Connector Customization
26 Aug 202524 minutes to read
The Diagram component provides extensive customization options for connectors, allowing developers to modify visual appearance, behavior, and interaction properties. This guide covers decorator shapes, styling options, spacing controls, bridging effects, and advanced connector features.
Decorator shapes and customization
Decorators are visual elements that appear at the starting and ending points of connectors, typically used to indicate direction or relationship types such as arrows, circles, diamonds, or custom shapes.
Basic decorator configuration
The connection end points can be decorated using the sourceDecorator and targetDecorator properties of the connector.
The shape property of sourceDecorator allows defining the shape of the source decorators. Similarly, the shape property of targetDecorator allows defining the shape of the target decorators.
To create custom shapes for decorators, use the pathData property to define SVG path strings for both source and target decorators.
The following code example illustrates how to create decorators of various shapes.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, ConnectorModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [DiagramModule],
providers: [],
standalone: true,
selector: 'app-container',
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" [connectors]="connectors" >
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None,
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild('diagram')
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public connectors: ConnectorModel[] = [
{
id: 'connector1',
type: 'Straight',
sourceDecorator: { shape: 'Circle' },
// Decorator shape - Diamond
targetDecorator: {
// Defines the custom shape for the connector's target decorator
shape: 'Custom',
//Defines the path for the connector's target decorator
pathData:
'M80.5,12.5 C80.5,19.127417 62.59139,24.5 40.5,24.5 C18.40861,24.5 0.5,19.127417 0.5,12.5' +
'C0.5,5.872583 18.40861,0.5 40.5,0.5 C62.59139,0.5 80.5,5.872583 80.5,12.5 z',
},
sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 200, y: 200 }
},
{
id: 'connectors2',
type: 'Straight',
sourceDecorator: { shape: 'IndentedArrow' },
targetDecorator: { shape: 'OutdentedArrow' },
sourcePoint: { x: 400, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 300, y: 200 }
}
];
};import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Customize the decorator appearance
The visual appearance of decorators can be customized using stroke and fill properties to match design requirements or highlight specific connector types.
o customize the border of a decorator, use the strokeColor, strokeWidth, and strokeDashArray properties on the sourceDecorator and targetDecorator objects. Similarly, use the width and height properties to control the size of each decorator.
The following code example illustrates how to customize the appearance of the decorator.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, ConnectorModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [DiagramModule],
providers: [],
standalone: true,
selector: 'app-container',
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" [connectors]="connectors" >
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None,
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild('diagram')
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public connectors: ConnectorModel[] = [
{
id: 'connector1',
type: 'Straight',
// Decorator shape- circle
sourceDecorator: {
shape: 'Circle',
// Defines the style for the sourceDecorator
style: {
// Defines the strokeWidth for the sourceDecorator
strokeWidth: 3,
// Defines the strokeColor for the sourceDecorator
strokeColor: 'red',
},
},
// Decorator shape - Diamond
targetDecorator: {
// Defines the custom shape for the connector's target decorator
shape: 'Custom',
//Defines the path for the connector's target decorator
pathData:
'M80.5,12.5 C80.5,19.127417 62.59139,24.5 40.5,24.5 C18.40861,24.5 0.5,19.127417 0.5,12.5' +
'C0.5,5.872583 18.40861,0.5 40.5,0.5 C62.59139,0.5 80.5,5.872583 80.5,12.5 z',
//defines the style for the target decorator
style: {
// Defines the strokeWidth for the targetDecorator
strokeWidth: 3,
// Defines the strokeColor for the sourceDecorator
strokeColor: 'green',
// Defines the opacity for the sourceDecorator
opacity: 0.8,
},
},
sourcePoint: {
x: 100,
y: 100,
},
targetPoint: {
x: 200,
y: 200,
}
},
{
id: 'connectors2',
type: 'Straight',
// Decorator shape - IndentedArrow
sourceDecorator: {
shape: 'IndentedArrow',
style: {
strokeWidth: 3,
strokeColor: 'blue',
},
},
// Decorator shape - OutdentedArrow
targetDecorator: {
shape: 'OutdentedArrow',
style: {
strokeWidth: 3,
strokeColor: 'yellow',
},
},
sourcePoint: { x: 400, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 300, y: 200 }
}
];
};import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Gradient styling for decorators
The gradient property applies smooth color transitions to decorators, providing enhanced visual appeal for complex diagrams or when highlighting important connections.
