How can I help you?
Remote Data Binding with Custom REST API using WebMethod
23 Feb 202624 minutes to read
The WebMethodAdaptor in Syncfusion® React Grid facilitates data binding from remote services using web methods. This powerful feature enables efficient communication between the client-side application and the server. The WebMethodAdaptor, like the URLAdaptor, sends query parameters encapsulated within an object named value. Within this value object, various datamanager properties such as requiresCounts, skip, take, sorted, and where queries are included.
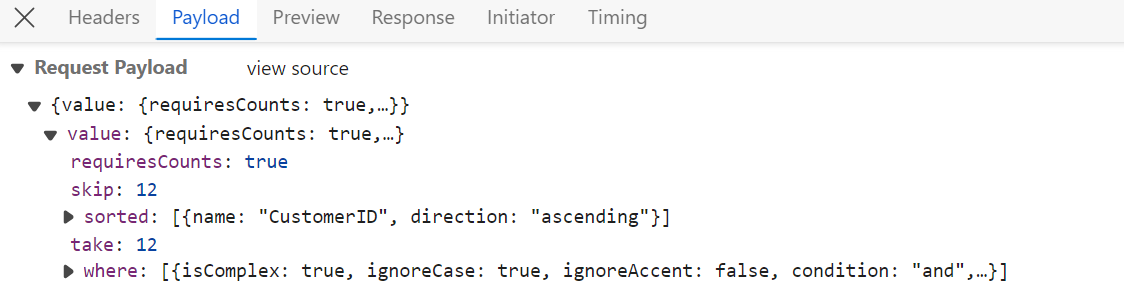
For complete server‑side configuration and additional implementation details, refer to the DataManager Webmethod Adaptor documentation, which covers endpoint setup, query processing, and best practices for integrating WebMethod‑based services.
Once the project creation and backend setup are complete, the next step is to render the Syncfusion® React Grid Component on the client side.
Project structure:
WebMethodAdaptor/
├── WebMethodAdaptor.client/ # React frontend (Vite/React project).
│ ├── src/
│ │ ├── App.css
│ │ └── App.jsx # Add WebMethodAdaptor here.
│ └── package.json
└── WebMethodAdaptor.Server/ # ASP.NET Core backend (API).
├── Controllers/ # API controllers (will be created here).
├── Models/ # Data models (will be created here).
└── Program.cs # Server configuration.
React Grid frontend setup using Syncfusion WebMethodAdaptor
After finishing the backend setup for the WebMethodAdaptor ASP.NET Core project, next step is to integrate the Syncfusion® React Grid on the client side by following these instructions.
Step 1: Install Syncfusion packages
Right‑click the WebMethodAdaptor.client folder in Solution Explorer and select Open in Terminal (available in newer Visual Studio versions), or open a Developer Command prompt/PowerShell from the Start menu and navigate manually to the WebMethodAdaptor.client. Once inside the folder, confirm that package.json is present, then run the following commands to install the required Syncfusion® packages:
npm install @syncfusion/ej2-react-grids --save
npm install @syncfusion/ej2-data --saveStep 2: Add CSS styles
Navigate to the src folder and open (or create) the stylesheet such as styles.css or App.css, then add the required CSS import statements to apply the Grid’s styling.
/* Base styles - Required for all Syncfusion components */
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-base/styles/material3.css';
/* Component-specific styles */
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-buttons/styles/material3.css';
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-calendars/styles/material3.css';
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-dropdowns/styles/material3.css';
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-inputs/styles/material3.css';
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-navigations/styles/material3.css';
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-popups/styles/material3.css';
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/material3.css';
/* Grid component styles - Required */
@import '../node_modules/@syncfusion/ej2-react-grids/styles/material3.css';Import the App.css in the application entry point(App.jsx).
import "./App.css";
...
...Step 3: Create React Grid component with WebMethodAdaptor
Grid integration with server‑side Web Methods is enabled through the WebMethodAdaptor, which acts as a bridge between the Syncfusion DataManager and Web Forms based endpoints such as ASMX services and Page Methods. It automatically converts Grid actions such as paging, sorting, filtering, searching, and grouping into structured POST requests that the server can process.
By delegating these operations to the server rather than executing them in the browser, the Grid ensures that only the required data is retrieved for each request.
import { DataManager, WebMethodAdaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
import { ColumnDirective, ColumnsDirective, GridComponent } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-grids';
function App() {
const data = new DataManager({
url:'https://localhost:xxxx/api/grid', // Here xxxx represents the port number
adaptor: new WebMethodAdaptor(),
crossDomain: true
});
return <GridComponent dataSource={data} >
<ColumnsDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='OrderID' headerText='Order ID' isPrimaryKey={true} width='150'textAlign='Right'></ColumnDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='CustomerID' headerText='Customer ID' width='150'></ColumnDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='ShipCity' headerText='Ship City' width='150'/>
<ColumnDirective field='ShipCountry' headerText='Ship Country' width='150'/>
</ColumnsDirective>
</GridComponent>
};
export default App;The Grid sends a
DataManagerRequestvia POST to a Web Method, and the server returns JSON in the format { result: […], count: N } for proper data binding and paging.
Server-side data operations
React Grid optimizes large datasets by relying on server‑side data operations such as filtering, sorting, and paging rather than processing everything in the browser. The Syncfusion.EJ2.AspNet.Core package supports this approach by providing built‑in methods that efficiently handle these operations on the server, ensuring smooth performance even with heavy data loads.
