Connectors in Angular Diagram component
26 Aug 202524 minutes to read
Connectors are objects used to create links between two points, nodes, or ports to represent relationships between them. They provide visual connections that help illustrate data flow, process sequences, hierarchical relationships, and other logical connections in diagrams.
Create Connector
Connectors can be created by defining the source and target points. The path to be drawn can be defined with a collection of segments. To explore the properties of a connector, refer to Connector Properties. The id property of a connector is used to define its unique identifier and can later be used to find the connector at runtime for customization.
<e-connectors>
<e-connector id='connector1' type='Straight' sourcePoint='sourcePoint' targetPoint='targetPoint'></e-connector>
</e-connectors> NOTE
When setting a connector’s ID, ensure it follows these naming rules: no spaces, must start with a letter, and should contain only alphanumeric characters and hyphens for optimal compatibility.
To create and customize the connectors easily in the Angular Diagram component, refer to the below video link.
Add connectors through connectors collection
The sourcePoint and targetPoint properties of connector allow you to define the end points of a connector.
The following code example illustrates how to add a connector through connector collection.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, PointModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" >
<e-connectors>
<e-connector id='connector' type='Straight' [sourcePoint]='sourcePoint' [targetPoint]='targetPoint'>
</e-connector>
</e-connectors>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public sourcePoint?: PointModel;
public targetPoint?: PointModel;
ngOnInit(): void {
this.sourcePoint = { x: 100, y: 100 };
this.targetPoint = { x: 200, y: 200 };
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Add/Remove connector at runtime
Connectors can be added at runtime by using the public method add and can be removed at runtime by using the public method remove. These methods are useful when you need to dynamically modify diagram structure based on user interactions or data changes.
The following code example illustrates how to add a connector at runtime.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, ConnectorModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `
<button (click)="add()">add</button>
<button (click)="remove()">remove</button>
<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" (created)='created($event)'>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public connectors: ConnectorModel = { id: 'connector1', sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 }, targetPoint: { x: 150, y: 150 } } as ConnectorModel;
public connector: ConnectorModel = {id: 'connector2', type: 'Orthogonal', sourcePoint: { x: 150, y: 170 }, targetPoint: { x: 300, y: 300 } } as ConnectorModel;
public bezierconnector: ConnectorModel = { id: 'connector3', type: 'Bezier', sourcePoint: { x: 320, y: 320 }, targetPoint: { x: 400, y: 400 } } as ConnectorModel;
add() {
(this.diagram as any).add(this.connector as any)
}
remove() {
(this.diagram as any).remove(this.connector as any);
}
public created(args: Object): void {
// Adds to the Diagram
(this.diagram as DiagramComponent).add(this.connectors as any);
(this.diagram as DiagramComponent).add(this.bezierconnector as any);
// Remove from the diagram
(this.diagram as DiagramComponent).remove(this.connectors as any);
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Add collection of connectors at runtime
The collection of connectors can be dynamically added using the addElements method. Each time an element is added to the diagram canvas, the collectionChange event will be triggered.
The following code illustrates how to add a collection of connectors at runtime.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, OnInit, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, ConnectorModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" (created)='created($event)'>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public connectors: ConnectorModel[] = [
{ id: 'connector1', sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 }, targetPoint: { x: 150, y: 150 } },
{id: 'connector2', type: 'Orthogonal', sourcePoint: { x: 170, y: 170 }, targetPoint: { x: 300, y: 300 }},
{ id: 'connector3', type: 'Bezier', sourcePoint: { x: 320, y: 320 }, targetPoint: { x: 400, y: 400 } }
] as ConnectorModel[];
public created(args: Object): void {
//Add collection of connectors
(this.diagram as DiagramComponent).addElements(this.connectors as any);
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Add Connectors from Palette
Connectors can be predefined and added to the symbol palette. You can drop those connectors into the diagram when required. This approach is useful for creating reusable connector templates that users can easily drag and drop into their diagrams.
The following code example illustrates how to add connectors to the palette.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { SymbolPaletteModule,PaletteModel,DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, ConnectorModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule,SymbolPaletteModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `
<ejs-symbolpalette #symbolpalette id="symbolpalette"width="100%" height="120px" [palettes]="palettes" [getConnectorDefaults] ='getConnectorDefaults' [symbolHeight]=80 [symbolWidth]=80 >
</ejs-symbolpalette>
<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="480px" >
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None,
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public connectorSymbols: ConnectorModel[] = [
{
id: 'orthogonal',
type: 'Orthogonal',
sourcePoint: { x: 0, y: 0 },
targetPoint: { x: 40, y: 40 },
},
{
id: 'orthogonaldashed',
type: 'Orthogonal',
sourcePoint: { x: 0, y: 0 },
targetPoint: { x: 40, y: 40 },
style: { strokeDashArray: '4 4' },
},
{
id: 'straight',
type: 'Straight',
sourcePoint: { x: 0, y: 0 },
targetPoint: { x: 40, y: 40 },
},
{
id: 'bezier',
type: 'Bezier',
sourcePoint: { x: 0, y: 0 },
targetPoint: { x: 40, y: 50 },
},
];
public palettes: PaletteModel[] = [
{
id: 'connectors',
expanded: true,
symbols: this.connectorSymbols,
title: 'Connectors',
iconCss: 'e-ddb-icons e-connector',
},
];
public getConnectorDefaults(obj: ConnectorModel): void {
obj.style= { strokeWidth: 2, strokeColor: '#757575' },
obj.targetDecorator = {
shape: 'Arrow',
style: { strokeColor: '#757575', fill: '#757575' },
}
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Draw Connectors
Connectors can be interactively drawn by clicking and dragging on the diagram surface. This feature enables users to create connections dynamically during diagram creation or editing.