The gradient property supports two types of gradients:
- Linear - Creates a straight-line color transition
- Radial - Creates a circular color transition from center outward
The following code example illustrates how to apply gradient effects to decorators.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramModule, DiagramComponent, ConnectorModel, GradientModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [DiagramModule],
providers: [],
standalone: true,
selector: 'app-container',
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="900px" [connectors]="connectors" (created)='created($event)' >
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None,
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild('diagram')
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public created(args: Object): void {
(this.diagram as DiagramComponent).zoomTo({
type: 'ZoomIn',
zoomFactor: 2,
focusPoint: { x: 0, y: 0.5 },
});
(this.diagram as DiagramComponent).fitToPage();
}
public connectors: ConnectorModel[] = [
{
id: 'connector1',
type: 'Straight',
style: {
strokeColor: '#6BA5D7',
fill: '#6BA5D7',
strokeWidth: 2,
},
bridgeSpace: 20,
// Cutomize the target decorator
targetDecorator: {
style: {
strokeWidth: 1,
opacity: 0.5,
gradient: {
x1: 20,
y1: 20,
x2: 70,
y2: 70,
stops: [
{
color: 'green',
offset: 50,
opacity: 1,
},
{
color: 'yellow',
offset: 100,
opacity: 1,
},
],
type: 'Linear',
} as GradientModel,
}
},
sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 200, y: 200 }
},
{
id: 'connector2',
type: 'Straight',
style: {
strokeColor: '#6BA5D7',
fill: '#6BA5D7',
strokeWidth: 2,
},
bridgeSpace: 20,
// Cutomize the target decorator
targetDecorator: {
style: {
gradient: {
cx: 50,
cy: 50,
fx: 50,
fy: 50,
stops: [
{ color: '#00555b', offset: 0 },
{ color: 'yellow', offset: 90 },
],
type: 'Radial',
},
},
},
sourcePoint: { x: 300, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 400, y: 200 }
}];
};import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Spacing and padding controls
Padding between connectors and nodes
Padding creates visual separation between connector endpoints and the nodes they connect, preventing connectors from appearing to touch or overlap with node boundaries.
The sourcePadding property of the connector defines space between the source point and the source node of the connector.
The targetPadding property of the connector defines space between the end point and the target node of the connector.
The following code example illustrates how to leave space between the connection endpoints and source and target nodes.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, NodeModel, ConnectorModel, ShapeStyleModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" [getNodeDefaults] ='getNodeDefaults' [getConnectorDefaults] ='getConnectorDefaults'>
<e-nodes>
<e-node id='node1' [offsetX]=150 [offsetY]=150>
<e-node-annotations>
<e-node-annotation content="Node1">
</e-node-annotation>
</e-node-annotations>
</e-node>
<e-node id='node2' [offsetX]=350 [offsetY]=150>
<e-node-annotations>
<e-node-annotation content="Custom Template">
</e-node-annotation>
</e-node-annotations>
</e-node>
</e-nodes>
<e-connectors>
<e-connector id='connector' type='Straight' sourceID='node1' targetID='node2'>
</e-connector>
</e-connectors>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public getNodeDefaults(node: NodeModel | any): NodeModel {
node.height = 100;
node.width = 100;
((node as NodeModel).style as ShapeStyleModel).fill = "#6BA5D7";
((node as NodeModel).style as ShapeStyleModel).strokeColor = "White";
return node;
}
public getConnectorDefaults(connector: ConnectorModel): void {
// Set Source Padding value
connector.sourcePadding = 20
// Set Target Padding value
connector.targetPadding = 20
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Advanced connector features
Line bridging for intersection handling
Line bridging creates visual bridges where connectors intersect, helping users distinguish between different connection paths in complex diagrams. By default, bridgeDirection is set to top, with the bridge appearing based on the specified direction.