Server-side operation methods
The Syncfusion.EJ2.Base namespace provides these methods:
| Operation | Method(s) | Purpose | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paging |
PerformSkip, PerformTake
|
Load specific page of data. | Show “10” records at a time from “100K” records. |
| Filtering | PerformFiltering |
Apply filter conditions. | Show only orders from “Germany”. |
| Searching | PerformSearching |
Search across columns | Find all records containing “ALFKI”. |
| Sorting | PerformSorting |
Sort by one/multiple columns. | Order by “CustomerID” ascending. |
| Grouping | PerformGrouping |
Group data with aggregates. | Group by “ShipCountry” with totals. |
Add the following package import to enable server‑side DataManager operations:
[GridController.cs]
using Syncfusion.EJ2.Base; // DataManagerRequest, QueryableOperation, DataOperations
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using WebMethodAdaptorDemo.Server.Models;
namespace WebMethodAdaptorDemo.Controllers
{
. . .
. . .
}It must have
Syncfusion.EJ2.AspNet.CoreNuGet package installed (covered in WebMethod backend setup documentation).
In the WebMethodAdaptor configuration, the DataManager request payload is wrapped inside a value object. To properly access the DataManagerRequest on the server, a dedicated class is defined to represent this value wrapper. This ensures that the server can deserialize the incoming request and retrieve the DataManagerRequest details correctly.
[GridController.cs]
using Syncfusion.EJ2.Base; // DataManagerRequest, QueryableOperation, DataOperations
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using WebMethodAdaptorDemo.Server.Models;
namespace WebMethodAdaptorDemo.Controllers
{
// Model for handling data manager requests
public class DataManager
{
public required DataManagerRequest Value { get; set; }
}
}Paging
The paging feature is enabled by setting the allowPaging property to true and injecting the Page module from @syncfusion/ej2-react-grids into the grid.
<GridComponent dataSource={data} allowPaging={true}>
. . .
. . .
. . .
<Inject services={[Page]}/>
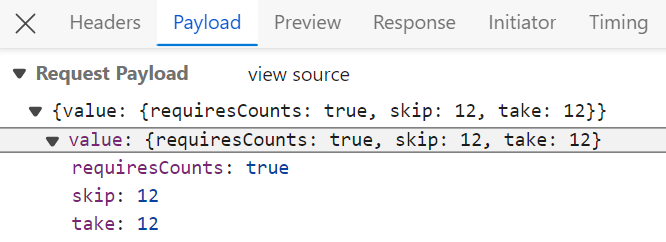
</GridComponent>After enabling paging on the client side, the server processes the incoming page requests using the PerformSkip and PerformTake methods. These methods, provided by the QueryableOperation class, apply paging based on the values received in the DataManagerRequest.
[HttpPost]
public object Post([FromBody] DataManager DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database)
IQueryable<OrdersDetails> DataSource = GetOrderData().AsQueryable();
// Get the total records count
int totalRecordsCount = DataSource.Count();
QueryableOperation queryableOperation = new QueryableOperation(); // Initialize QueryableOperation instance
// Retrieve data manager value
DataManagerRequest DataManagerParams = DataManagerRequest.Value;
// Handling paging operation.
if (DataManagerParams.Skip != 0)
{
// Paging
DataSource = queryableOperation.PerformSkip(DataSource, DataManagerParams.Skip);
}
if (DataManagerParams.Take != 0)
{
DataSource = queryableOperation.PerformTake(DataSource, DataManagerParams.Take);
}
// Return data based on the request
return new { result = DataSource, count = totalRecordsCount };
}
// Model for handling data manager requests
public class DataManager
{
public required DataManagerRequest Value { get; set; }
}import { DataManager, WebMethodAdaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
import { ColumnDirective, ColumnsDirective, GridComponent, Page, Inject } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-grids';
function App() {
const data = new DataManager({
url:'https://localhost:xxxx/api/grid', // Here xxxx represents the port number.
adaptor: new WebMethodAdaptor()
});
return <GridComponent dataSource={data} allowPaging={true} height={320}>
<ColumnsDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='OrderID' headerText='Order ID' isPrimaryKey={true} width='150'textAlign='Right'></ColumnDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='CustomerID' headerText='Customer ID' width='150'></ColumnDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='ShipCity' headerText='Ship City' width='150'/>
</ColumnsDirective>
<Inject services={[Page]} />
</GridComponent>
};
export default App;The following example demonstrates the server’s handling of paging requests sent from the client.
Filtering
The filtering feature is enabled by setting the allowFiltering property to true and injecting the Filter module from @syncfusion/ej2-react-grids into the grid.
<GridComponent dataSource={data} allowFiltering={true}>
. . .
. . .
. . .
