How can I help you?
Virtual scrolling in Angular Grid component
13 Sep 202524 minutes to read
The virtual scrolling feature in the Grid enables efficient handling and display of large datasets without compromising performance. By rendering only the rows visible in the Grid viewport, virtual scrolling drastically reduces DOM elements, resulting in faster initial loads and smoother interactions, especially with thousands of records.
To enable virtualization, inject the VirtualScrollService, which manages virtual scrolling behavior and optimized data rendering for performance.
Row virtualization
Row virtualization loads and renders only the rows visible within the viewport of the Syncfusion Grid. Instead of displaying all rows initially, data is loaded dynamically during vertical scrolling. This paging-like approach enhances performance and reduces initial load times for large data sources.
To configure row virtualization, set the enableVirtualization property to true and define the grid’s content height using the height property.
The number of visible records is determined by the height of the content area, but you can specify an explicit record count using pageSettings.pageSize. Loaded data blocks are cached for improved navigation and performance.
The following example enables row virtualization using the enableVirtualization property:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser'
import { GridModule, PageService, ToolbarService, EditService } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-grids'
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { VirtualScrollService } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-grids';
import { PageSettingsModel, EditSettingsModel, ToolbarItems } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-grids';
const names = ['TOM', 'Hawk', 'Jon', 'Chandler', 'Monica', 'Rachel', 'Phoebe', 'Gunther', 'Ross', 'Geller', 'Joey', 'Bing', 'Tribbiani',
'Janice', 'Bong', 'Perk', 'Green', 'Ken', 'Adams'];
const hours = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10];
const designation = ['Manager', 'Engineer 1', 'Engineer 2', 'Developer', 'Tester'];
const status = ['Completed', 'Open', 'In Progress', 'Review', 'Testing']
const data = (count: any) => {
const result = [];
for (let i = 0; i < count; i++) {
result.push({
TaskID: i + 1,
Engineer: names[Math.round(Math.random() * names.length)] || names[0],
Designation: designation[Math.round(Math.random() * designation.length)] || designation[0],
Estimation: hours[Math.round(Math.random() * hours.length)] || hours[0],
Status: status[Math.round(Math.random() * status.length)] || status[0]
});
}
return result;
};
@Component({
imports: [
GridModule
],
providers: [PageService, ToolbarService, EditService, VirtualScrollService],
standalone: true,
selector: 'app-root',
template: `<ejs-grid [dataSource]='data' height='290px' [enableVirtualization]=true [pageSettings]='options' [editSettings]='editSettings' [toolbar]='toolbar'>
<e-columns>
<e-column field='TaskID' headerText='Task ID' textAlign='Right' width=100 isPrimaryKey='true' [validationRules]='rules'></e-column>
<e-column field='Engineer' width=100></e-column>
<e-column field='Designation' width=100 editType='dropdownedit' [validationRules]='rules'></e-column>
<e-column field='Estimation' textAlign='Right' width=100 editType='numericedit' [validationRules]='rules'></e-column>
<e-column field='Status' width=100 editType='dropdownedit'></e-column>
</e-columns>
</ejs-grid>`
})
export class AppComponent implements OnInit {
public data?: object[];
public options?: PageSettingsModel;
public rules: object = { required: true };
public editSettings?: EditSettingsModel;
public toolbar?: ToolbarItems[];
ngOnInit(): void {
this.editSettings = { allowEditing: true, allowAdding: true, allowDeleting: true, mode: 'Normal' };
this.toolbar = ['Add', 'Edit', 'Delete', 'Update', 'Cancel'];
this.data = data(5000);
this.options = { pageSize: 50 };
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Limitations
- Row virtual scrolling is incompatible with these features:
- Batch editing
- Detail template
- Row template
- Rowspan
- Autofill
- Hierarchy grid
- Copy-paste and drag-and-drop are limited to rows currently visible in the viewport.
- Cell-based selection is not supported.
- Different row heights within a template column (when template heights vary by row) are not supported.
- For remote data, group expand/collapse state is not persisted.
- The total maximum number of records that can be virtualized is limited by browser scroll height capabilities.
- Content height is calculated from row height and record count, so features altering row heights (like text wrapping) are not supported.