To draw a connector, you have to activate the drawing tool by setting DrawOnce or ContinuousDraw to the tool property and you need to set the connector object by using the drawingObject property. The following code example illustrates how to draw a connector at runtime.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, ConnectorModel, DiagramTools,DiagramModule} from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px"
[drawingObject]="drawingObject" [tool]="tool">
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None,
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild('diagram', { static: true })
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public tool?: DiagramTools = DiagramTools.ContinuousDraw;
public drawingObject: ConnectorModel = {
type: 'Orthogonal',
};
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));For more information about drawing connectors, refer to Draw Connectors.
Update Connector at Runtime
Various connector properties such as sourcePoint, targetPoint, style, sourcePortID, targetPortID, and others can be updated at runtime. This flexibility allows for dynamic modification of connector appearance and behavior based on application logic or user interactions.
The following code example illustrates how to update a connector’s source point, target point, and style properties at runtime.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, PointModel, StrokeStyleModel, DecoratorModel, ShapeStyleModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: ` <button (click)="Update()">Update</button>
<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" >
<e-connectors>
<e-connector id='connector' type='Straight' [sourcePoint]='sourcePoint' [targetPoint]='targetPoint'>
</e-connector>
</e-connectors>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public sourcePoint?: PointModel;
public targetPoint?: PointModel;
ngOnInit(): void {
this.sourcePoint = { x: 100, y: 100 };
this.targetPoint = { x: 200, y: 200 };
}
Update() {
// Update the connector properties at the run time
((this.diagram as DiagramComponent).connectors[0].style as StrokeStyleModel).strokeColor = '#0000FF';
((this.diagram as DiagramComponent).connectors[0].style as StrokeStyleModel).fill = '#0000FF';
((this.diagram as DiagramComponent).connectors[0].style as StrokeStyleModel).strokeWidth = 2;
(((this.diagram as DiagramComponent).connectors[0].targetDecorator as DecoratorModel).style as StrokeStyleModel).fill = '#0000FF';
(((this.diagram as DiagramComponent).connectors[0].targetDecorator as DecoratorModel).style as ShapeStyleModel).strokeColor = '#0000FF';
((this.diagram as DiagramComponent).connectors[0].sourcePoint as PointModel).x = 150;
((this.diagram as DiagramComponent).connectors[0].targetPoint as PointModel).x = 150;
(this.diagram as DiagramComponent).dataBind();
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Clone Connector at Runtime
Cloning a connector creates a new connector instance with identical properties and attributes. This feature is useful when you need to duplicate existing connectors while maintaining their configuration.
The following code example illustrates how to clone a connector.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, ConnectorModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [DiagramModule],
providers: [],
standalone: true,
selector: 'app-container',
template: ` <input type="button" value="clone" id="clone" (click)="cloneConnector()"/>
<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" (created)='created($event)' >
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None,
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild('diagram')
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public connectors: ConnectorModel[] = [{
id: "connector1",
type: 'Straight',
sourcePoint: {
x: 100,
y: 100
},
targetPoint: {
x: 200,
y: 200
}
}];
public created(args: Object): void {
//Add collection of connectors
(this.diagram as DiagramComponent).add(this.connectors[0] as any);
}
cloneConnector() {
if (this.diagram) {
let diagram = this.diagram as DiagramComponent;
diagram.copy();
diagram.paste();
}
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Configure default connector properties
The connector defaults functionality allows you to define default properties for all connectors in the diagram. This is triggered when the diagram is initialized, providing an opportunity to customize connector properties globally rather than setting them individually for each connector.
The following code example explains how to customize connector defaults using getConnectorDefaults.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, ConnectorModel, PointModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" [getConnectorDefaults] ='getConnectorDefaults'>
<e-connectors>
<e-connector id='connector' type='Straight' [sourcePoint]='sourcePoint' [targetPoint]='targetPoint'>
</e-connector>
<e-connector id='connector2' type='Straight' [sourcePoint]='sourcePoint1' [targetPoint]='targetPoint1'>
</e-connector>
</e-connectors>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public sourcePoint?: PointModel;
public targetPoint?: PointModel;
public sourcePoint1?: PointModel;
public targetPoint1?: PointModel;
ngOnInit(): void {
this.sourcePoint = { x: 100, y: 100 };
this.targetPoint = { x: 200, y: 200 };
this.sourcePoint1 = { x: 300, y: 100 };
this.targetPoint1 = { x: 400, y: 200 };
}
public getConnectorDefaults(connector: ConnectorModel): void {
connector.style = {
strokeColor: 'red',
fill: '#6BA5D7',
strokeWidth: 2
}
connector.targetDecorator = {
style: {
fill: '#6BA5D7',
strokeColor: '#6BA5D7',
},
}
connector.sourceDecorator = {
style: {
fill: 'black',
strokeColor: 'black',
},
shape : 'Circle',
}
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Connections
Connection with nodes
The sourceID and targetID properties allow you to define the nodes to be connected. When these properties are set, the connector will automatically attach to the specified nodes and move with them when the nodes are repositioned.