<Inject services={[Filter]}/>
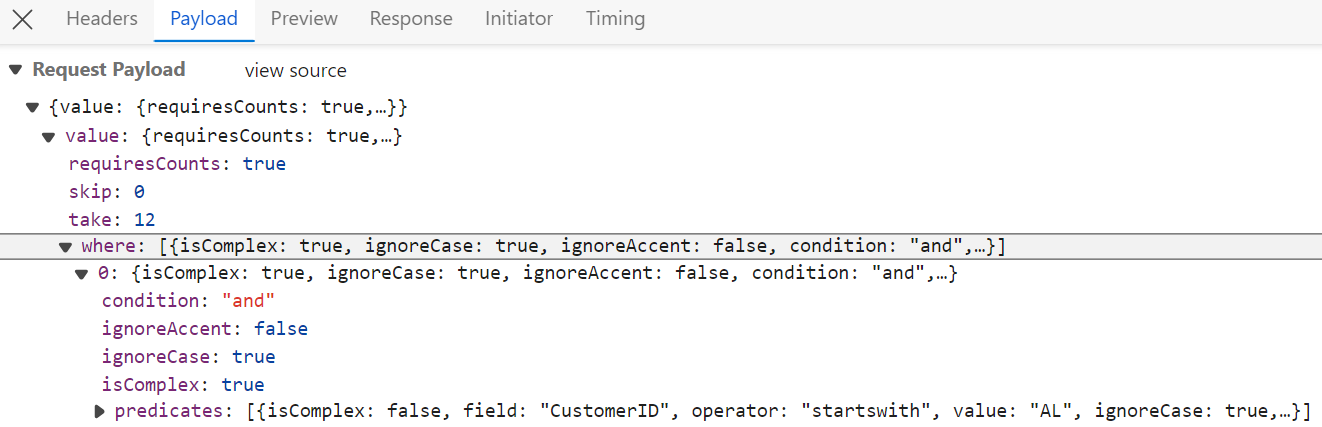
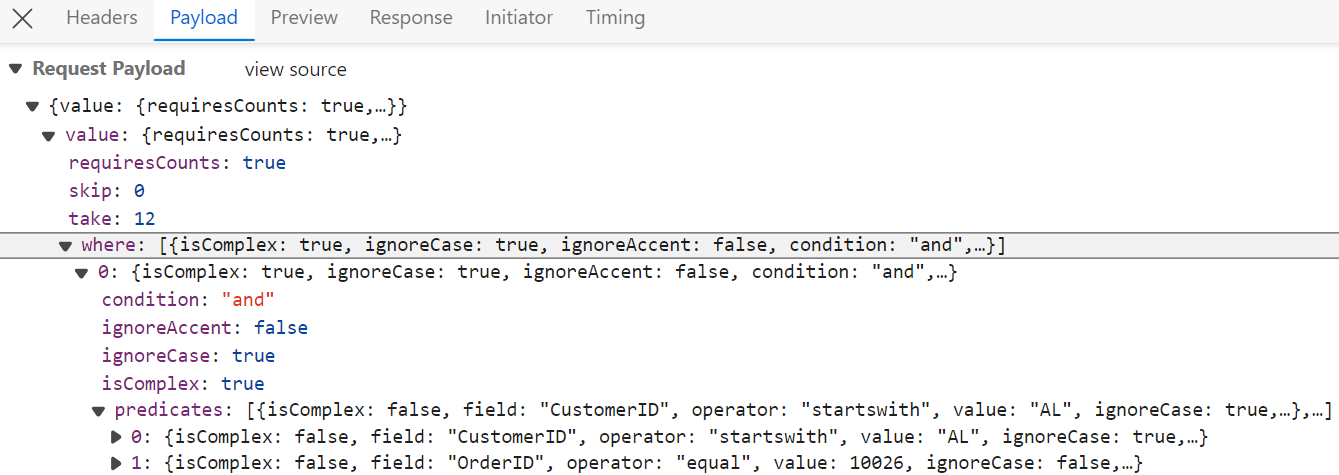
</GridComponent>After enabling filtering on the client side, the server processes incoming filter requests using the PerformFiltering method. This method, provided by the QueryableOperation class, applies filtering based on the conditions received in the DataManagerRequest.
Single column filtering
Multi column filtering
[HttpPost]
public object Post([FromBody] DataManager DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database)
IQueryable<OrdersDetails> DataSource = GetOrderData().AsQueryable();
QueryableOperation queryableOperation = new QueryableOperation(); // Initialize QueryableOperation instance
// Retrieve data manager value
DataManagerRequest DataManagerParams = DataManagerRequest.Value;
if (DataManagerParams.Where != null && DataManagerParams.Where.Count > 0)
{
// Handling filtering operation
foreach (var condition in DataManagerParams.Where)
{
foreach (var predicate in condition.predicates)
{
DataSource = queryableOperation.PerformFiltering(DataSource, DataManagerParams.Where, predicate.Operator);
}
}
}
// Get the total records count
int totalRecordsCount = DataSource.Count();
// Return data based on the request
return new { result = DataSource, count = totalRecordsCount };
}
// Model for handling data manager requests
public class DataManager
{
public required DataManagerRequest Value { get; set; }
}import { DataManager, WebMethodAdaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
import { ColumnDirective, ColumnsDirective, GridComponent, Inject, Filter } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-grids';
function App() {
const data = new DataManager({
url:'https://localhost:xxxx/api/grid', // Here xxxx represents the port number.
adaptor: new WebMethodAdaptor()
});
return <GridComponent dataSource={data} allowFiltering={true}>
<ColumnsDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='OrderID' headerText='Order ID' isPrimaryKey={true} width='150'textAlign='Right'></ColumnDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='CustomerID' headerText='Customer ID' width='150'></ColumnDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='ShipCity' headerText='Ship City' width='150'/>
</ColumnsDirective>
<Inject services={[Filter]} />
</GridComponent>
};
export default App;Searching
The searching feature is enabled by configuring the toolbar property with Search item and injecting the Toolbar and Search modules from @syncfusion/ej2-react-grids into the grid.