-
To support larger content or text-wrapped rows, set a uniform row height using CSS:
.e-grid .e-row { height: 2em; } - Aggregates and group totals show values only for the current visible view. For totals across all data, see Group with paging.
- Set a static height for the grid or its parent container; 100% height only works if both the component and its parent have explicit static heights.
Column virtualization
Column virtualization displays only the columns visible in the viewport, with horizontal scrolling to access additional columns. This improves performance when dealing with grids containing many columns, minimizing initial load time and DOM usage.
To enable column virtualization, set enableColumnVirtualization to true. The Grid will then render only visible columns during horizontal scrolling.
The following example enables column virtualization using the enableColumnVirtualization property:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser'
import { GridModule, PageService, ToolbarService, EditService } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-grids'
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { VirtualScrollService } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-grids';
import { PageSettingsModel, EditSettingsModel, ToolbarItems } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-grids';
let virtualData: any = [];
let names: string[] = ['hardire', 'abramjo01', 'aubucch01', 'Hook', 'Rumpelstiltskin', 'Belle', 'Emma', 'Regina', 'Aurora', 'Elsa', 'Anna',
'Snow White', 'Prince Charming', 'Cora', 'Zelena', 'August', 'Mulan', 'Graham', 'Discord', 'Will', 'Robin Hood',
'Jiminy Cricket', 'Henry', 'Neal', 'Red', 'Aaran', 'Aaren', 'Aarez', 'Aarman', 'Aaron', 'Aaron-James', 'Aarron',
'Aaryan', 'Aaryn', 'Aayan', 'Aazaan', 'Abaan', 'Abbas', 'Abdallah', 'Abdalroof', 'Abdihakim', 'Abdirahman',
'Abdisalam', 'Abdul', 'Abdul-Aziz', 'Abdulbasir', 'Abdulkadir', 'Abdulkarem', 'Abdulkhader', 'Abdullah',
'Abdul-Majeed', 'Abdulmalik', 'Abdul-Rehman', 'Abdur', 'Abdurraheem', 'Abdur-Rahman', 'Abdur-Rehmaan', 'Abel',
'Abhinav', 'Abhisumant', 'Abid', 'Abir', 'Abraham', 'Abu', 'Abubakar', 'Ace', 'Adain', 'Adam', 'Adam-James',
'Addison', 'Addisson', 'Adegbola', 'Adegbolahan', 'Aden', 'Adenn', 'Adie', 'Adil', 'Aditya', 'Adnan', 'Adrian',
'Adrien', 'Aedan', 'Aedin', 'Aedyn', 'Aeron', 'Afonso', 'Ahmad', 'Ahmed', 'Ahmed-Aziz', 'Ahoua', 'Ahtasham',
'Aiadan', 'Aidan', 'Aiden', 'Aiden-Jack', 'Aiden-Vee'];
function dataSource(): void {
for (let i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
virtualData.push({
SNo: i + 1,
FIELD1: names[Math.floor(Math.random() * names.length)],
FIELD2: 1967 + (i % 10), FIELD3: Math.floor(Math.random() * 200),
FIELD4: Math.floor(Math.random() * 100), FIELD5: Math.floor(Math.random() * 2000), FIELD6: Math.floor(Math.random() * 1000),
FIELD7: Math.floor(Math.random() * 100), FIELD8: Math.floor(Math.random() * 10), FIELD9: Math.floor(Math.random() * 10),
FIELD10: Math.floor(Math.random() * 100), FIELD11: Math.floor(Math.random() * 100), FIELD12: Math.floor(Math.random() * 1000),
FIELD13: Math.floor(Math.random() * 10), FIELD14: Math.floor(Math.random() * 10), FIELD15: Math.floor(Math.random() * 1000),
FIELD16: Math.floor(Math.random() * 200), FIELD17: Math.floor(Math.random() * 300), FIELD18: Math.floor(Math.random() * 400),
FIELD19: Math.floor(Math.random() * 500), FIELD20: Math.floor(Math.random() * 700), FIELD21: Math.floor(Math.random() * 800),
FIELD22: Math.floor(Math.random() * 1000), FIELD23: Math.floor(Math.random() * 2000), FIELD24: Math.floor(Math.random() * 150),
FIELD25: Math.floor(Math.random() * 1000), FIELD26: Math.floor(Math.random() * 100), FIELD27: Math.floor(Math.random() * 400),
FIELD28: Math.floor(Math.random() * 600), FIELD29: Math.floor(Math.random() * 500), FIELD30: Math.floor(Math.random() * 300),
});
}
}
dataSource();
@Component({
imports: [
GridModule
],
providers: [PageService, ToolbarService, EditService, VirtualScrollService],
standalone: true,
selector: 'app-root',
template: `<ejs-grid [dataSource]='data' height='290px' [enableColumnVirtualization]=true
[pageSettings]='options' [editSettings]='editSettings' [toolbar]='toolbar'>
<e-columns>