The following code example illustrates how to connect two nodes.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, NodeModel, ShapeStyleModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" [getNodeDefaults] = 'getNodeDefaults'>
<e-nodes>
<e-node id='node1' [offsetX]=150 [offsetY]=150>
<e-node-annotations>
<e-node-annotation content="Node1">
</e-node-annotation>
</e-node-annotations>
</e-node>
<e-node id='node2' [offsetX]=350 [offsetY]=150>
<e-node-annotations>
<e-node-annotation content="Custom Template">
</e-node-annotation>
</e-node-annotations>
</e-node>
</e-nodes>
<e-connectors>
<e-connector id='connector' type='Orthogonal' sourceID='node1' targetID='node2' connectorSpacing='connectorSpacing'>
</e-connector>
</e-connectors>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public connectorSpacing?: number;
ngOnInit(): void {
this.connectorSpacing = 7;
}
public getNodeDefaults(node: NodeModel | any): void {
node.height = 100;
node.width = 100;
((node as NodeModel).style as ShapeStyleModel).fill = "#6BA5D7";
((node as NodeModel).style as ShapeStyleModel).strokeColor = "White";
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));When you remove NodeConstraints InConnect from Default, the node accepts only an outgoing connection to dock in it. Similarly, when you remove NodeConstraints OutConnect from Default, the node accepts only an incoming connection to dock in it.
When you remove both InConnect and OutConnect NodeConstraints from Default, the node restricts connectors from establishing connections to it.
The following code illustrates how to disable InConnect constraints.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from "@angular/core";
import { NodeConstraints } from "@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams";
@Component({
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px">
<e-nodes>
<e-node id='node1' [height]=60 [width]=100 [offsetX]=300 [offsetY]=80 [constraints]='nodeConstraints'>
</e-node>
</e-nodes>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public nodeConstraints: NodeConstraints;
ngOnInit(): void {
//Disable InConnect constraints
this.nodeConstraints = NodeConstraints.Default & ~NodeConstraints.InConnect;
}
}Connections with ports
The sourcePortID and targetPortID properties allow you to create connections between specific points of source and target nodes. This provides more precise control over where connectors attach to nodes.
The following code example illustrates how to create port to port connections.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, NodeModel, PointPortModel, PortVisibility, ShapeStyleModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" [getNodeDefaults] ='getNodeDefaults'>
<e-nodes>
<e-node id='node1' [offsetX]=150 [offsetY]=150 [ports]='port1'>
<e-node-annotations>
<e-node-annotation content="Node1">
</e-node-annotation>
</e-node-annotations>
</e-node>
<e-node id='node2' [offsetX]=350 [offsetY]=150 [ports]='port2'>
<e-node-annotations>
<e-node-annotation content="Node2">
</e-node-annotation>
</e-node-annotations>
</e-node>
</e-nodes>
<e-connectors>
<e-connector id='connector' type='Orthogonal' sourceID='node1' sourcePortID='port1' targetID='node2' targetPortID='port2'>
</e-connector>
</e-connectors>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public port1: PointPortModel[] = [{
id: 'port1',
offset: {
x: 0,
y: 0.5
},
shape: 'X',
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
}]
public port2: PointPortModel[] = [
{
id: 'port2',
offset: {
x: 1,
y: 0.5
},
shape: 'Circle',
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
},
{
id: 'port3',
offset: {
x: 0.5,
y: 0
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
}
]
public getNodeDefaults(node: NodeModel | any): NodeModel {
node.height = 100;
node.width = 100;
((node as NodeModel).style as ShapeStyleModel).fill = "#6BA5D7";
((node as NodeModel).style as ShapeStyleModel).strokeColor = "White";
return node;
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));The sourcePortID or targetPortID can be changed at runtime by modifying these properties programmatically.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, NodeModel, PointPortModel ,PortVisibility, ShapeStyleModel} from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `
<button (click)="Update()">Update</button>
<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" [getNodeDefaults] ='getNodeDefaults' >
<e-nodes>
<e-node id='node1' [offsetX]=150 [offsetY]=150 [ports]='port1'>
<e-node-annotations>
<e-node-annotation content="Node1">
</e-node-annotation>
</e-node-annotations>
</e-node>
<e-node id='node2' [offsetX]=350 [offsetY]=150 [ports]='port2'>
<e-node-annotations>