<GridComponent dataSource={data} toolbar={['Search']}>
. . .
. . .
. . .
<Inject services={[Search,Toolbar]}/>
</GridComponent>After enabling the search feature on the client side, the server processes incoming search requests using the PerformSearching method. This method, provided by the QueryableOperation class, applies search criteria based on the values received in the DataManagerRequest.
[HttpPost]
public object Post([FromBody] DataManager DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database)
IQueryable<OrdersDetails> DataSource = GetOrderData().AsQueryable();
QueryableOperation queryableOperation = new QueryableOperation(); // Initialize QueryableOperation instance
// Retrieve data manager value
DataManagerRequest DataManagerParams = DataManagerRequest.Value;
// Handling Searching
if (DataManagerParams.Search != null && DataManagerParams.Search.Count > 0)
{
DataSource = queryableOperation.PerformSearching(DataSource, DataManagerParams.Search);
}
// Get the total records count
int totalRecordsCount = DataSource.Count();
// Return data based on the request
return new { result = DataSource, count = totalRecordsCount };
}
// Model for handling data manager requests
public class DataManager
{
public required DataManagerRequest Value { get; set; }
}import { DataManager, WebMethodAdaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
import { ColumnDirective, ColumnsDirective, GridComponent, Toolbar, ToolbarItems } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-grids';
function App() {
const data = new DataManager({
url:'https://localhost:xxxx/api/grid', // Here xxxx represents the port number.
adaptor: new WebMethodAdaptor()
});
const toolbar: ToolbarItems[] = ['Search'];
return <GridComponent dataSource={data} toolbar={toolbar} height={320}>
<ColumnsDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='OrderID' headerText='Order ID' isPrimaryKey={true} width='150'textAlign='Right'></ColumnDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='CustomerID' headerText='Customer ID' width='150'></ColumnDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='ShipCity' headerText='Ship City' width='150'/>
</ColumnsDirective>
<Inject services={[Toolbar]} />
</GridComponent>
};
export default App;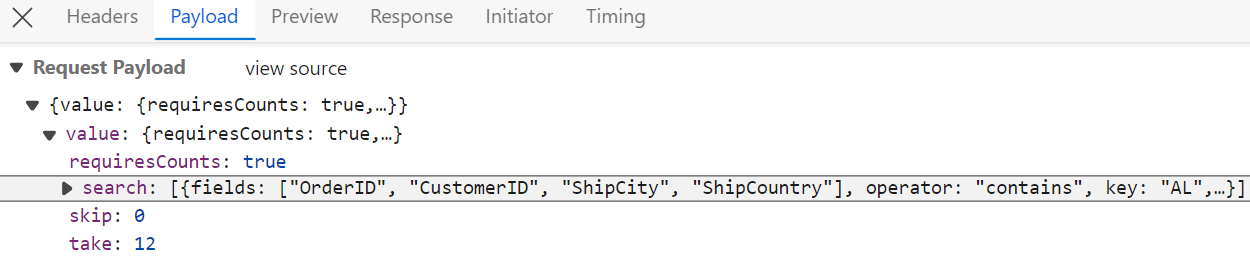
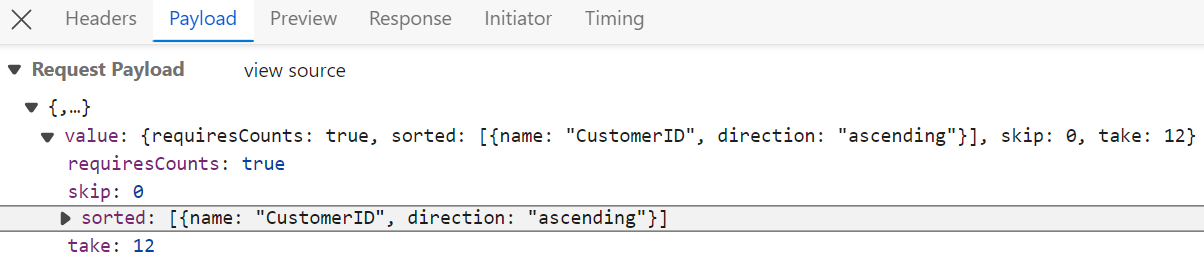
Sorting
The sorting feature is enabled by setting the allowSorting property to true and injecting the Sort module from @syncfusion/ej2-react-grids into the grid.
<GridComponent dataSource={data} allowSorting={true}>
. . .
. . .
. . .
<Inject services={[Sort]}/>
</GridComponent>After enabling sorting on the client side, the server processes incoming sort requests using the PerformSorting method. This method, provided by the QueryableOperation class, applies the sorting rules received in the DataManagerRequest.