<e-column field='SNo' headerText='S.No' width=140 isPrimaryKey='true' [validationRules]='rules'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD1' headerText='Player Name' width=140 editType='dropdownedit' [validationRules]='rules'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD2' headerText='Year' width=120 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD3' headerText='Stint' width=120 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD4' headerText='TMID' width=120 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD5' headerText='LGID' width=120 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD6' headerText='GP' width=120 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD7' headerText='GS' width=120 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD8' headerText='Minutes' width=120 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD9' headerText='Points' width=120 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD10' headerText='oRebounds' width=130 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD11' headerText='dRebounds' width=130 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD12' headerText='Rebounds' width=120 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD13' headerText='Assists' width=120 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD14' headerText='Steals' width=120 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD15' headerText='Blocks' width=120 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD16' headerText='Turnovers' width=130 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD17' headerText='PF' width=130 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD18' headerText='fgAttempted' width=150 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD19' headerText='fgMade' width=120 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD20' headerText='ftAttempted' width=150 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD21' headerText='ftMade' width=120 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD22' headerText='ThreeAttempted' width=150 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD23' headerText='ThreeMade' width=130 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD24' headerText='PostGP' width=120 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD25' headerText='PostGS' width=120 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD26' headerText='PostMinutes' width=120 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD27' headerText='PostPoints' width=130 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD28' headerText='PostoRebounds' width=130 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD29' headerText='PostdRebounds' width=130 textAlign='Right'></e-column>
<e-column field='FIELD30' headerText='PostRebounds' width=130 textAlign='Right' editType='numericedit' [validationRules]='rules'></e-column>
</e-columns>
</ejs-grid>`
})
export class AppComponent implements OnInit {
public data?: object[];
public options?: PageSettingsModel;
public editSettings?: EditSettingsModel;
public toolbar?: ToolbarItems[];
public rules: object = { required: true };
ngOnInit(): void {
this.editSettings = { allowEditing: true, allowAdding: true, allowDeleting: true, mode: 'Normal' };
this.toolbar = ['Add', 'Edit', 'Delete', 'Update', 'Cancel'];
this.data = virtualData;
this.options = { pageSize: 50 };
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));For column virtualization, column width must be defined. If not specified, the Grid defaults to 200px per column.
Limitations
- Only pixel values are supported for column width; percentage widths are not supported.
- Selected column states are only retained within the visible viewport—selections are lost when scrolling to new columns.
- Cell selection is not supported.
- Ctrl + Home and Ctrl + End keyboard shortcuts are not available.
- The following features work within the viewport:
- Column resizing
- Column reordering
- Auto-fit
- Clipboard
- Column menu - AutofitAll
- Column virtual scrolling is not compatible with these features:
- Grouping
- Column Spanning
- Batch editing
- Stacked header
- Row template
- Detail template
- Hierarchy grid
- Autofill
Browser height limitation in virtual scrolling and solutions
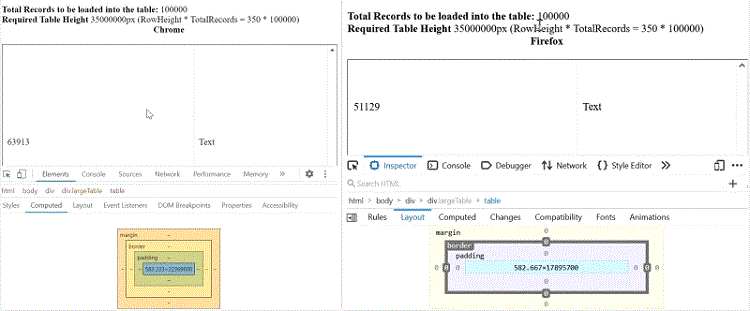
Virtual scrolling enables loading of millions of records by rendering only the visible rows during scrolling. The total grid height is calculated as: Total Records Count * Row Height.