<e-node-annotation content="Custom Template">
</e-node-annotation>
</e-node-annotations>
</e-node>
</e-nodes>
<e-connectors>
<e-connector id='connector' type='Orthogonal' sourceID='node1' sourcePortID='port1' targetID='node2' targetPortID='port3'>
</e-connector>
</e-connectors>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public port1: PointPortModel[] = [
{
id: 'port1',
offset: {
x: 0,
y: 0.5
},
shape: 'X',
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
},
{
id: 'port2',
offset: {
x: 1,
y: 0.5
},
shape: 'Circle',
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
},
]
public port2: PointPortModel[] = [
{
id: 'port3',
offset: {
x: 0.5,
y: 0
},
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
},
{
id: 'port4',
offset: {
x: 0.5,
y: 1
},
shape: 'Circle',
visibility: PortVisibility.Visible
}
]
public getNodeDefaults(node: NodeModel | any): NodeModel {
node.height = 100;
node.width = 100;
((node as NodeModel).style as ShapeStyleModel).fill = "#6BA5D7";
((node as NodeModel).style as ShapeStyleModel).strokeColor = "White";
return node;
}
Update()
{
//update port at runtime
if (this.diagram ) {
this.diagram.connectors[0].sourcePortID = 'port2';
this.diagram.connectors[0].targetPortID = 'port4';
this.diagram.dataBind(); // Assuming dataBind is a method of the diagram
}
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));When you set PortConstraints to InConnect, the port accepts only an incoming connection to dock in it. Similarly, when you set PortConstraints to OutConnect, the port accepts only an outgoing connection to dock in it.
When you set PortConstraints to None, the port restricts connectors from establishing connections to it.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from "@angular/core";
import { PointPortModel, PortConstraints } from "@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams";
@Component({
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px">
<e-nodes>
<e-node id='node1' [height]=60 [width]=100 [offsetX]=300 [offsetY]=80 [ports]='port1'>
</e-node>
</e-nodes>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public port1: PointPortModel[];
ngOnInit(): void {
this.port1 = [{
id: 'port1',
shape: 'Circle',
offset: { x: 0, y: 0.5 },
text: 'In - 1',
//Enable portConstraints InConnect
constraints: PortConstraints.InConnect
}];
}
}Automatic line routing
Diagram provides additional flexibility to re-route diagram connectors automatically. Connectors automatically re-route themselves when nodes move nearby, ensuring optimal path routing. This feature can be activated by including the LineRouting constraint in the diagram’s constraints.
The LineRouting module should be injected to the application as shown in the following code snippet.
import { LineRouting, Diagram } from '@syncfusion/ej2-diagrams';
/**
* Injecting the automatic line routing module.
*/
Diagram.Inject(LineRouting);The line routing constraints must be included in the default diagram constraints to enable automatic line routing support as shown below.
<!--
Initialize the Diagram
-->
<ejs-diagram #diagram [constraints]='constraints'> // Enable line routing constraints.
public constraints: DiagramConstraints = DiagramConstraints.Default | DiagramConstraints.LineRouting;The following code block shows how to create the diagram with specified nodes, connectors, constraints, and necessary modules for line routing.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { Diagram, DiagramComponent, NodeModel, ConnectorModel,DiagramModule } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
import { LineRouting, DiagramConstraints} from '@syncfusion/ej2-diagrams';
Diagram.Inject(LineRouting);
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="645px" [nodes]='nodes' [connectors]='connectors' [getNodeDefaults]='getNodeDefaults' [constraints]='constraints'>`, encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild('diagram')
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public constraints: DiagramConstraints = DiagramConstraints.Default | DiagramConstraints.LineRouting;
public nodes: NodeModel[] = [
{ id: 'shape1', offsetX: 100, offsetY: 100, width: 120, height: 50 },
{ id: 'shape2', offsetX: 300, offsetY: 300, width: 120, height: 50 },
{ id: 'shape3', offsetX: 150, offsetY: 200, width: 120, height: 50 }
];
public connectors: ConnectorModel[] = [
{ id: 'connector', sourceID: 'shape1', targetID: 'shape2', type: 'Orthogonal' }
];
public getNodeDefaults(obj: NodeModel): NodeModel {
obj = { style: { strokeColor: '#6BA5D7', fill: '#6BA5D7' } };
return obj;
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));The following gif illustrates how the connector automatically re-routes the segments.