[HttpPost]
public object Post([FromBody] DataManager DataManagerRequest)
{
// Retrieve data from the data source (e.g., database)
IQueryable<OrdersDetails> DataSource = GetOrderData().AsQueryable();
QueryableOperation queryableOperation = new QueryableOperation(); // Initialize QueryableOperation instance
// Retrieve data manager value
DataManagerRequest DataManagerParams = DataManagerRequest.Value;
// Handling Sorting operation
if (DataManagerParams.Sorted != null && DataManagerParams.Sorted.Count > 0)
{
DataSource = queryableOperation.PerformSorting(DataSource, DataManagerParams.Sorted);
}
// Get the total count of records
int totalRecordsCount = DataSource.Count();
// Return data based on the request
return new { result = DataSource, count = totalRecordsCount };
}
// Model for handling data manager requests
public class DataManager
{
public required DataManagerRequest Value { get; set; }
}import { DataManager, WebMethodAdaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
import { ColumnDirective, ColumnsDirective, GridComponent, Sort } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-grids';
function App() {
const data = new DataManager({
url:'https://localhost:xxxx//Orders', // Here xxxx represents the port number.
adaptor: new WebMethodAdaptor()
});
return <GridComponent dataSource={data} allowSorting={true} height={320}>
<ColumnsDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='OrderID' headerText='Order ID' isPrimaryKey={true} width='150'textAlign='Right'></ColumnDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='CustomerID' headerText='Customer ID' width='150'></ColumnDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='ShipCity' headerText='Ship City' width='150'/>
</ColumnsDirective>
<Inject services={[Sort]} />
</GridComponent>
};
export default App;Single column sorting
Multi column sorting
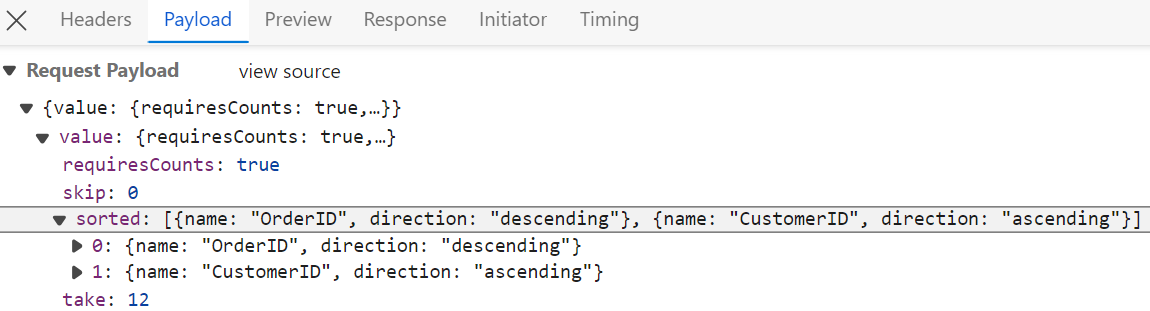
Sort indicator legend:
- ↑ (Up arrow): Indicates ascending sort direction.
- ↓ (Down arrow): Indicates descending sort direction.
- Numeric indicator (1, 2, 3): Displays sort priority in multi-column sorting scenarios.
The Grid has now been successfully created with including paging, sorting, filtering. the next step is to enabling CRUD operations.
CRUD operations
The Syncfusion® React Grid Component seamlessly integrates CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations with server-side controller actions through specific properties: insertUrl, removeUrl, updateUrl, crudUrl, and batchUrl. These properties enable the grid to communicate with the data service for every grid action, facilitating server-side operations.
CRUD Operations Mapping
CRUD operations within the grid can be mapped to server-side controller actions using specific properties:
- insertUrl: Specifies the URL for inserting new data.
- removeUrl: Specifies the URL for removing existing data.
- updateUrl: Specifies the URL for updating existing data.
- crudUrl: Specifies a single URL for all CRUD operations.
- batchUrl: Specifies the URL for batch editing.
To enable editing in React Grid component, refer to the editing documentation. In the below example, the inline edit mode is enabled and toolbar property is configured to display toolbar items for editing purposes.
import { DataManager, WebMethodAdaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
import { ColumnDirective, ColumnsDirective, GridComponent, ToolbarItems, EditSettingsModel, Toolbar, Edit, Inject } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-grids';
function App() {
const data = new DataManager({
url: 'https://localhost:xxxx/api/grid', // Here xxxx represents the port number.
insertUrl: 'https://localhost:xxxx/api/grid/Insert',
updateUrl: 'https://localhost:xxxx/api/grid/Update',
removeUrl: 'https://localhost:xxxx/api/grid/Remove',
adaptor: new WebMethodAdaptor()
});
const editSettings: EditSettingsModel = { allowEditing: true, allowAdding: true, allowDeleting: true, mode: 'Batch' };
const toolbar: ToolbarItems[] = ['Add', 'Edit', 'Delete', 'Update', 'Cancel'];
return <GridComponent dataSource={data} toolbar={toolbar} editSettings={editSettings}>
<ColumnsDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='OrderID' headerText='Order ID' isPrimaryKey={true} width='150'textAlign='Right'></ColumnDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='CustomerID' headerText='Customer ID' width='150'></ColumnDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='ShipCity' headerText='Ship City' width='150'/>
<ColumnDirective field='ShipCountry' headerText='Ship Country' width='150'/>
</ColumnsDirective>
<Inject services={[Edit, Toolbar]}/>
</GridComponent>
};
export default App;Normal/Inline editing is the default edit mode for the Grid component. To enable CRUD operations, ensure that the isPrimaryKey property is set to
truefor a specific Grid column, ensuring that its value is unique.
