How can I help you?
Getting Started with the Vue Image Editor Component in Vue 2
10 Feb 20265 minutes to read
This article provides a step-by-step guide for setting up a Vue 2 project using Vue-CLI and integrating the Syncfusion® Vue ImageEditor component.
Prerequisites
System requirements for Syncfusion® Vue UI components
Setup the Vue 2 project
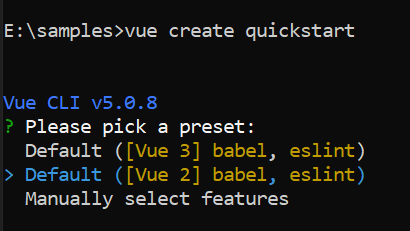
To generate a Vue 2 project using Vue-CLI, use the vue create command. Follow these steps to install Vue CLI and create a new project:
npm install -g @vue/cli
vue create quickstart
cd quickstart
npm run serveor
yarn global add @vue/cli
vue create quickstart
cd quickstart
yarn run serveWhen creating a new project, choose the option Default ([Vue 2] babel, eslint) from the menu.
Once the quickstart project is set up with default settings, proceed to add Syncfusion® components to the project.
Add Syncfusion® Vue packages
Syncfusion® packages are available at npmjs.com. To use Vue components, install the required npm package.
This article uses the Vue ImageEditor component as an example. Install the @syncfusion/ej2-vue-image-editor package by running the following command:
npm install @syncfusion/ej2-vue-image-editor --saveor
yarn add @syncfusion/ej2-vue-image-editorImport Syncfusion® CSS styles
Syncfusion® components require CSS stylesheets to display correctly. You can import themes in various ways, such as using CSS or SASS styles from npm packages, CDN, CRG, and Theme Studio. Refer to themes topic to learn more about built-in themes and different ways to reference themes in a Vue project.
In this article, the Material3 theme is applied using CSS styles, which are available in installed packages. The necessary Material3 CSS styles for the ImageEditor component and its dependents were imported into the <style> section of the src/App.vue file.
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-buttons/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-lists/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-inputs/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-dropdowns/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-image-editor/styles/material.css";
</style>The order of CSS imports matters. Import base styles first, then component-specific styles. Missing CSS imports can result in misaligned layouts, buttons without styling, or missing visual elements in popups and dialogs.
Add Syncfusion® Vue component
Follow the below steps to add the Vue ImageEditor component:
1. First, import and register the ImageEditor component in the script section of the src/App.vue file.
<script setup>
import { ImageEditorComponent as EjsImageeditor } from "@syncfusion/ej2-vue-image-editor";
</script><script setup>
import { ImageEditorComponent } from "@syncfusion/ej2-vue-image-editor";
export default {
components: {
'ejs-imageeditor': ImageEditorComponent
}
}
</script><script>
import { ImageEditorComponent } from "@syncfusion/ej2-vue-image-editor";
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
"ejs-imageeditor':":Imageeditor':Component
},
components: {
'ejs-imageeditor': ImageEditorComponent
}
}
</script>2. In the template section, define the Image Editor component with the height and width property.
<template>
<div>
<ejs-imageeditor id="image-editor" height="350px" width="550px"></ejs-imageeditor>
</div>
</template>Here is the summarized code for the above steps in the src/App.vue file:
<template>
<div>
<ejs-imageeditor id="image-editor" height="350px" width="550px"></ejs-imageeditor>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ImageEditorComponent as EjsImageeditor } from "@syncfusion/ej2-vue-image-editor";
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-buttons/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-lists/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-inputs/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-dropdowns/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-image-editor/styles/material.css";
#image-editor {
width: 550px !important;
height: 350px !important;
}
</style><template>
<div>
<ejs-imageeditor id="image-editor" height="350px" width="550px"></ejs-imageeditor>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ImageEditorComponent } from "@syncfusion/ej2-vue-image-editor";
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
'ejs-imageeditor': ImageEditorComponent
},
data: function() {
return {};
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-buttons/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-lists/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-inputs/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-dropdowns/styles/material.css";
@import "../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-image-editor/styles/material.css";
#image-editor {
width: 550px !important;
height: 350px !important;
}
</style>Run the project
To run the project, use the following command:
npm run serveor
yarn run serve