How can I help you?
Container in EJ2 JavaScript Diagram control
27 Jun 202513 minutes to read
A Container is a group of logically related shapes surrounded by a visible boundary. Shapes can be added or removed from the container at runtime. Changes made to the container do not affect its child elements, which can be individually selected, moved, or edited.
Create Container
Add a Container
The following code illustrates how to create a container node:
// Define a collection of nodes used in the diagram
var nodes = [
// First rectangle node
{
id: 'node1',
// Margin from the left and top
margin: { left: 50, top: 30 },
width: 100, height: 100,
style: { fill: 'white', strokeColor: '#2546BB', strokeWidth: 1 },
shape: { type: 'Basic', shape: 'Rectangle', cornerRadius: 4 },
annotations: [{ content: 'Node 1' }]
},
// Second rectangle node
{
id: 'node2',
// Margin from the left and top
margin: { left: 200, top: 130 },
width: 100, height: 100,
style: { fill: 'white', strokeColor: '#2546BB', strokeWidth: 1 },
shape: { type: 'Basic', shape: 'Rectangle', cornerRadius: 4 },
annotations: [{ content: 'Node 2' }]
},
// Container node configuration to contain node1 and node2
{
id: 'container',
width: 350, height: 280, // Width and height of the container
offsetX: 250, offsetY: 250, // Position of the container
shape: {
// Define the type as a container
type: 'Container',
// Includes node1 and node2 as children
children: ['node1', 'node2'],
},
// Style properties for the container
style: { fill: '#E9EEFF', strokeColor: '#2546BB', strokeWidth: 1 }
},
];
// Initialize the Diagram
var diagram = new ej.diagrams.Diagram({
width: '100%',
height: '500px',
nodes: nodes,
}, '#element');
diagram.select([diagram.getObject('container')]);<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>EJ2 Diagram</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta name="description" content="Typescript UI Controls">
<meta name="author" content="Syncfusion">
<link href="index.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-base/styles/tailwind3.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-buttons/styles/tailwind3.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-popups/styles/tailwind3.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/tailwind3.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-diagrams/styles/tailwind3.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-navigations/styles/tailwind3.css" rel="stylesheet">
<script src="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/dist/ej2.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/syncfusion-helper.js" type ="text/javascript"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="container">
<div id="element"></div>
</div>
<script>
var ele = document.getElementById('container');
if (ele) {
ele.style.visibility = "visible";
}
</script>
<script src="index.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</body>
</html>Setting a Header
You can provide a textual description for a container using its header property. Also, users can customize the header’s appearance using the header’s style property.
The following code example explains how to define a container header and its customization:
var nodes = [
{
id: 'node1',
margin: { left: 50, top: 30 },
width: 100, height: 100,
style: { fill: '#357BD2', strokeColor: 'white' },
annotations: [{ content: 'Node 1', style: { color: 'white', fontFamily: 'Arial' } }],
},
{
id: 'node2',
margin: { left: 200, top: 130 },
width: 100, height: 100,
style: { fill: '#357BD2', strokeColor: 'white' },
annotations: [{ content: 'Node 2', style: { color: 'white', fontFamily: 'Arial' } }],
},
// Container Node
{
id: 'container',
// Container Size
width: 350, height: 300,
// Container Position
offsetX: 250, offsetY: 250,
// Define Shape
shape: {
// Set type as Container
type: 'Container',
// Define header for container
header: {
annotation: {
content: 'Container Title',
// Style of container title text
style: { fontSize: 18, bold: true, color: 'white' },
},
// Height of container header
height: 40,
// Style of container header
style: { fill: '#3c63ac', strokeColor: '#30518f' },
},
// children of container
children: ['node1', 'node2'],
},
// style of container
style: { fill: 'white', strokeColor: '#30518f', strokeDashArray: '4 4' },
},
];
var diagram = new ej.diagrams.Diagram({
width: '100%',
height: '500px',
nodes: nodes,
}, '#element');<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>EJ2 Diagram</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta name="description" content="Typescript UI Controls">
<meta name="author" content="Syncfusion">
<link href="index.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-base/styles/tailwind3.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-buttons/styles/tailwind3.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-popups/styles/tailwind3.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/tailwind3.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-diagrams/styles/tailwind3.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-navigations/styles/tailwind3.css" rel="stylesheet">
<script src="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/dist/ej2.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/syncfusion-helper.js" type ="text/javascript"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="container">
<div id="element"></div>
</div>
<script>
var ele = document.getElementById('container');
if (ele) {
ele.style.visibility = "visible";
}
</script>
<script src="index.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</body>
</html>NOTE
You can edit the header by double-clicking the region of the container’s header.