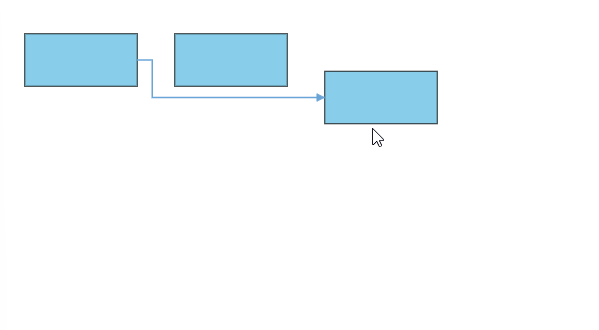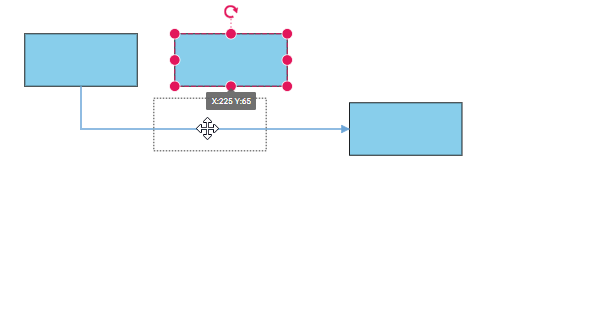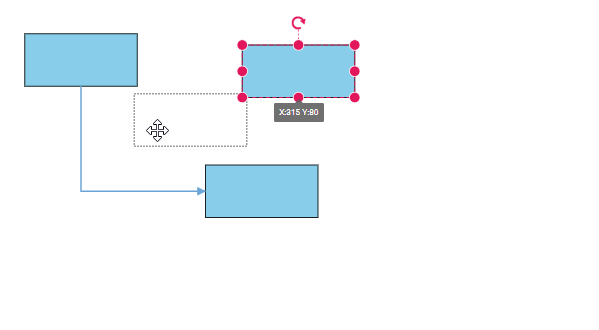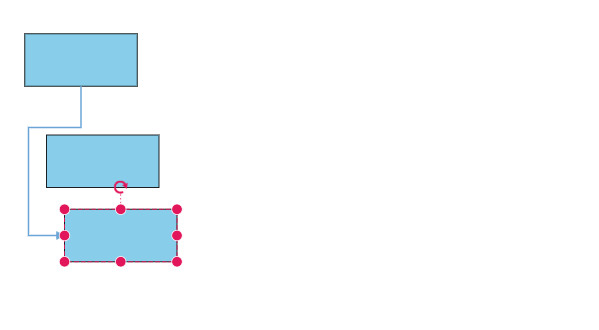
In some situations, diagrams with automatic line routing enabled may need to exclude specific connectors from automatic routing. The auto routing feature can be disabled for specific connectors using the constraints property of the connector as shown in the following code snippet.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { Diagram, DiagramComponent, NodeModel, ConnectorModel,DiagramModule } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
import { LineRouting, DiagramConstraints, ConnectorConstraints} from '@syncfusion/ej2-diagrams';
Diagram.Inject(LineRouting);
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="645px" [nodes]='nodes' [connectors]='connectors' [getNodeDefaults]='getNodeDefaults' [constraints]='constraints'>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild('diagram')
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public constraints: DiagramConstraints = DiagramConstraints.Default | DiagramConstraints.LineRouting;
public nodes: NodeModel[] = [
{ id: 'shape1', offsetX: 100, offsetY: 100, width: 120, height: 50 },
{ id: 'shape2', offsetX: 350, offsetY: 300, width: 120, height: 50 },
{ id: 'shape3', offsetX: 150, offsetY: 200, width: 120, height: 50 },
{ id: 'shape4', offsetX: 300, offsetY: 200, width: 120, height: 50 }
];
public connectors: ConnectorModel[] = [
{ id: 'connector', sourceID: 'shape1', targetID: 'shape2', type: 'Orthogonal', annotations: [{ offset: .7, content: ' Routing \n enabled', style: { fill: "white" } }] },
{ id: 'connector2', sourceID: 'shape1', targetID: 'shape2', annotations: [{ offset: .6, content: ' Routing \n disabled', style: { fill: "white" } }], type: 'Orthogonal', constraints: ConnectorConstraints.Default & ~ConnectorConstraints.InheritLineRouting }
];
public getNodeDefaults(obj: NodeModel): NodeModel {
obj = { style: { strokeColor: '#6BA5D7', fill: '#6BA5D7' } };
return obj;
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Avoid line overlapping
The diagram provides flexibility to prevent connectors from overlapping, ensuring better clarity and readability. This feature intelligently adjusts connector paths to avoid stacking orthogonal connectors on top of each other, reducing visual clutter and enhancing diagram structure. It is especially useful in complex diagrams with multiple orthogonal connectors, where overlapping lines can make interpretation difficult.
To enable this feature, inject both the LineRouting and AvoidLineOverlapping modules into the application and add the corresponding constraints to the diagram.
import { LineRouting, AvoidLineOverlapping, Diagram } from '@syncfusion/ej2-diagrams';
/**
* Injecting the line routing and avoid line overlapping module.
*/
Diagram.Inject(LineRouting, AvoidLineOverlapping);Add LineRouting and AvoidLineOverlapping constraints to the diagram constraints to enable line routing with avoid line overlapping support.
