Syncfusion® Angular Components - Security
14 Aug 20257 minutes to read
Security is paramount in web application development to guard against various threats and vulnerabilities. Essential practices include using HTTPS for data encryption, validating and sanitizing user inputs, and implementing robust authentication measures such as multi-factor authentication.
Syncfusion® Angular components are engineered with these critical security measures in mind, integrating seamlessly with Angular’s built-in security features.
Security Vulnerabilities
Security vulnerabilities in web applications arise from weaknesses in the design, implementation, or configuration, potentially compromising the resources and data. Below are some common vulnerabilities:
-
Cross-Site Scripting - XSS is a security vulnerability that can occur in web applications. These scripts can steal session cookies, redirect users to malicious websites, or deface the website. XSS vulnerabilities typically arise when the application fails to properly validate or encode user-supplied input before rendering it in the browser.
-
Cross-Site Request Forgery - CSRF is a type of web security vulnerability that allows an attacker to force a logged-in user to perform actions on a web application without their consent or knowledge. CSRF attacks exploit the trust that a web application has in the user’s browser by tricking it into sending unauthorized requests to the vulnerable application.
-
Injection Attacks - These occur when an attacker injects malicious code (such as SQL injection, XML injection, or command injection) into input fields or parameters of a web application. If the application does not properly sanitize or validate user inputs, it can execute unintended commands or gain unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Syncfusion® Angular components support the implementation of secure web applications by addressing these vulnerabilities.
Security Considerations
Security should be a foundational aspect of software development. Syncfusion® adheres to comprehensive security protocols in the development of Angular components, focusing on the following aspects:
Content Security Policy
Content Security Policy (CSP) is a one of the security feature, that helps the detect the cross-site-scripting(XSS) attacks and malicious code injection. It will throw the errors and warnings while using the inline-styles and inline scripts, eval, new Function, etc in your applications.
Syncfusion® has taken significant steps to ensure that all EJ2 components are fully CSP-compliant. This means that our components no longer rely on practices that violate CSP directives, such as embedding inline styles or scripts. Instead, we have adopted secure coding practices that align with CSP standards, ensuring that our components can be seamlessly integrated into applications with strict CSP policies.
Our Document Editor product offers robust support for a strict Content Security Policy (CSP) to enhance security by preventing unauthorized content from being executed. While most features comply with strict CSP settings, there is one notable exception related to custom fonts. The setCustomFonts method is incompatible with strict CSP settings. Therefore, when enforcing a strict CSP, setCustomFonts may not function as expected.
Benefits of CSP Compliance in Syncfusion® EJ2 Components
-
Enhanced Security: By eliminating the use of unsafe practices, Syncfusion® EJ2 components reduce the risk of XSS attacks and other client-side vulnerabilities.
-
Seamless Integration: Developers can use Syncfusion® Angular components in applications with strict CSP configurations without requiring additional adjustments or exceptions.
-
Future-Proof Design: Adhering to CSP standards ensures compatibility with modern web security requirements, making Syncfusion® components a reliable choice for secure application development.
-
No Additional Configuration: Since Syncfusion® EJ2 components are CSP-compliant by design, developers do not need to include specific CSP directives or modify their existing policies to accommodate our components.
By adhering to CSP standards, Syncfusion® components provide a robust foundation for building secure and scalable web applications. This ensures that your applications are not only protected against common vulnerabilities but also meet the highest security standards.
To know more information about the CSP, refer this documentation.
CSP Directives
For using Syncfusion® Angular components effectively, the following directives are advised:
| Directives | Description | Examples |
|——————|——————-|—————-|
| font-src | Defines the allowed sources for loading fonts. It helps prevent font-related security issues by restricting the locations from which fonts can be loaded. | font-src 'self' https://fonts.googleapis.com/ https://fonts.gstatic.com/ data: cdn.syncfusion.com 'unsafe-inline'; |
| img-src | Specifies the allowed sources for loading images. It helps control from where images can be displayed on the web page. | img-src 'self' data:" |
Utilizing a web worker within the Spreadsheet Control for exporting necessitates the addition of a specific directive to ensure proper functionality during the export process.
worker-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' * blob:;
CSP Sources
The following sources refer to the origins from which resources such as styles, images and fonts are allowed to be loaded and executed on a web page.
| Source | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
self |
Refers to the origin from which the protected document is being served, including the same URL scheme and port number | style-src 'self' |
data |
Enables a website to fetch resources using the data scheme, such as loading Base64-encoded images. | img-src 'self' data: |
Note: While using the PDF Viewer component for standalone components, you need to use unsafe-eval to avoid CSP issues. The PDF Viewer component is not yet converted to be fully CSP-compliant.
HTML Sanitizer
An HTML sanitizer removes potentially harmful code from HTML documents, preventing XSS attacks by eliminating malicious code like script tags or inline styles.
