How can I help you?
Getting Started with the Vue Maps Component in Vue 2
10 Feb 202624 minutes to read
This article provides a step-by-step guide for setting up a Vue 2 project using Vue-CLI and integrating the Syncfusion® Vue Maps component. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a working Maps component displaying geographic data with features like legends, tooltips, and data labels.
Note: If you’re using Vue 3, refer to the Vue 3 Getting Started guide.
You can explore the Maps component’s capabilities using the following video:
Prerequisites
System requirements for Syncfusion® Vue UI components
Dependencies
Below is the list of minimum dependencies required to use the Maps.
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-vue-maps
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-base
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-data
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-buttons
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-popups
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-vue-base
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-svg-base
|-- @syncfusion/ej2-mapsSetting up the Vue 2 project
To generate a Vue 2 project using Vue-CLI, use the vue create command. Follow these steps to install Vue CLI and create a new project:
npm install -g @vue/cli
vue create quickstart
cd quickstart
npm run serveor
yarn global add @vue/cli
vue create quickstart
cd quickstart
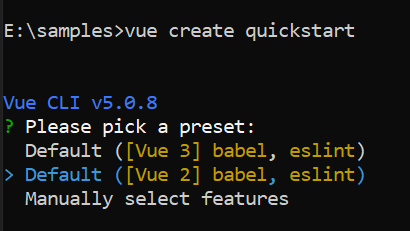
yarn run serveWhen creating a new project, choose the option Default ([Vue 2] babel, eslint) from the menu.
Once the quickstart project is set up with default settings, proceed to add Syncfusion® components to the project.
Add Syncfusion® Vue packages
Syncfusion® packages are available at npmjs.com. To use Vue components, install the required npm package.
This article uses the Vue Maps component as an example. Install the @syncfusion/ej2-vue-maps package by running the following command:
npm install @syncfusion/ej2-vue-maps --saveor
yarn add @syncfusion/ej2-vue-mapsAdding Syncfusion® Vue Maps component
1. Import and register the Maps component in the script section of the src/App.vue file.
<script>
import { MapsComponent, LayerDirective, LayersDirective } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-maps';
import { world_map } from './world-map.js';
export default {
components: {
'ejs-maps' : MapsComponent,
'e-layers' : LayersDirective,
'e-layer' : LayerDirective
},
data () {
return {
shapeData: world_map
}
}
}
</script>2. In the template section, define the Maps component.
<template>
<div class="wrapper">
<ejs-maps id='maps'>
<e-layers>
<e-layer :shapeData='shapeData'></e-layer>
</e-layers>
</ejs-maps>
</div>
</template>Here is the summarized code for the above steps in the src/App.vue file:
<template>
<div id="app">
<div class='wrapper'>
<ejs-maps id='maps'>
<e-layers>
<e-layer :shapeData='shapeData'></e-layer>
</e-layers>
</ejs-maps>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { MapsComponent, LayersDirective, LayerDirective } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-maps';
import { world_map } from './world-map.js';
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-maps":MapsComponent,
"e-layers":LayersDirective,
"e-layer":LayerDirective
},
data () {
return {
shapeData: world_map
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.wrapper {
max-width: 400px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>Run the project
To run the project, use the following command:
npm run serveor
yarn run serveModule Injection
The Vue Maps component uses a modular architecture where features are segregated into individual modules. To use advanced features, you must explicitly inject the corresponding modules using the Vue provide option. This approach optimizes performance by loading only the features you need.
The following modules are available:
- Annotations - Inject this provider to use annotations feature.
- Bubble - Inject this provider to use bubble feature.
- DataLabel - Inject this provider to use data label feature.
- Highlight - Inject this provider to use highlight feature.
- Legend - Inject this provider to use legend feature.
- Marker - Inject this provider to use marker feature.
- MapsTooltip - Inject this provider to use tooltip series.
- NavigationLine - Inject this provider to use navigation lines feature.
- Selection - Inject this provider to use selection feature.
- Zoom - Inject this provider to use zooming and panning feature.
- Polygon - Inject this provider to use polygon feature.
In the current application, we are going to modify the above basic Maps to visualize 2016 USA president election results.
For this application we are going to use tooltip, data label and legend features of the Maps. Now import the MapsTooltip, DataLabel and Legend modules from Maps package and inject it into the Maps component using provide option.
<template>
<div class="wrapper">
<ejs-maps id='maps'></ejs-maps>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { MapsComponent, Legend, DataLabel, MapsTooltip } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-maps';
export default {
components: {
'ejs-maps': MapsComponent
}
data:function(){
return{ };
},
provide: {
maps: [Legend, DataLabel, MapsTooltip]
}
}
</script>
Render shapes from GeoJSON data
This section explains how to bind GeoJSON data to the map.
let usMap: Object =
{
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"crs": { "type": "name", "properties": { "name": "urn:ogc:def:crs:OGC:1.3:CRS84" } },
"features": [
{ "type": "Feature", "properties": { "iso_3166_2": "MA", "name": "Massachusetts", "admin": "United States of America" }, "geometry": { "type": "MultiPolygon", "coordinates": [ [ [ [ -70.801756294617277, 41.248076234530558 ]] ] ] }
}
]
//https://ej2.syncfusion.com/vue/documentation
};Elements in the Maps will get rendered in the layers. So add a layer collection to the Maps by using layers property. Now bind the GeoJSON data to the shapeData property.