The below class is used to structure data sent during CRUD operations.
The following class on the server side defines the structure of data exchanged during CRUD operations:
public class CRUDModel<T> where T : class
{
public string? action { get; set; }
public string? keyColumn { get; set; }
public object? key { get; set; }
public T? value { get; set; }
public List<T>? added { get; set; }
public List<T>? changed { get; set; }
public List<T>? deleted { get; set; }
public IDictionary<string, object>? @params { get; set; }
}Insert operation:
To insert a new record, utilize the insertUrl property to specify the controller action mapping URL for the insert operation. The newly added record details are bound to the newRecord parameter.

/// <summary>
/// Inserts a new data item into the data collection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="newRecord">It contains the new record detail which is need to be inserted.</param>
/// <returns>Returns void</returns>
[HttpPost]
[Route("api/[controller]/Insert")]
public void Insert([FromBody] CRUDModel<OrdersDetails> newRecord)
{
// Check if new record is not null
if (newRecord.value != null)
{
// Insert new record
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Insert(0, newRecord.value);
}
}Update operation:
For updating existing records, utilize the updateUrl property to specify the controller action mapping URL for the update operation. The updated record details are bound to the updatedRecord parameter.
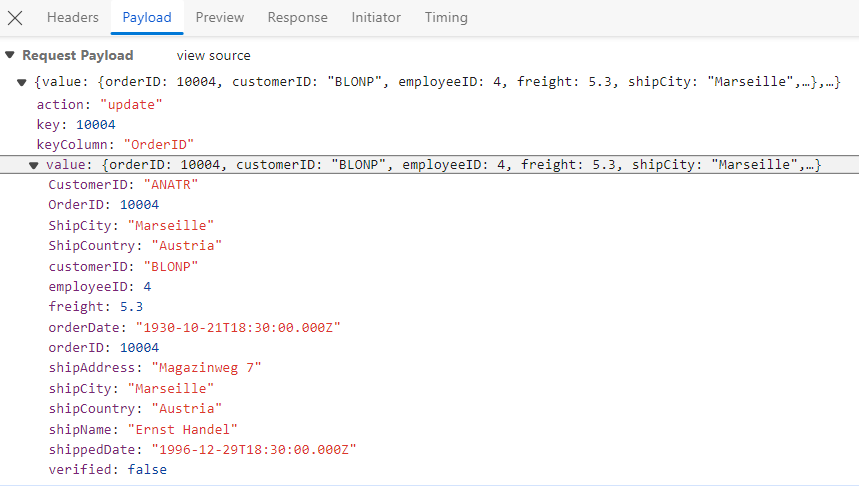
/// <summary>
/// Update a existing data item from the data collection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="updatedRecord">It contains the updated record detail which is need to be updated.</param>
/// <returns>Returns void</returns>
[HttpPost]
[Route("api/[controller]/Update")]
public void Update([FromBody] CRUDModel<OrdersDetails> updatedRecord)
{
// Retrieve updated order
var updatedOrder = updatedRecord.value;
if (updatedOrder != null)
{
// Find existing record
var data = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().FirstOrDefault(or => or.OrderID == updatedOrder.OrderID);
if (data != null)
{
// Update existing record
data.OrderID = updatedOrder.OrderID;
data.CustomerID = updatedOrder.CustomerID;
data.ShipCity = updatedOrder.ShipCity;
data.ShipCountry = updatedOrder.ShipCountry;
// Update other properties similarly
}
}
}Delete operation:
To delete existing records, use the removeUrl property to specify the controller action mapping URL for the delete operation. The primary key value of the deleted record is bound to the deletedRecord parameter.
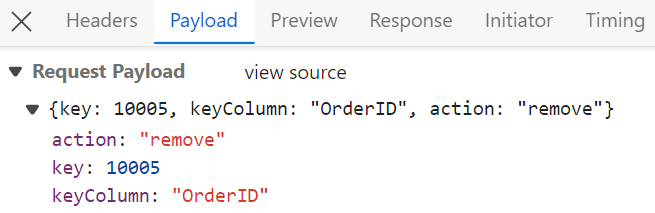
/// <summary>
/// Remove a specific data item from the data collection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="deletedRecord">It contains the specific record detail which is need to be removed.</param>
/// <return>Returns void</return>
[HttpPost]
[Route("api/[controller]/Remove")]
public void Remove([FromBody] CRUDModel<OrdersDetails> deletedRecord)
{
int orderId = int.Parse(deletedRecord.key.ToString()); // get key value from the deletedRecord
var data = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().FirstOrDefault(orderData => orderData.OrderID == orderId);
if (data != null)
{
// Remove the record from the data collection
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Remove(data);
}
}Single method for performing all CRUD operations
Using the crudUrl property, the controller action mapping URL can be specified to perform all the CRUD operation at server-side using a single method instead of specifying separate controller action method for CRUD (insert, update and delete) operations.
The following code example describes the above behavior.