Bridging can be enabled or disabled using either connector.constraints or diagram.constraints. The following code example illustrates how to enable line bridging.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, OnInit, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, ConnectorModel , ConnectorBridgingService, NodeModel, ShapeStyleModel, DiagramConstraints } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ConnectorBridgingService],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" [nodes] = 'nodes' [connectors] = 'connectors' [getNodeDefaults] ='getNodeDefaults' [constraints]='diagramConstraints'></ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public diagramConstraints?: DiagramConstraints;
ngOnInit(): void {
this.diagramConstraints = DiagramConstraints.Default | DiagramConstraints.Bridging;
}
public nodes: NodeModel[] = [{
id: 'Transaction',
width: 150,
height: 60,
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 60,
shape: {
type: 'Flow',
shape: 'Terminator'
},
annotations: [{
id: 'label1',
content: 'Start Transaction',
offset: { x: 0.5, y: 0.5 }
}]
},
{
id: 'Verification',
width: 150,
height: 60,
offsetX: 300,
offsetY: 250,
shape: {
type: 'Flow',
shape: 'Process'
},
annotations: [{
id: 'label2',
content: 'Verification',
offset: { x: 0.5, y: 0.5 }
}]
}];
public connectors: ConnectorModel[] = [{
id: 'connector1',
type: 'Straight',
sourceID: 'Transaction',
targetID: 'Verification'
},
{
id: 'connector2',
type: 'Straight',
sourcePoint: { x: 200, y: 130 },
targetPoint: { x: 400, y: 130 }
},
{
id: 'connector3',
type: 'Straight',
sourcePoint: { x: 200, y: 170 },
targetPoint: { x: 400, y: 170 }
}];
public getNodeDefaults(node: NodeModel): void {
node.height = 100;
node.width = 100;
((node as NodeModel).style as ShapeStyleModel).fill = "#6BA5D7";
((node as NodeModel).style as ShapeStyleModel).strokeColor = "White";
};
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Note: The
ConnectorBridgingmodule must be injected into the diagram to use this feature.
The bridgeSpace property of connectors defines the width for line bridging.
Limitation: Bezier segments do not support bridging functionality.
Hit padding for interaction
The hitPadding property defines the clickable area around the connector path, making it easier for users to select connectors, especially thin ones. This improves user experience by expanding the interactive zone without changing the visual appearance. The default value for hitPadding is 10.
The following code example illustrates how to specify hit padding for connectors.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, Diagram, DiagramModule,PointModel,ConnectorConstraints,ConnectorEditing } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
Diagram.Inject(ConnectorEditing);
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" >
<e-connectors>
<e-connector id='connector' type='Orthogonal' [sourcePoint]='sourcePoint' [targetPoint]='targetPoint' [constraints]="constraints" [hitPadding]="hitPadding">
</e-connector>
</e-connectors>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public constraints?: ConnectorConstraints;
public sourcePoint?: PointModel;
public targetPoint?: PointModel;
public hitPadding?:number;
ngOnInit(): void {
this.sourcePoint = { x: 100, y: 100 };
this.targetPoint = { x: 200, y: 200 };
this.hitPadding = 50;
this.constraints = ConnectorConstraints.Default | ConnectorConstraints.DragSegmentThumb
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Corner radius for rounded connectors
Corner radius creates connectors with rounded corners instead of sharp angles, providing a more polished appearance for diagrams. The radius of the rounded corner is set with the cornerRadius property.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, NodeModel, ConnectorModel, ShapeStyleModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [],
standalone: true,
selector: 'app-container',
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" [getNodeDefaults] ='getNodeDefaults' >
<e-nodes>
<e-node id='node1' [offsetX]=150 [offsetY]=150>
</e-node>
<e-node id='node2' [offsetX]=350 [offsetY]=350>
</e-node>
</e-nodes>
<e-connectors>
<e-connector id='connector' type='Orthogonal' sourceID='node1' sourcrPortID='port1' targetID='node2' targetPortID='port2' [cornerRadius]='cornerRadius'>
</e-connector>
</e-connectors>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public cornerRadius?: number;
ngOnInit(): void {
this.cornerRadius = 10;
}
public getNodeDefaults(node: NodeModel): void {
node.height = 100;
node.width = 100;
((node as NodeModel).style as ShapeStyleModel).fill = "#6BA5D7";
((node as NodeModel).style as ShapeStyleModel).strokeColor = "White";
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Connector Appearance
-
The connector’s
strokeWidth,strokeColor,strokeDashArray, andopacityproperties are used to customize the appearance of the connector segments. -
The
visibleproperty of the connector enables or disables the visibility of connector. -
Default values for all the
connectorscan be set using thegetConnectorDefaultsproperties. For example, if all connectors have the same type or having the same property then such properties can be moved intogetConnectorDefaults.