<template>
<div id="map">
<div class='wrapper'>
<ejs-maps >
<e-layers>
<e-layer :shapeData='shapeData' ></e-layer>
</e-layers>
</ejs-maps>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { MapsComponent, LayerDirective, LayersDirective } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-maps';
import { world_map } from './world-map.js';
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-maps":MapsComponent,
"e-layers":LayersDirective,
"e-layer":LayerDirective
},
data (){
return{
shapeData: world_map
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.wrapper {
max-width: 400px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>Note: Refer the data values for
world_maphere.
Bind data source to map
Use the following properties in layers to bind external data to map shapes:
-
dataSource- Accepts an array of data objects used for tooltips, data labels, bubbles, legends, and color mapping. -
shapeDataPath- Specifies the property in the dataSource that contains the unique identifier for each data record. -
shapePropertyPath- Specifies the property in the shapeData that contains the identifier to match against shapeDataPath.
The shape matching process works as follows: when a value in the shapeDataPath property matches a value in the shapePropertyPath property, the Maps component binds the corresponding data object to that shape. This enables you to associate custom data with specific geographic shapes.
The following example demonstrates binding UN Security Council membership data to world map shapes:
<template>
<div id="map">
<div class='wrapper'>
<ejs-maps >
<e-layers>
<e-layer :shapeData='shapeData' :shapePropertyPath='shapePropertyPath' :shapeDataPath='shapeDataPath' :dataSource='dataSource' ></e-layer>
</e-layers>
</ejs-maps>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { MapsComponent, LayerDirective, LayersDirective } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-maps';
import { world_map } from './world-map.js';
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-maps":MapsComponent,
"e-layers":LayersDirective,
"e-layer":LayerDirective
},
data (){
return{
shapeData: world_map,
dataSource: [{ "Country": "China", "Membership": "Permanent"},
{"Country": "France","Membership": "Permanent" },
{ "Country": "Russia","Membership": "Permanent"},
{"Country": "Kazakhstan","Membership": "Non-Permanent"},
{ "Country": "Poland","Membership": "Non-Permanent"},
{"Country": "Sweden","Membership": "Non-Permanent"}],
shapePropertyPath: 'name',
shapeDataPath: 'Country'
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.wrapper {
max-width: 400px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>Note: Refer the data values for
world_maphere.
Apply Color Mapping
The Color Mapping feature customizes shape colors based on the data values associated with each shape. Use the colorValuePath property in shapeSettings to specify which data field determines the color assignment.
Specify color and value in colorValuePath property. Here ‘#D84444’ is specified for ‘Permanent’ and ‘#316DB5’ is specified for ‘Non-Permanent’.
<template>
<div id="map">
<div class='wrapper'>
<ejs-maps >
<e-layers>
<e-layer :shapeData='shapeData' :shapePropertyPath='shapePropertyPath' :shapeDataPath='shapeDataPath' :dataSource='dataSource' :shapeSettings='shapeSettings' ></e-layer>
</e-layers>
</ejs-maps>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { MapsComponent, LayerDirective, LayersDirective } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-maps';
import { world_map } from './world-map.js';
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-maps":MapsComponent,
"e-layers":LayersDirective,
"e-layer":LayerDirective
},
data (){
return{
shapeData: world_map,
dataSource: [{ "Country": "China", "Membership": "Permanent"},
{"Country": "France","Membership": "Permanent" },
{ "Country": "Russia","Membership": "Permanent"},
{"Country": "Kazakhstan","Membership": "Non-Permanent"},
{ "Country": "Poland","Membership": "Non-Permanent"},
{"Country": "Sweden","Membership": "Non-Permanent"}],
shapePropertyPath: 'name',
shapeDataPath: 'Country',
shapeSettings: {
colorValuePath: 'Membership',
colorMapping: [
{
value: 'Permanent', color: '#D84444'
},
{
value: 'Non-Permanent', color: '#316DB5'
}]
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.wrapper {
max-width: 400px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>Add Title for Maps
Add a title to your map using the titleSettings property to provide context about the data or geographic region displayed.
<template>
<div id="map">
<div class='wrapper'>
<ejs-maps :titleSettings='titleSettings' >
<e-layers>
<e-layer :shapeData='shapeData' :shapePropertyPath='shapePropertyPath' :shapeDataPath='shapeDataPath' :dataSource='dataSource' :shapeSettings='shapeSettings' ></e-layer>
</e-layers>
</ejs-maps>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { MapsComponent, LayerDirective, LayersDirective } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-maps';
import { world_map } from './world-map.js';
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-maps":MapsComponent,
"e-layers":LayersDirective,
"e-layer":LayerDirective
},
data (){
return{
titleSettings: {
text: 'UN security council countries'
},
shapeData: world_map,
dataSource: [{ "Country": "China", "Membership": "Permanent"},
{"Country": "France","Membership": "Permanent" },
{ "Country": "Russia","Membership": "Permanent"},
{"Country": "Kazakhstan","Membership": "Non-Permanent"},
{ "Country": "Poland","Membership": "Non-Permanent"},
{"Country": "Sweden","Membership": "Non-Permanent"}],
shapePropertyPath: 'name',
shapeDataPath: 'Country',
shapeSettings: {
colorValuePath: 'Membership',
colorMapping: [
{
value: 'Permanent', color: '#D84444'
},
{
value: 'Non-Permanent', color: '#316DB5'
}]
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.wrapper {
max-width: 400px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>Enable Legend
Display a legend to help users interpret shape colors and categories. Set the visible property to true in legendSettings, and inject the Legend module using the provide option.