Browsers have a maximum allowable scrollable element height. When the grid’s content height exceeds this limit, vertical scrolling cannot access records beyond the browser’s max height. For example, with a row height of 30px and 1,000,000 records, the height could exceed 22,369,600 pixels—a hard limit in Chrome or Firefox. This restricts virtual scrolling beyond a certain record count in both grids and standard HTML tables.
Illustrations:
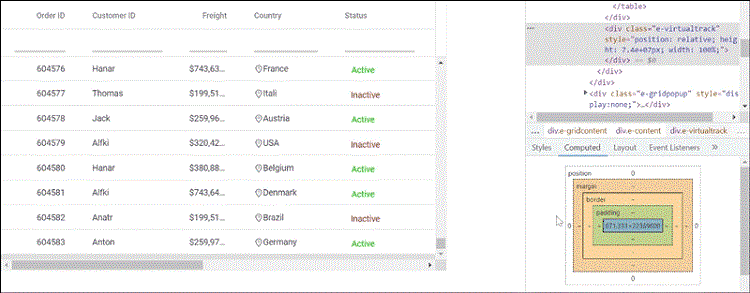
To address this browser limitation, consider the following approaches:
Solution 1: Using external buttons
You can prevent the height limitation problem in the browser when scrolling through millions of records by loading the segment of data through different strategy.
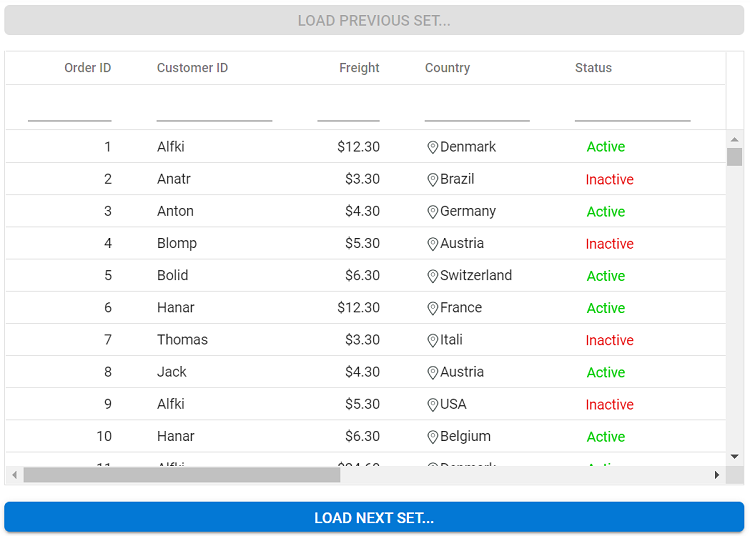
In the following sample, Grid is rendered with a large number of records(nearly 2 million). Here, you can scroll 0.5 million records at a time in Grid. Once you reach the last page of 0.5 million records, the Load Next Set button will be shown at the bottom of the Grid. By clicking that button, you can view the next set of 0.5 million records in Grid. Also, the Load Previous Set button will be shown at the top of the Grid to load the previous set of 0.5 million records.
Let’s see the step by step procedure for how we can overcome the limitation in the Syncfusion Grid component.
-
Create a custom adaptor by extending UrlAdaptor and binding it to the grid DataSource property. In the processQuery method of the custom adaptor, we handled the Skip query based on the current page set to perform the data operation with whole records on the server.
class CustomUrlAdaptor extends UrlAdaptor { processQuery(args) { if (arguments[1].queries) { for (const i = 0; i < arguments[1].queries.length; i++) { if (arguments[1].queries[i].fn === 'onPage') { // pageSet - defines the number of segments going to split the 2million records. In this example 0.5 million records are considered for each set so the pageSet is 1, 2, 3 and 4. // maxRecordsPerPageSet - In this example the value is define as 0.5 million. // gridPageSize - the pageSize defined in the Grid as pageSettings->pageSize property // customize the pageIndex based on the current pageSet (It send the skip query including the previous pageSet ) so that the other operations performed for total 2millions records instead of 0.5 million alone. arguments[1].queries[i].e.pageIndex = (((pageSet - 1) * maxRecordsPerPageSet) / gridPageSize) + arguments[1].queries[i].e.pageIndex; } } } let original = super.processQuery.apply(this, arguments); return original; } } this.data = new DataManager({ adaptor: new CustomUrlAdaptor(), url: "Home/UrlDatasource" }); -
Render the grid by define the following features.