Segment appearance
The following code example illustrates how to customize the segment appearance.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, ConnectorModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" [connectors] ='connectors' [getConnectorDefaults] ='getConnectorDefaults'>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public connectors: ConnectorModel[] = [
{
id: 'connector1',
sourcePoint: { x: 100, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 200, y: 200 },
},
{
id: 'connector2',
// Set the visibility of the connector to false
visible: true,
type: 'Orthogonal',
sourcePoint: { x: 300, y: 300 },
targetPoint: { x: 400, y: 400 },
segments: [{
type: 'Orthogonal',
direction: 'Right',
length: 50,
}]
},
{
id: 'connector3',
// Set the visibility of the connector to false
visible: true,
type: 'Bezier',
sourcePoint: { x: 500, y: 100 },
targetPoint: { x: 600, y: 300 },
segments: [{ type: 'Bezier' }]
}
];
public getConnectorDefaults(connector: ConnectorModel): void {
connector.targetDecorator = {
style: {
strokeColor: '#6BA5D7',
fill: '#6BA5D7',
strokeWidth: 2,
}
};
connector.style = {
// Stroke color
strokeColor: '#6BA5D7',
fill: '#6BA5D7',
// Stroke width of the line
strokeWidth: 5,
// Line style
strokeDashArray: '2,2'
}
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Connector constraints and behavior
The constraints property of connectors enables or disables specific features such as selection, editing, deletion, or interaction behaviors.
To enable or disable constraints, refer to constraints.
The following code illustrates how to disable selection for a connector.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, PointModel, ConnectorConstraints } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" >
<e-connectors>
<e-connector id='connector1' type='Straight' [sourcePoint]='sourcePoint1' [targetPoint]='targetPoint1' [constraints]='constraints1'>
<e-connector-annotations>
<e-connector-annotation content="Connector Selection disabled">
</e-connector-annotation>
</e-connector-annotations>
</e-connector>
<e-connector id='connector2' type='Straight' [sourcePoint]='sourcePoint2' [targetPoint]='targetPoint2' [constraints]='constraints2'>
<e-connector-annotations>
<e-connector-annotation content="Connector Drag disabled">
</e-connector-annotation>
</e-connector-annotations>
</e-connector>
<e-connector id='connector3' type='Straight' [sourcePoint]='sourcePoint3' [targetPoint]='targetPoint3' [constraints]='constraints3'>
<e-connector-annotations>
<e-connector-annotation content="Connector Source end disabled">
</e-connector-annotation>
</e-connector-annotations>
</e-connector>
<e-connector id='connector4' type='Straight' [sourcePoint]='sourcePoint4' [targetPoint]='targetPoint4' [constraints]='constraints4'>
<e-connector-annotations>
<e-connector-annotation content="Connector Target end disabled">
</e-connector-annotation>
</e-connector-annotations>
</e-connector>
</e-connectors>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public sourcePoint1?: PointModel;
public targetPoint1?: PointModel;
public sourcePoint2?: PointModel;
public targetPoint2?: PointModel;
public sourcePoint3?: PointModel;
public targetPoint3?: PointModel;
public sourcePoint4?: PointModel;
public targetPoint4?: PointModel;
public constraints1?: ConnectorConstraints;
public constraints2?: ConnectorConstraints;
public constraints3?: ConnectorConstraints;
public constraints4?: ConnectorConstraints;
ngOnInit(): void {
this.sourcePoint1 = { x: 100, y: 100 };
this.targetPoint1 = { x: 200, y: 200 };
this.sourcePoint2 = { x: 300, y: 100 };
this.targetPoint2 = { x: 400, y: 200 };
this.sourcePoint3 = { x: 500, y: 100 };
this.targetPoint3 = { x: 600, y: 200 };
this.sourcePoint4 = { x: 700, y: 100 };
this.targetPoint4 = { x: 800, y: 200 };
this.constraints1 = ConnectorConstraints.Default & ~ConnectorConstraints.Select;
this.constraints2 = ConnectorConstraints.Default & ~ConnectorConstraints.Drag;
this.constraints3 = ConnectorConstraints.Default & ~ConnectorConstraints.DragSourceEnd;
this.constraints4 = ConnectorConstraints.Default & ~ConnectorConstraints.DragTargetEnd;
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Additional connector properties
Adding custom information
The addInfo property of connectors allows maintaining additional information or metadata associated with connectors for application-specific requirements.