<template>
<div id="map">
<div class='wrapper'>
<ejs-maps :legendSettings='legendSettings' >
<e-layers>
<e-layer :shapeData='shapeData' :shapePropertyPath='shapePropertyPath' :shapeDataPath='shapeDataPath' :dataSource='dataSource' :shapeSettings='shapeSettings' ></e-layer>
</e-layers>
</ejs-maps>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { MapsComponent, LayerDirective, LayersDirective, Legend } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-maps';
import { world_map } from './world-map.js';
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-maps":MapsComponent,
"e-layers":LayersDirective,
"e-layer":LayerDirective
},
data () {
return{
shapeData: world_map,
dataSource: [{ "Country": "China", "Membership": "Permanent"},
{"Country": "France","Membership": "Permanent" },
{ "Country": "Russia","Membership": "Permanent"},
{"Country": "Kazakhstan","Membership": "Non-Permanent"},
{ "Country": "Poland","Membership": "Non-Permanent"},
{"Country": "Sweden","Membership": "Non-Permanent"}],
shapePropertyPath: 'name',
shapeDataPath: 'Country',
shapeSettings: {
colorValuePath: 'Membership',
colorMapping: [
{
value: 'Permanent', color: '#D84444'
},
{
value: 'Non-Permanent', color: '#316DB5'
}]
},
legendSettings: {
visible: true
}
}
},
provide: {
maps: [Legend]
}
}
</script>
<style>
.wrapper {
max-width: 400px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>Add Data Label
Display text labels directly on map shapes to show relevant information. Set the visible property to true in the dataLabelSettings object, and inject the DataLabel module using the provide option.
<template>
<div id="app">
<div class='wrapper'>
<ejs-maps :legendSettings='legendSettings' >
<e-layers>
<e-layer :shapeData='shapeData' :shapeSettings='shapeSettings' :dataLabelSettings='dataLabelSettings'></e-layer>
</e-layers>
</ejs-maps>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { MapsComponent, LayerDirective, LayersDirective, Legend, DataLabel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-maps';
import { world_map } from './world-map.js';
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-maps":MapsComponent,
"e-layers":LayersDirective,
"e-layer":LayerDirective
},
data () {
return{
shapeData: world_map,
shapeSettings:{
autofill: true
},
dataLabelSettings: {
visible: true,
labelPath: 'name',
smartLabelMode: 'Trim'
},
legendSettings: {
visible: true
}
}
},
provide: {
maps: [Legend, DataLabel]
}
}
</script>
<style>
.wrapper {
max-width: 400px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>Enable Tooltip
Tooltips provide an alternative way to display information on hover, which is particularly useful when space constraints prevent static data labels. Enable tooltips by setting the visible property to true in the tooltipSettings object, and inject the MapsTooltip module using the provide option.
<template>
<div id="app">
<div class='wrapper'>
<ejs-maps :titleSettings='titleSettings' :legendSettings='legendSettings' >
<e-layers>
<e-layer :shapeData='shapeData' :shapePropertyPath='shapePropertyPath' :shapeDataPath='shapeDataPath' :dataSource='dataSource' :shapeSettings='shapeSettings' :tooltipSettings='tooltipSettings' :dataLabelSettings='dataLabelSettings'></e-layer>
</e-layers>
</ejs-maps>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { MapsComponent, LayerDirective, LayersDirective, Legend, DataLabel, MapsTooltip } from '@syncfusion/ej2-vue-maps';
import { usMap } from './usa.js';
import { electionData } from './election-data.js';
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-maps":MapsComponent,
"e-layers":LayersDirective,
"e-layer":LayerDirective
},
data () {
return{
titleSettings: {
text: 'USA Election Results - 2016'
},
shapeData: usMap,
dataSource: electionData,
shapePropertyPath: 'name',
shapeDataPath: 'State',
shapeSettings: {
colorValuePath: 'Candidate',
colorMapping: [
{
value: 'Trump', color: '#D84444'
},
{
value: 'Clinton', color: '#316DB5'
}]
},
dataLabelSettings: {
visible: true,
labelPath: 'State',
smartLabelMode: 'Trim'
},
tooltipSettings: {
visible: true,
valuePath: 'State'
},
legendSettings: {
visible: true
}
}
},
provide: {
maps: [Legend, DataLabel, MapsTooltip]
}
}
</script>
<style>
.wrapper {
max-width: 400px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>