Syncfusion® ensures security by offering the enableHtmlSanitizer API. It sanitizes HTML strings, reducing potential threats.
The enableHtmlSanitizer property, when enabled, ensures content undergoes rigorous sanitization to mitigate XSS risks, strengthening component security.
Here is a sample code to sanitize input values using Syncfusion®:
import { SanitizeHtmlHelper } from '@syncfusion/ej2-base';
let html: string = '<script>alert("XSS");</script>';
let sanitizedHtml: string = SanitizeHtmlHelper.sanitize(html);When enableHtmlSanitizer is true, the content will be sanitized and displays the code.
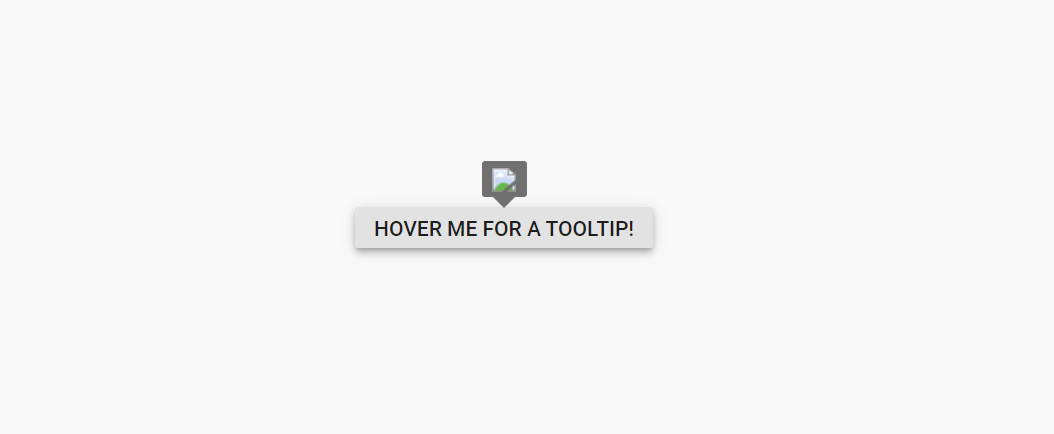
When enableHtmlSanitizer is false or not included this property, the malicious code will be interpreted as script, and the alert pop-up window will be open.
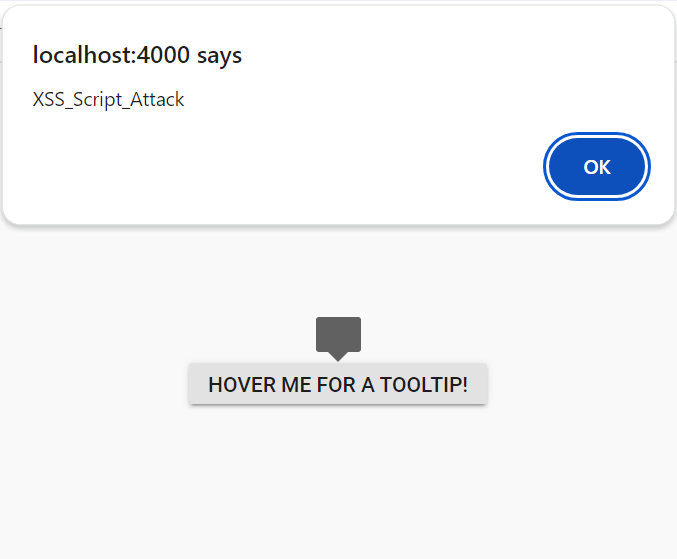
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser'
import { TooltipModule } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-popups'
import { ButtonModule } from '@syncfusion/ej2-angular-buttons'
import { Component, ViewEncapsulation } from '@angular/core';
import { Droppable } from '@syncfusion/ej2-base';
@Component({
imports: [
TooltipModule,
ButtonModule
],
standalone: true,
selector: 'app-root',
template: `
<div id='container' style="display: inline-block; position: relative; left: 50%;top: 100px;transform: translateX(-50%);">
<ejs-tooltip id='tooltip' content='<img src=text onerror=alert("XSS_Script_Attack") \/>' target="#target">
<button ejs-button id="target">Hover me for a tooltip!</button>
</ejs-tooltip>
</div>`,
encapsulation: ViewEncapsulation.None
})
export class AppComponent {
}import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import 'zone.js';
bootstrapApplication(AppComponent).catch((err) => console.error(err));Browser Storage
Browser storage refers to the mechanisms provided by web browsers to store data locally on a user’s device. Syncfusion® Angular components utilize the following storage options only.
- Local Storage
Local Storage
Local Storage allows persistent data storage on client devices using key-value pairs, accessible through Angular. Syncfusion® uses local storage only when persistence is enabled.