<!--
Initialize the Diagram
-->
<ejs-diagram #diagram [constraints]='constraints'>// Enable line routing and avoid line overlapping constraints.
public constraints: DiagramConstraints = DiagramConstraints.Default | DiagramConstraints.LineRouting | DiagramConstraints.AvoidLineOverlapping;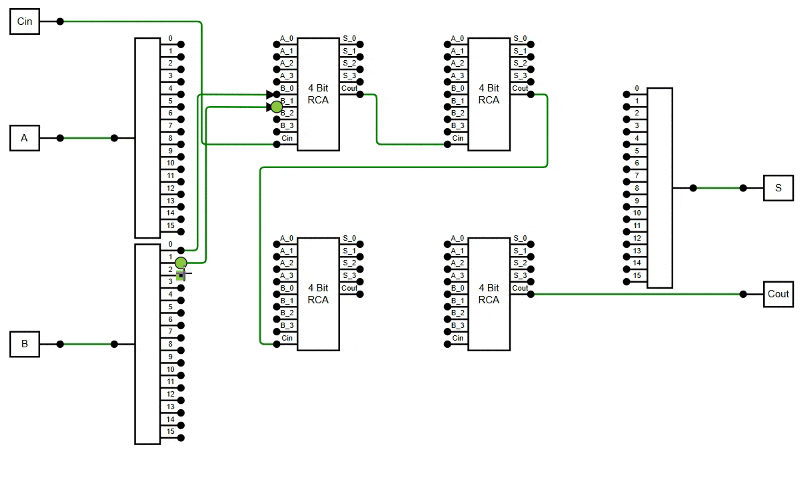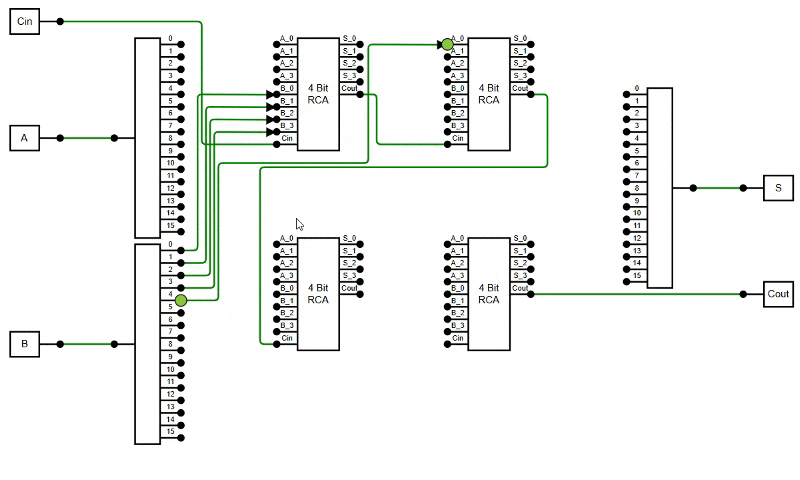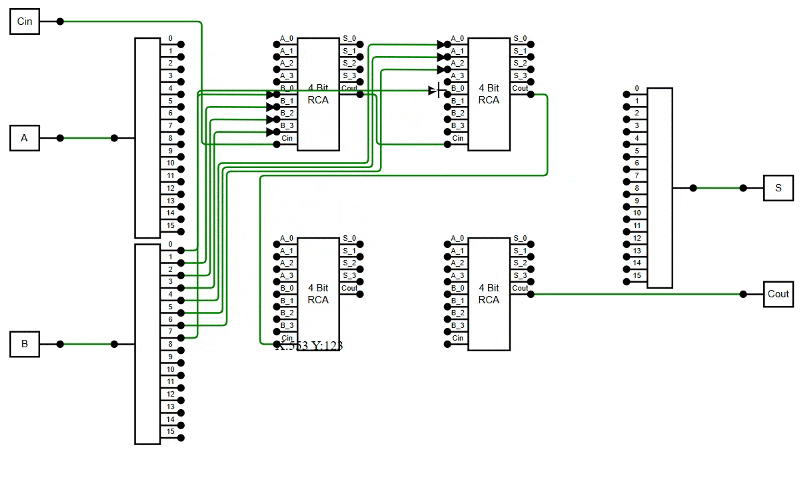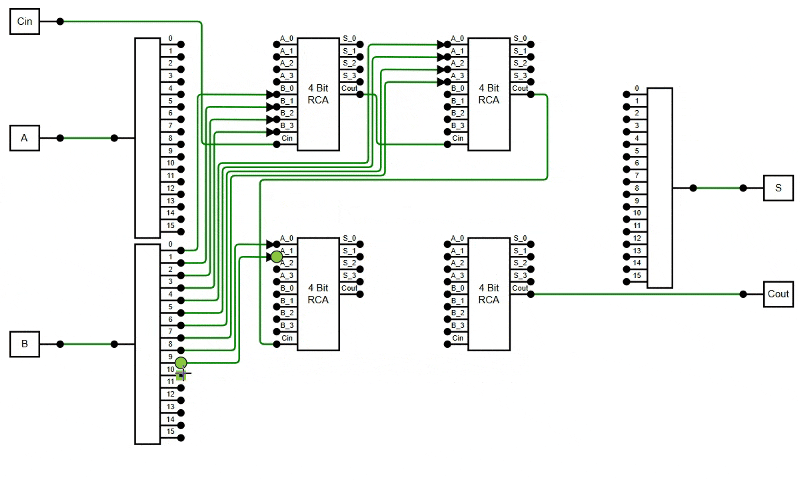
The following example demonstrates how to enable the AvoidLineOverlapping feature in the diagram.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, OnInit, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { Diagram, DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, NodeModel, ConnectorModel, PointPortModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
import { LineRouting, AvoidLineOverlapping, Snapping, RulerSettingsModel, DiagramConstraints, PortVisibility } from '@syncfusion/ej2-diagrams';
// Inject line routing and avoid line overlapping module.