[src/app.jsx]
import { DataManager, WebMethodAdaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
import { ColumnDirective, ColumnsDirective, GridComponent, ToolbarItems, EditSettingsModel, Toolbar, Edit, Inject } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-grids';
function App() {
const data = new DataManager({
url: 'https://localhost:xxxx/api/grid', // Here xxxx represents the port number.
crudUrl:'https://localhost:xxxx/api/grid/CrudUpdate',
adaptor: new WebMethodAdaptor()
});
const editSettings: EditSettingsModel = { allowEditing: true, allowAdding: true, allowDeleting: true, mode: 'Batch' };
const toolbar: ToolbarItems[] = ['Add', 'Edit', 'Delete', 'Update', 'Cancel'];
return <GridComponent dataSource={data} toolbar={toolbar} editSettings={editSettings}>
<ColumnsDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='OrderID' headerText='Order ID' isPrimaryKey={true} width='150'textAlign='Right'></ColumnDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='CustomerID' headerText='Customer ID' width='150'></ColumnDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='ShipCity' headerText='Ship City' width='150'/>
<ColumnDirective field='ShipCountry' headerText='Ship Country' width='150'/>
</ColumnsDirective>
<Inject services={[Edit, Toolbar]}/>
</GridComponent>
};
export default App;[Controller/GridController.cs]
[HttpPost]
[Route("api/[controller]/CrudUpdate")]
public void CrudUpdate([FromBody] CRUDModel<OrdersDetails> request)
{
// perform update operation
if (request.action == "update")
{
var orderValue = request.value;
OrdersDetails existingRecord = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Where(or => or.OrderID == orderValue.OrderID).FirstOrDefault();
existingRecord.OrderID = orderValue.OrderID;
existingRecord.CustomerID = orderValue.CustomerID;
existingRecord.ShipCity = orderValue.ShipCity;
}
// perform insert operation
else if (request.action == "insert")
{
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Insert(0, request.value);
}
// perform remove operation
else if (request.action == "remove")
{
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Remove(OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Where(or => or.OrderID == int.Parse(request.key.ToString())).FirstOrDefault());
}
}Batch operation
To perform batch operation, define the edit mode as Batch and specify the batchUrl property in the DataManager. Use the Add toolbar button to insert new row in batch editing mode. To edit a cell, double-click the desired cell and update the value as required. To delete a record, simply select the record and press the Delete toolbar button. Now, all CRUD operations will be executed in single request. Clicking the Update toolbar button will update the newly added, edited, or deleted records from the “OrdersDetails” table using a single API POST request.
[App.tsx]
import { DataManager, WebMethodAdaptor } from '@syncfusion/ej2-data';
import { ColumnDirective, ColumnsDirective, GridComponent, ToolbarItems, EditSettingsModel, Toolbar, Edit, Inject } from '@syncfusion/ej2-react-grids';