<ejs-grid #grid [dataSource]='data' [enableVirtualization]='true' [pageSettings]='pageSettings' [height]='360' (beforeDataBound)='beforeDataBound($event)' > <e-columns> <e-column field='OrderID' headerText='Order ID' textAlign='Right' width=100></e-column> ...... ...... </e-columns> </ejs-grid> -
In the beforeDataBound event, we set the args.count as 0.5 million to perform scrolling with 0.5 million records and all the data operations are performed with whole records which is handled using the custom adaptor. And also particular segment records count is less than 0.5 million means it will directly assigned the original segmented count instead of 0.5 million.
beforeDataBound(args) { // storing the total records count which means 2 million records count totalRecords = args.count; // change the count with respect to maxRecordsPerPageSet (maxRecordsPerPageSet = 500000) args.count = args.count - ((pageSet - 1) * maxRecordsPerPageSet) > maxRecordsPerPageSet ?maxRecordsPerPageSet : args.count - ((pageSet - 1) * maxRecordsPerPageSet); } -
Render “Load Next Set” button and “Load Previous Set” button at bottom and top of the grid component.
<button ejs-button cssClass="e-info prevbtn" (onClick)="prevBtnClick($event)" content="Load Previous Set..."></button> <ejs-grid #grid [dataSource]='data' [enableVirtualization]='true' [pageSettings]='pageSettings' [height]='360' (beforeDataBound)='beforeDataBound($event)' > <e-columns> <e-column field='OrderID' headerText='Order ID' textAlign='Right' width=100></e-column> ...... ...... </e-columns> </ejs-grid> <button ejs-button cssClass="e-info nxtbtn" (onClick)="nxtBtnClick($event)" content="Load Next Set..."></button> -
While click on the
Load Next Set/Load Previous Setbutton corresponding page data set is loaded to view remaining records of total 2 millions records after doing some simple calculation.// Triggered when clicking the Previous/ Next button. prevNxtBtnClick(args) { if (grid.element.querySelector('.e-content') && grid.element.querySelector('.e-content').getAttribute('aria-busy') === 'false') { // Increase/decrease the pageSet based on the target element. pageSet = args.target.classList.contains('prevbtn') ? --pageSet : ++pageSet; this.rerenderGrid(); // Re-render the Grid component. } }
Grid actions like filtering and sorting apply across the entire data set, not just the currently loaded segment.
Solution 2: Using RowHeight property
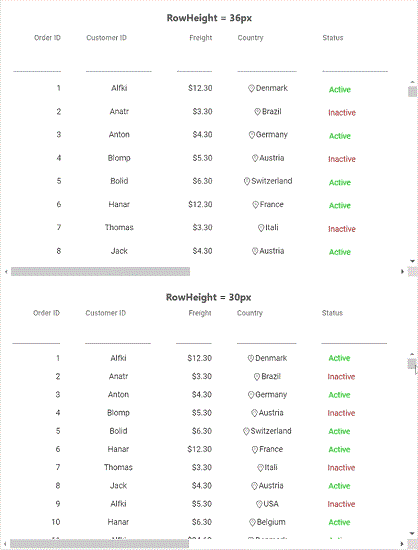
Reduce the row height using the rowHeight property to minimize total grid height before hitting the browser limit. If the limitation persists even after reduction, use segment navigation or paging.
Demonstration - scrollable records at 36px and 30px row heights:
Solution 3: Using paging instead of virtual scrolling
Similar to virtual scrolling, the paging feature also loads the data in an on-demand concept. Pagination is also compatible with all the other features(Grouping, Editing, etc.) in Grid. So, use the paging feature instead of virtual scrolling to view a large number of records in the Grid without any kind of performance degradation or browser height limitation.