Diagram.Inject(LineRouting, AvoidLineOverlapping, Snapping);
@Component({
imports: [DiagramModule],
standalone: true,
selector: 'app-container',
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="700px" [rulerSettings]='rulerSettings'
[nodes]='nodes' [connectors]='connectors' [constraints]='constraints'
[getConnectorDefaults]='getConnectorDefaults'>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent implements OnInit {
@ViewChild('diagram')
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public rulerSettings: RulerSettingsModel = { showRulers: true };
// Configure constraints with Line Routing and AvoidLineOverlapping
public constraints: DiagramConstraints = DiagramConstraints.Default | DiagramConstraints.LineRouting | DiagramConstraints.AvoidLineOverlapping;
public nodes?: NodeModel[];
public connectors?: ConnectorModel[];
ngOnInit(): void {
const orData = 'M21.7,76.5L21.7,76.5c6.4-18.1,6.4-37.8,0-55.9l0-0.1h1.6c21.5,0,41.7,10.4,54.2,28l0,0l0,0 c-12.5,17.6-32.7,28-54.2,28H21.7z M99.5,48.5l-22,0 M0,31.5h25 M0,65.5h25';
const andData = 'M21.5,20.5h28a28,28,0,0,1,28,28v0a28,28,0,0,1-28,28h-28a0,0,0,0,1,0,0v-56a0,0,0,0,1,0,0Z M78,48.5 L 100,48.5Z M0,32.5 L 21.4,32.5Z M0,65.5 L 21.4,65.5Z';
const notData = 'M75.5,50.5l-52,28v-56L75.5,50.5z M81.5,50.5h18 M1.5,50.5h22 M78.5,47.5c-1.7,0-3,1.3-3,3s1.3,3,3,3s3-1.3,3-3 S80.2,47.5,78.5,47.5z';
const orPort: PointPortModel[] = [
{ id: 'Or_port1', offset: { x: 0.01, y: 0.1963 }, visibility: PortVisibility.Visible, style: { fill: 'black' }, shape: 'Circle' },
{ id: 'Or_port2', offset: { x: 0.26, y: 0.5 } },
{ id: 'Or_port3', offset: { x: 0.01, y: 0.805 }, visibility: PortVisibility.Visible, style: { fill: 'black' }, shape: 'Circle' },
{ id: 'Or_port4', offset: { x: 0.99, y: 0.5 }, visibility: PortVisibility.Visible, style: { fill: 'black' }, shape: 'Circle' }
];
const andPort: PointPortModel[] = [
{ id: 'And_port1', offset: { x: 0.01, y: 0.215 }, visibility: PortVisibility.Visible, style: { fill: 'black' }, shape: 'Circle' },
{ id: 'And_port2', offset: { x: 0.22, y: 0.5 } },
{ id: 'And_port3', offset: { x: 0.01, y: 0.805 }, visibility: PortVisibility.Visible, style: { fill: 'black' }, shape: 'Circle' },
{ id: 'And_port4', offset: { x: 0.99, y: 0.5 }, visibility: PortVisibility.Visible, style: { fill: 'black' }, shape: 'Circle' }
];
const notPort: PointPortModel[] = [
{ id: 'Not_port1', offset: { x: 0.01, y: 0.5 }, visibility: PortVisibility.Visible, style: { fill: 'black' }, shape: 'Circle' },
{ id: 'Not_port2', offset: { x: 0.99, y: 0.5 }, visibility: PortVisibility.Visible, style: { fill: 'black' }, shape: 'Circle' }
];
this.nodes = [
{ id: 'switch', offsetX: 80, offsetY: 50, width: 50, height: 50, ports: [{ id: 'port1', offset: { x: 1, y: 0.5 }, visibility: PortVisibility.Visible, style: { fill: 'black' }, shape: 'Circle' }], annotations: [{ content: 'A' }] },
{ id: 'Push', offsetX: 80, offsetY: 150, width: 50, height: 50, ports: [{ id: 'port1', offset: { x: 1, y: 0.5 }, visibility: PortVisibility.Visible, style: { fill: 'black' }, shape: 'Circle' }], annotations: [{ content: 'B' }] },
{ id: 'clock', offsetX: 80, offsetY: 250, width: 50, height: 50, ports: [{ id: 'port1', offset: { x: 1, y: 0.5 }, visibility: PortVisibility.Visible, style: { fill: 'black' }, shape: 'Circle' }], annotations: [{ content: 'C' }] },
{ id: 'switch2', offsetX: 80, offsetY: 350, width: 50, height: 50, ports: [{ id: 'port1', offset: { x: 1, y: 0.5 }, visibility: PortVisibility.Visible, style: { fill: 'black' }, shape: 'Circle' }], annotations: [{ content: 'D' }] },