Container from symbol palette
Container nodes can be preconfigured and added to the symbol palette. Users can drag and drop these container nodes into the diagram as needed.
To learn more, refer to the Symbol Palette documentation.
Interactively add or remove diagram elements into Container
You can interactively add or remove diagram elements from the Container in the runtime. When a diagram element is dropped near the container’s edge, the container automatically resizes to accommodate it.
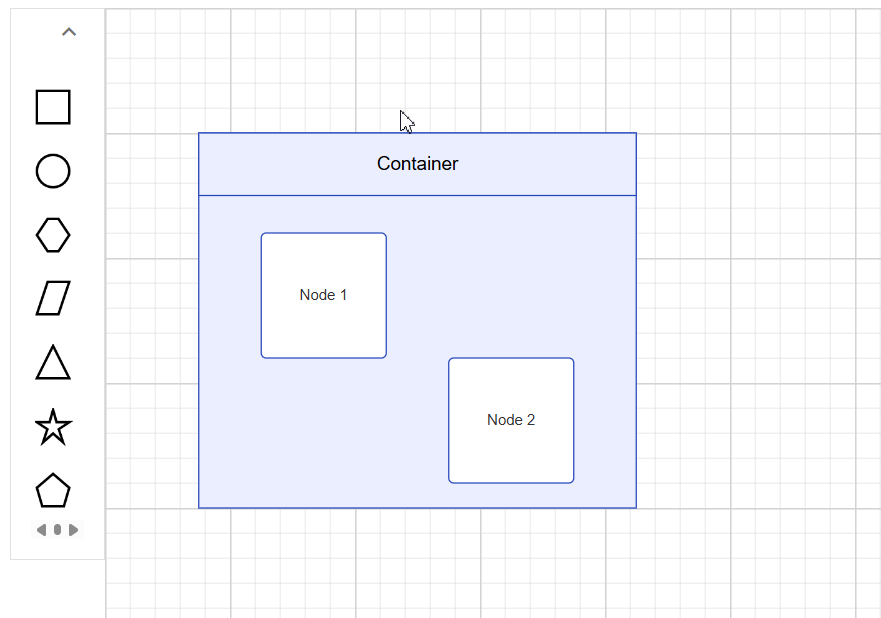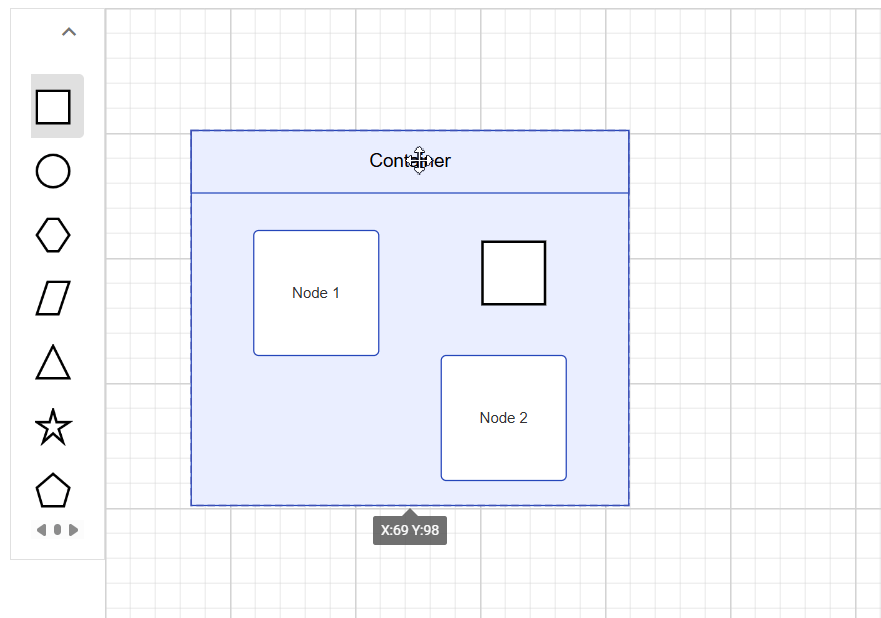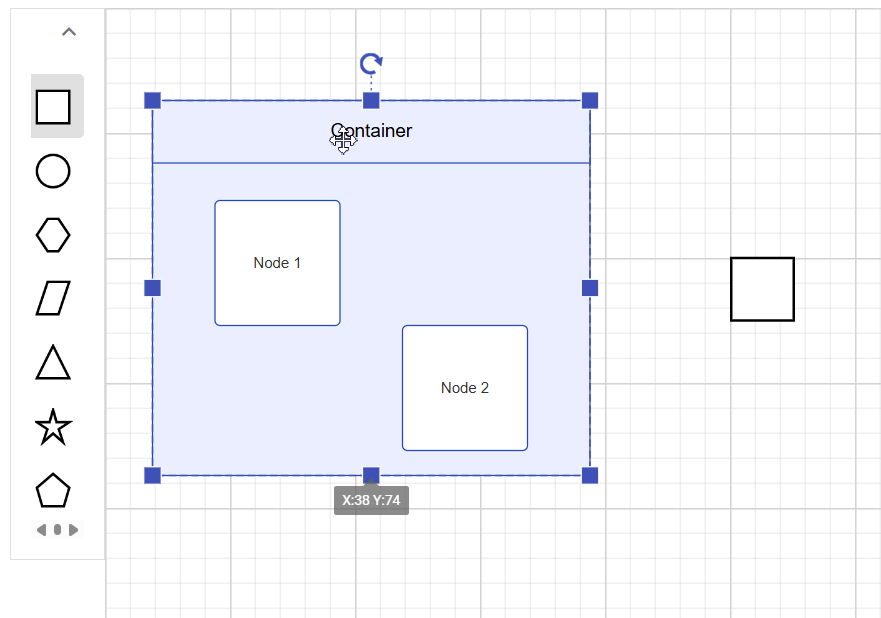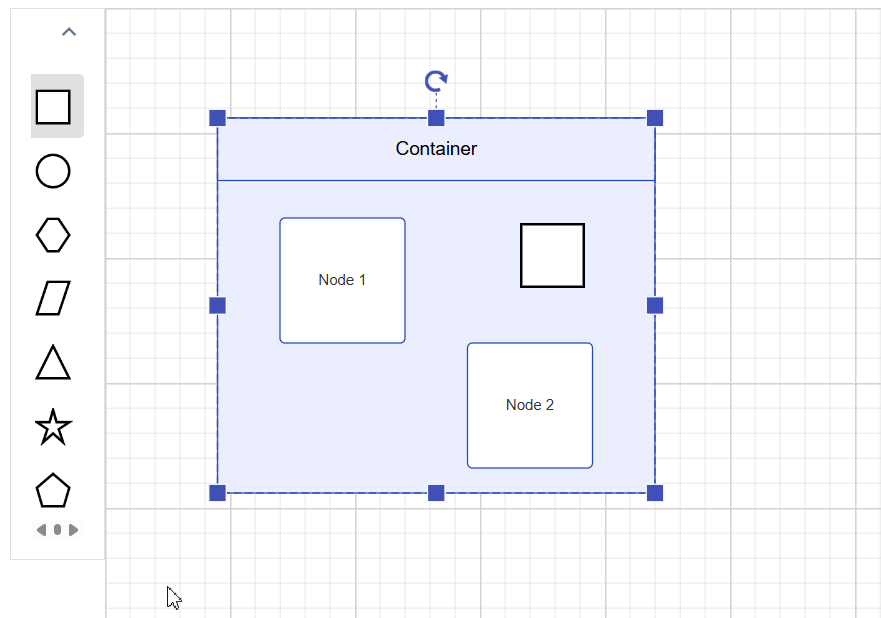
Interaction
Containers support the same interactions as regular nodes—such as selection, dragging, resizing, and rotating. For more information refer to the nodes interactions
Events
The events triggered when interacting with container nodes are similar to those for individual nodes. For more information, refer to the nodes events