function App() {
const data = new DataManager({
url: 'https://localhost:xxxx/api/grid', // Here xxxx represents the port number.
batchUrl:'https://localhost:xxxx/api/grid/BatchUpdate',
adaptor: new WebMethodAdaptor()
});
const editSettings: EditSettingsModel = { allowEditing: true, allowAdding: true, allowDeleting: true, mode: 'Batch' };
const toolbar: ToolbarItems[] = ['Add', 'Edit', 'Delete', 'Update', 'Cancel'];
return <GridComponent dataSource={data} toolbar={toolbar} editSettings={editSettings}>
<ColumnsDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='OrderID' headerText='Order ID' isPrimaryKey={true} width='150'textAlign='Right'></ColumnDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='CustomerID' headerText='Customer ID' width='150'></ColumnDirective>
<ColumnDirective field='ShipCity' headerText='Ship City' width='150'/>
<ColumnDirective field='ShipCountry' headerText='Ship Country' width='150'/>
</ColumnsDirective>
<Inject services={[Edit, Toolbar]}/>
</GridComponent>
};
export default App;[HttpPost]
[Route("api/[controller]/BatchUpdate")]
public IActionResult BatchUpdate([FromBody] CRUDModel<OrdersDetails> batchOperation)
{
if (batchOperation.added != null)
{
foreach (var addedOrder in batchOperation.added)
{
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Insert(0, addedOrder);
}
}
if (batchOperation.changed != null)
{
foreach (var changedOrder in batchOperation.changed)
{
var existingOrder = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().FirstOrDefault(or => or.OrderID == changedOrder.OrderID);
if (existingOrder != null)
{
existingOrder.CustomerID = changedOrder.CustomerID;
existingOrder.ShipCity = changedOrder.ShipCity;
// Update other properties as needed
}
}
}
if (batchOperation.deleted != null)
{
foreach (var deletedOrder in batchOperation.deleted)
{
var orderToDelete = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().FirstOrDefault(or => or.OrderID == deletedOrder.OrderID);
if (orderToDelete != null)
{
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Remove(orderToDelete);
}
}
}
return Json(batchOperation);
}Run the application
Run the application in Visual Studio, accessible on a URL like https://localhost:xxxx. Verify the API returns order data at https://localhost:xxxx/api/grid, where xxxx is the port. Grid displays order data fetched from the backend API:
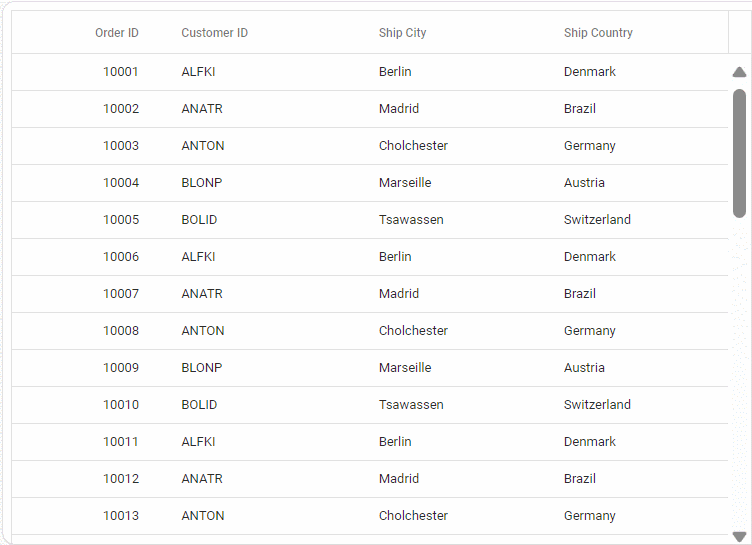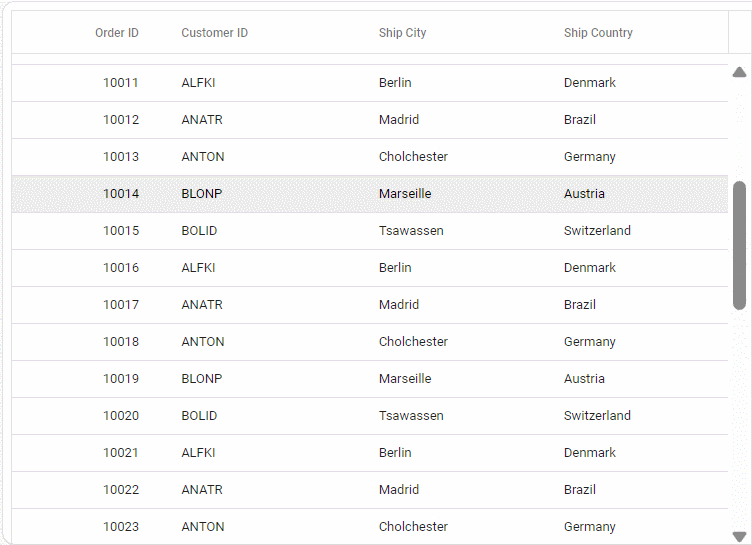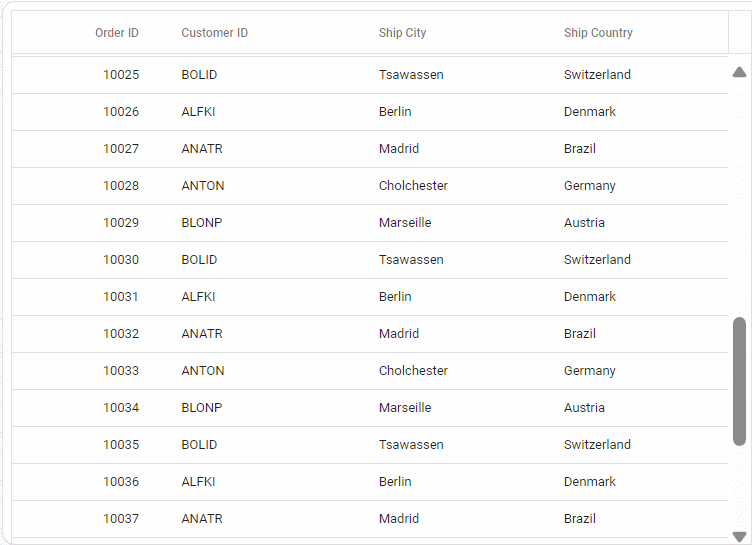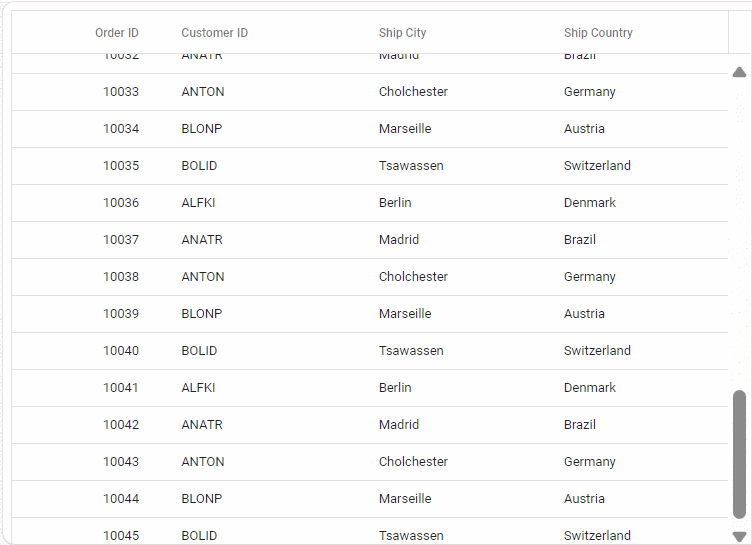
Troubleshooting
| Issue | Resolution |
|---|---|
| Empty Grid | Check the browser console for errors and verify that the API URL is correct. |
| CORS Error | Ensure the backend has proper CORS configuration in Program.cs. |
| Network Error | Confirm the backend service is running and accessible. |
| Wrong Data Format | API responses must return JSON in the format { result: [...], count: number }. |
Complete sample repository
For the complete working implementation of this example, refer to the GitHub repository.