{ id: 'AND21', offsetX: 200, offsetY: 100, width: 60, height: 40, shape: { type: 'Path', data: andData }, ports: andPort },
{ id: 'OR22', offsetX: 200, offsetY: 200, width: 60, height: 40, shape: { type: 'Path', data: orData }, ports: orPort },
{ id: 'AND23', offsetX: 200, offsetY: 300, width: 60, height: 40, shape: { type: 'Path', data: andData }, ports: andPort },
{ id: 'AND31', offsetX: 300, offsetY: 250, width: 60, height: 40, shape: { type: 'Path', data: andData }, ports: andPort },
{ id: 'OR41', offsetX: 400, offsetY: 150, width: 60, height: 40, shape: { type: 'Path', data: orData }, ports: orPort },
{ id: 'NOT42', offsetX: 400, offsetY: 350, width: 60, height: 40, shape: { type: 'Path', data: notData }, ports: notPort },
{
id: 'Exor5', ports: orPort, offsetX: 500, offsetY: 250, width: 60, height: 40,
shape: { type: 'Path', data: 'M21.7,76.5L21.7,76.5c6.4-18.1,6.4-37.8,0-55.9l0-0.1h1.6c21.5,0,41.7,10.4,54.2,28l0,0l0,0 c-12.5,17.6-32.7,28-54.2,28H21.7z M73.4,48.5L73.4,48.5 M17.5,76.8L17.5,76.8c6.7-18.2,6.7-38.1,0-56.3l0-0.1 M77.5,48.5h22 M0,32.5h21 M0,65.5h21' }
},
{ id: 'bulb', offsetX: 600, offsetY: 150, width: 50, height: 50, ports: [{ id: 'bulbPort', offset: { x: 0.5, y: 1 }, visibility: PortVisibility.Visible, style: { fill: 'black' }, shape: 'Circle' }], annotations: [{ content: 'Out' }] }
];
this.connectors = [
{ id: 'ExOr-Output', sourceID: 'Exor5', targetID: 'bulb', sourcePortID: 'Or_port4', targetPortID: 'bulbPort', type: 'Orthogonal' },
{ id: '4-ExOr1', sourceID: 'OR41', targetID: 'Exor5', sourcePortID: 'Or_port4', targetPortID: 'Or_port1', type: 'Orthogonal' },
{ id: '4-ExOr2', sourceID: 'NOT42', targetID: 'Exor5', sourcePortID: 'Not_port2', targetPortID: 'Or_port3', type: 'Orthogonal' },
{ id: '3-AND-OR', sourceID: 'AND31', targetID: 'OR41', sourcePortID: 'And_port4', targetPortID: 'Or_port3', type: 'Orthogonal' },
{ id: '2AND1-4AND1', sourceID: 'AND21', targetID: 'OR41', sourcePortID: 'And_port4', targetPortID: 'Or_port1', type: 'Orthogonal' },
{ id: '2OR2-3AND', sourceID: 'OR22', targetID: 'AND31', sourcePortID: 'Or_port4', targetPortID: 'And_port1', type: 'Orthogonal' },
{ id: '2AND3-3AND', sourceID: 'AND23', targetID: 'AND31', sourcePortID: 'And_port4', targetPortID: 'And_port3', type: 'Orthogonal' },
{ id: 'switch-Not42', sourceID: 'switch', targetID: 'NOT42', sourcePortID: 'port1', targetPortID: 'Not_port1', type: 'Orthogonal' },
{ id: 'Push-AND21', sourceID: 'Push', targetID: 'AND21', sourcePortID: 'port1', targetPortID: 'And_port3', type: 'Orthogonal' },
{ id: 'Push-OR22', sourceID: 'Push', targetID: 'OR22', sourcePortID: 'port1', targetPortID: 'Or_port1', type: 'Orthogonal' },
{ id: 'Push-AND23', sourceID: 'Push', targetID: 'AND23', sourcePortID: 'port1', targetPortID: 'And_port1', type: 'Orthogonal' },
{ id: 'clock-OR22', sourceID: 'clock', targetID: 'OR22', sourcePortID: 'port1', targetPortID: 'Or_port3', type: 'Orthogonal' },
{ id: 'clock-AND23', sourceID: 'clock', targetID: 'AND23', sourcePortID: 'port1', targetPortID: 'And_port3', type: 'Orthogonal' },
{ id: 'switch2-And21', sourceID: 'switch2', targetID: 'AND21', sourcePortID: 'port1', targetPortID: 'And_port1', type: 'Orthogonal' }
];
}
public getConnectorDefaults(connector: ConnectorModel): ConnectorModel {
connector.cornerRadius = 5;
return connector;
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));NOTE
The
AvoidLineOverlappingfeature applies only to orthogonal connectors and requires theLineRoutingmodule to be injected with its constraints enabled.