<e-connectors>
<e-connector id='connector1' type='Straight' addInfo='centralconnector' [sourcePoint]='sourcePoint1' [targetPoint]='targetPoint1' [constraints]='constraints'></e-connector>
</e-connectors>Z-index for layering control
The zIndex property specifies the stack order of connectors. A connector with a greater stack order appears in front of connectors with lower stack orders, enabling precise control over visual layering.
The following code illustrates how to render connector based on the stack order.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, PointModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" >
<e-connectors>
<e-connector id='connector1' type='Straight' zIndex=2 [sourcePoint]='sourcePoint1' [targetPoint]='targetPoint1'></e-connector>
<e-connector id='connector2' type='Straight' zIndex=1 [sourcePoint]='sourcePoint2' [targetPoint]='targetPoint2'></e-connector>
</e-connectors>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public sourcePoint1?: PointModel;
public targetPoint1?: PointModel;
public sourcePoint2?: PointModel;
public targetPoint2?: PointModel;
ngOnInit(): void {
this.sourcePoint1 = { x: 300, y: 100 };
this.targetPoint1 = { x: 300, y: 200 };
this.sourcePoint2 = { x: 100, y: 100 };
this.targetPoint2 = { x: 200, y: 200 };
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Connector spacing for routing
The connectorSpacing property defines the minimum distance between the source node and the connector when automatic routing occurs. This determines how far the connector will reroute around obstacles or the minimum length for new segments.
The following code example illustrates how to configure connector spacing.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, DiagramModule, NodeModel, FlowShapeModel, ConnectorModel, ShapeStyleModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" [getNodeDefaults] ='getNodeDefaults'>
<e-nodes>
<e-node id='Start' [offsetX]=300 [offsetY]=100 [shape] = "shape1">
<e-node-annotations>
<e-node-annotation
id='label1' content="Start">
</e-node-annotation>
</e-node-annotations>
</e-node>
<e-node id='Init' [offsetX]=300 [offsetY]=300 [shape] = "shape2">
<e-node-annotations>
<e-node-annotation content="var i = 0;">
</e-node-annotation>
</e-node-annotations>
</e-node>
</e-nodes>
<e-connectors>
<e-connector id='connector1' type='Orthogonal' sourceID='Start' targetID='Init' connectorSpacing='connectorSpacing'>
</e-connector>
</e-connectors>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public connectorSpacing?: number;
public shape1: FlowShapeModel = {
type: 'Flow',
shape: 'Terminator'
};
public shape2: FlowShapeModel = {
type: 'Flow',
shape: 'Process'
};
ngOnInit(): void {
this.connectorSpacing = 7;
};
public getNodeDefaults(node: NodeModel): void {
node.height = 100;
node.width = 100;
(node.style as ShapeStyleModel).fill = "#6BA5D7";
};
};import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Maximum segment thumbs
The maxSegmentThumb property limits the number of segment manipulation handles displayed on a connector, helping maintain clean interfaces in complex diagrams.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramModule, DiagramComponent, Diagram, OrthogonalSegmentModel, ConnectorEditing, PointModel,ConnectorConstraints } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
Diagram.Inject(ConnectorEditing);
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" >
<e-connectors>
<e-connector id='connector' type='Orthogonal' [sourcePoint]='sourcePoint' [targetPoint]='targetPoint' [segments]='segments' [constraints]= "constraints" [maxSegmentThumb]='maxSegmentThumb'>
</e-connector>
</e-connectors>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public sourcePoint?: PointModel;
