api/Orders" adaptor="WebApiAdaptor" crossdomain="true"></e-data-manager>
<e-grid-editSettings allowDeleting="true" allowEditing="true" allowAdding="true"></e-grid-editSettings>
<e-grid-columns>
<e-grid-column field="OrderId" headerText="Order ID" type="number" textAlign="Right" width="120" isPrimaryKey="true"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="CustomerId" headerText="Customer ID" type="string" width="140"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="Freight" headerText="Freight" textAlign="Right" format="C2" width="120"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="OrderDate" headerText="Order Date" format='yMd' textAlign="Right" width="140"></e-grid-column>
</e-grid-columns>
</ejs-grid>When you run the application, the Get() method will be called in your API controller.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using WEBAPICRUD.Models;
namespace WEBAPICRUD
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class OrdersController : ControllerBase
{
private OrdersDetailsContext _context;
public OrdersController(OrdersDetailsContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
// GET: api/<OrdersController>
[HttpGet]
public object Get()
{
return new { Items = _context.Orders, Count = _context.Orders.Count() };
}
...
}
}The response object from the Web API should contain the properties, Items and Count, whose values are a collection of entities and the total count of the entities, respectively.
{
"Items": [{..}, {..}, {..}, ...],
"Count": 830
}Handling CRUD operations with Syncfusion® Grid control
The grid control can enable editing by using the GridEditSettings component. Grid provides various modes of editing options such as Inline/Normal, Dialog, and Batch editing.
Here, Inline edit mode and Toolbar property are used to show toolbar items for editing.
<ejs-grid id="Grid" toolbar="@(new List<string>() { "Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Cancel", "Update" })">
<e-data-manager url="/api/Orders" adaptor="WebApiAdaptor" crossdomain="true"></e-data-manager>
<e-grid-editSettings allowDeleting="true" allowEditing="true" allowAdding="true" mode="Normal"></e-grid-editSettings>
<e-grid-columns>
<e-grid-column field="OrderId" headerText="Order ID" type="number" textAlign="Right" width="120" isPrimaryKey="true"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="CustomerId" headerText="Customer ID" type="string" width="140"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="Freight" headerText="Freight" textAlign="Right" format="C2" width="120"></e-grid-column>
<e-grid-column field="OrderDate" headerText="Order Date" format='yMd' textAlign="Right" width="140"></e-grid-column>
</e-grid-columns>
</ejs-grid>NOTE
Normal editing is the default edit mode for the Grid control. Set the IsPrimaryKey property of Column as true for a particular column, whose value is a unique value for editing purposes.
Insert a row
To insert a new row, click the Add toolbar button.
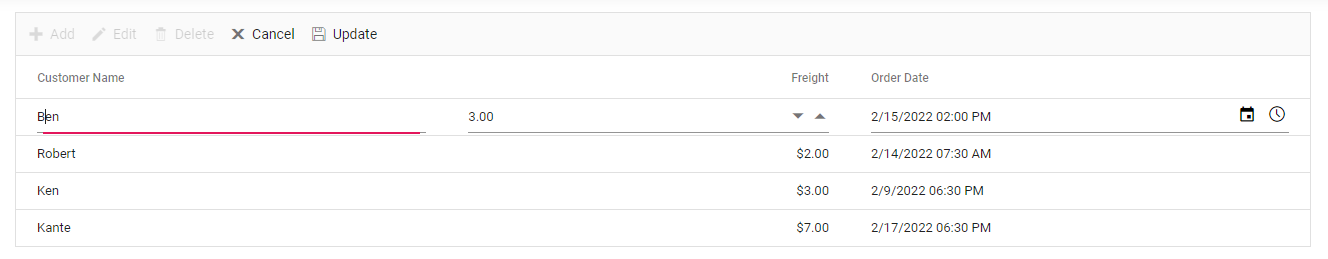
Clicking the Update toolbar button will insert the record in the Orders table by calling the following POST method of the Web API.
[HttpPost]
public void Post([FromBody] Orders book)
{
_context.Orders.Add(book);
_context.SaveChanges();
}
Update a row
To edit a row, select any row and click the Edit toolbar button. The edit form will look like below. Edit the Customer Name column.
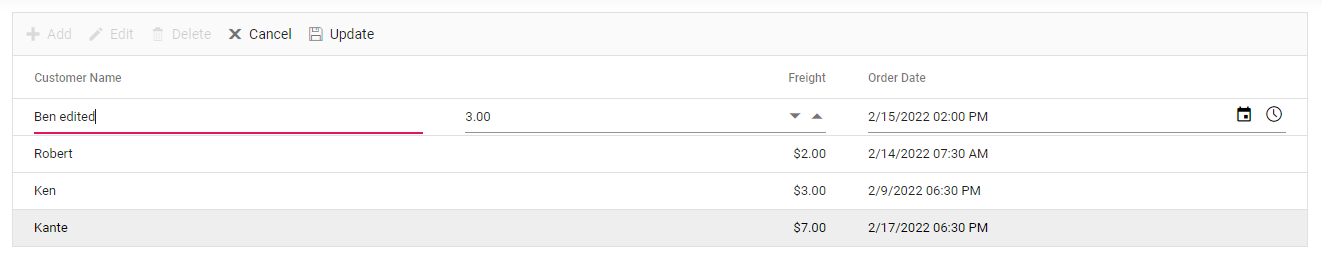
Clicking the Update toolbar button will update the record in the Orders table by calling the following PUT method of the Web API.
// PUT api/<OrdersController>
[HttpPut]
public void Put(long id, [FromBody] Order book)
{
Order _book = _context.Orders.Where(x => x.OrderId.Equals(book.OrderId)).FirstOrDefault();
_book.CustomerId = book.CustomerId;
_book.Freight = book.Freight;
_book.OrderDate = book.OrderDate;
_context.SaveChanges();
}
Delete a row
To delete a row, select any row and click the Delete toolbar button. Deleting operation will send a DELETE request to the Web API with the selected record`s primary key value to remove the corresponding record from the Orders table.
[HttpDelete("{id}")]
public void Delete(long id)
{
Order _book = _context.Orders.Where(x => x.OrderId.Equals(id)).FirstOrDefault();
_context.Orders.Remove(_book);
_context.SaveChanges();
}NOTE