public targetPoint?: PointModel;
public segments?: OrthogonalSegmentModel;
public maxSegmentThumb?: number;
public constraints ?: ConnectorConstraints ;
ngOnInit(): void {
this.maxSegmentThumb = 4;
this.constraints =ConnectorConstraints.Default | ConnectorConstraints.DragSegmentThumb;
this.sourcePoint = { x: 300, y: 100 };
this.targetPoint = { x: 350, y: 150 };
this.segments = [
{ type: 'Orthogonal', direction: 'Bottom', length: 150 },
{ type: 'Orthogonal', direction: 'Right', length: 150 },
{ type: 'Orthogonal', direction: 'Top', length: 100 },
{ type: 'Orthogonal', direction: 'Left', length: 100 }
];
};
};import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));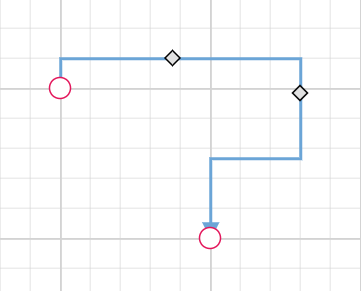
Reset segments to default state
The resetSegments method resets connector segments to their default state based on connection points. This operation removes custom segments and restores connectors to their original configuration, useful for cleaning up user modifications.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramComponent, Diagram, NodeModel, ConnectorModel, OrthogonalSegmentModel, ConnectorEditing, PointModel, ConnectorConstraints, HierarchicalTree, DiagramModule,ShapeStyleModel } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
Diagram.Inject(ConnectorEditing,HierarchicalTree);
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `
<button (click)="resetSegments()">resetSegments</button>
<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" [getNodeDefaults] ='getNodeDefaults'
>
<e-nodes>
<e-node id='node1' [offsetX]=150 [offsetY]=150
>
<e-node-annotations>
<e-node-annotation content="node 1">
</e-node-annotation>
</e-node-annotations>
</e-node>
<e-node id='node2' [offsetX]=350 [offsetY]=350>
<e-node-annotations>
<e-node-annotation content="node 2">
</e-node-annotation>
</e-node-annotations>
</e-node>
</e-nodes>
<e-connectors>
<e-connector id='connector' type='Orthogonal' sourceID='node1' sourcrPortID='port1' targetID='node2' targetPortID='port2' [constraints]='constraints'>
</e-connector>
</e-connectors>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public sourcePoint?: PointModel;
public targetPoint?: PointModel;
public segments?: OrthogonalSegmentModel;
public maxSegmentThumb?: number;
ngOnInit(): void {
this.sourcePoint = { x: 300, y: 100 };
this.targetPoint = { x: 350, y: 150 };
this.segments = [
{ type: 'Orthogonal', direction: 'Bottom', length: 150 },
{ type: 'Orthogonal', direction: 'Right', length: 150 },
{ type: 'Orthogonal', direction: 'Top', length: 100 },
{ type: 'Orthogonal', direction: 'Left', length: 100 }
];
};
public getNodeDefaults(node: NodeModel| any): void {
node.height = 100;
node.width = 100;
((node as NodeModel).style as ShapeStyleModel).fill = "#6BA5D7";
((node as NodeModel).style as ShapeStyleModel).strokeColor = "White";
node.expandIcon = {
height: 15,
width: 15,
shape: "Plus",
fill: 'lightgray',
offset: {
x: .5,
y: .85
}
};
node.collapseIcon.offset = {
x: .5,
y: .85
};
node.collapseIcon.height = 15;
node.collapseIcon.width = 15;
node.collapseIcon.shape = "Minus";
}
constraints = ConnectorConstraints.Default | ConnectorConstraints.DragSegmentThumb;
resetSegments() {
(this.diagram as any).resetSegments();
}
};import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Dynamic connector manipulation
Enable connector splitting
Connector splitting allows creating new connections when a node is dropped onto an existing connector. The connector splits at the drop point, creating connections between the new node and the existing connected nodes. Enable this feature by setting enableConnectorSplit to true. The default value is false.
The following code illustrates how to enable connector splitting functionality.
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, OnInit, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { DiagramModule, DiagramComponent, NodeModel, ConnectorModel,ConnectorConstraints } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" [enableConnectorSplit]="enableConnectorSplit" [nodes]='nodes' [connectors]='connectors'>
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public enableConnectorSplit: boolean = true;
public constraints?: ConnectorConstraints;
public nodes: NodeModel[] = [
{ id: 'node1', offsetX: 150, offsetY: 150, width: 100, height: 100, annotations: [{ content: 'node1' }] },
{ id: 'node2', offsetX: 650, offsetY: 150, width: 100, height: 100, annotations: [{ content: 'node2' }] },
{ id: 'node3', offsetX: 490, offsetY: 290, width: 100, height: 100, annotations: [{ content: 'node3' }] }
];
public connectors: ConnectorModel[] = [{
id: 'connector1',sourceID:"node1",targetID:"node2",
constraints: ConnectorConstraints.Default | ConnectorConstraints.AllowDrop
}
];
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));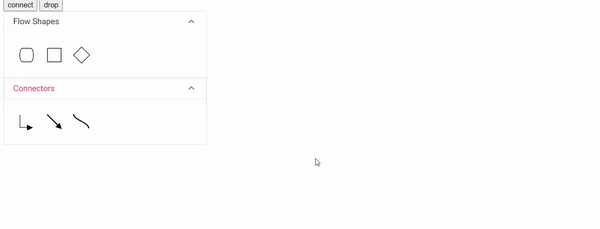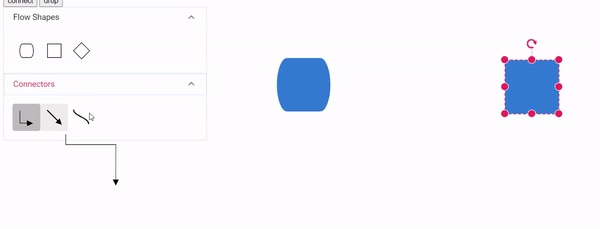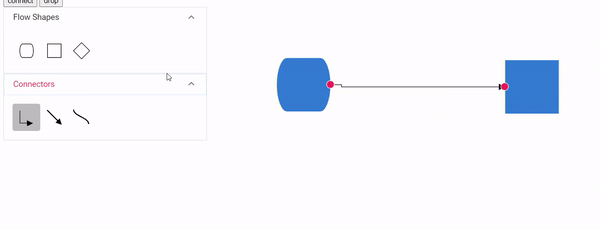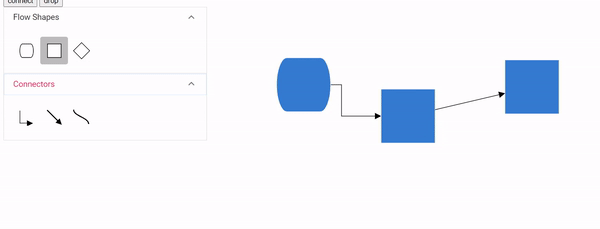
Preserve Connector Styling when Splitting
When splitting a connector using enableConnectorSplit, the newly created connector appears as a default connector without inheriting the original connector’s styling. To maintain consistent styling, use the collectionChange event to apply the original connector’s properties to the new connector.
The following example demonstrates how to preserve the original connector’s styling for newly created connectors during splitting:
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { Connector, DiagramModule, DiagramComponent, NodeModel, ConnectorModel,ConnectorConstraints,ICollectionChangeEventArgs,Node } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-diagrams';
@Component({
imports: [
DiagramModule
],
providers: [ ],
standalone: true,
selector: "app-container",
template: `<ejs-diagram #diagram id="diagram" width="100%" height="580px" [enableConnectorSplit]="enableConnectorSplit" [nodes]='nodes' [connectors]='connectors' [getConnectorDefaults] ='getConnectorDefaults' (collectionChange)="collectionChange($event)">
</ejs-diagram>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
@ViewChild("diagram")
public diagram?: DiagramComponent;
public enableConnectorSplit: boolean = true;
public nodes: NodeModel[] = [
{ id: 'node1', offsetX: 150, offsetY: 150, width: 100, height: 100, annotations: [{ content: 'node1' }] },
{ id: 'node2', offsetX: 650, offsetY: 150, width: 100, height: 100, annotations: [{ content: 'node2' }] },
{ id: 'node3', offsetX: 490, offsetY: 290, width: 100, height: 100, annotations: [{ content: 'node3' }] }
];
public connectors: ConnectorModel[] = [{
id: 'connector1',sourceID:"node1",targetID:"node2", style:{strokeColor: 'red', strokeWidth: 2, strokeDashArray: '3,3' },
}
];
public getConnectorDefaults(obj: ConnectorModel): void {
obj.constraints = ConnectorConstraints.Default | ConnectorConstraints.AllowDrop
}
public collectionChange(args: ICollectionChangeEventArgs): void {
if (args.state === 'Changed' && args.element instanceof Connector) {
let sourceNode: Node | null = this.diagram?.getObject(args.element.sourceID) as Node;
if (sourceNode) {
sourceNode.inEdges.forEach((edgeId) => {
let initialConnector = this.diagram?.getObject(edgeId) as ConnectorModel;
if (initialConnector) {
args.element.style = initialConnector.style
}
});
}
}
this.diagram?.dataBind();
}
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));