How can I help you?
CustomAdaptor in Syncfusion EJ2 JavaScript Grid
17 Apr 202524 minutes to read
The CustomAdaptor in the Syncfusion EJ2 JavaScript Grid allows to create their own custom adaptors by extending the built-in adaptors. The custom adaptor involves handling the query process, requests, and responses of the built-in adaptor. The CustomAdaptor can be used to extend OData V4 services, enabling efficient data fetching and manipulation. By default, there are three built-in methods available for CustomAdaptor.
Types of CustomAdaptor methods
There are three types of methods in custom adaptors.
ProcessQuery
The ProcessQuery method handles the execution of a query sent to a dataSource, such as a database or custom data service. This query is responsible for performing operations like data retrieval, insertion, updating, or deletion. The ProcessQuery method accepts two arguments:
-
DataManager: Used to modify the URL dynamically. -
Query: Allows setting additional parameter values or modifying queries such as sorting, filtering, and grouping, etc.
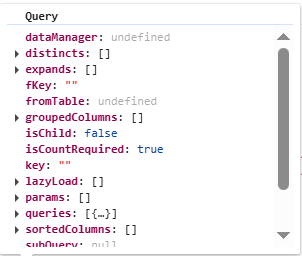
DataManager
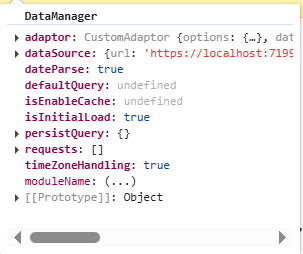
Query
public override processQuery(dm, query) {
dm.dataSource.url = 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/orders'; // Here xxxx represents the port number.
query.addParams('Syncfusion in EJ2 JavaScript Grid', 'true'); // Add the additional parameter.
return super.processQuery.apply(this, arguments);
}beforeSend
The beforeSend method is executed before a request is sent to the server. This function allows modifying parameters, request headers, and data, or performing validation before the request is processed. It accepts three arguments:
-
DataManager: Provides the dataSource andadaptorvalue. -
Request: Used to send custom headers, such as setting theAuthorizationheader. -
Settings: An optional argument that allows additional configurations.
DataManager

Request
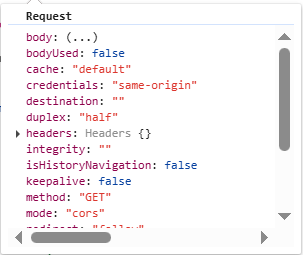
Settings
public override beforeSend(dm, request, settings) {
request.headers.set('Authorization', `true`);
super.beforeSend(dm, request, settings);
}processResponse
The processResponse method handles the response received from the server after an asynchronous request. It is responsible for parsing the response data, managing errors, and preparing the data for further processing. This method can accept multiple optional arguments, allowing customization based on specific requirements.
public override processResponse() {
let i = 0;
const original= super.processResponse.apply(this, arguments);
// Adding serial number.
if (original.result) {
original.result.forEach((item) => ej.base.setValue('SNo', ++i, item));
}
return original;
}This guide provides detailed instructions on binding data and performing CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) actions using the CustomAdaptor by extending the ODataV4Adaptor in your Syncfusion EJ2 JavaScript Grid.
Creating an Custom service
To configure a server with Syncfusion EJ2 JavaScript Grid, you need to follow the below steps:
Step 1: Create a new ASP.NET Core project:
To create a new ASP.NET Core Web API project named CustomAdaptor, follow these steps:
- Open Visual Studio.
- Select “Create a new project”
- Choose ASP.NET Core Web API project template.
- Name the project CustomAdaptor.
- Click “Create”
Step 2: Install NuGet packages:
Using the NuGet package manager in Visual Studio (Tools → NuGet Package Manager → Manage NuGet Packages for Solution), install the Microsoft.AspNetCore.OData NuGet package.
Step 3: Configure the server:
In the Program.cs file of your project, configure the server to serve static files by adding the following code.
var app = builder.Build();
app.UseDefaultFiles();
app.UseStaticFiles();Additionally, comment out the following line in the launchSettings.json file:
"https": {
"commandName": "Project",
"dotnetRunMessages": true,
"launchBrowser": true,
// "launchUrl": "swagger",
"applicationUrl": "https://localhost:xxxx;http://localhost:xxxx",
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
},This configuration enables the server to locate and serve the index.html file.
Step 4: Model class creation:
Create a model class named OrdersDetails.cs in the server-side Models folder to represent the order data.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace CustomAdaptor.Models
{
public class OrdersDetails
{
public static List<OrdersDetails> order = new List<OrdersDetails>();
public OrdersDetails()
{
}
public OrdersDetails(
int OrderID, string CustomerId, int EmployeeId, string ShipCountry)
{
this.OrderID = OrderID;
this.CustomerID = CustomerId;
this.EmployeeID = EmployeeId;
this.ShipCountry = ShipCountry;
}
public static List<OrdersDetails> GetAllRecords()
{
if (order.Count() == 0)
{
int code = 10000;
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
{
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 1, "ALFKI", i + 0, "Denmark"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 2, "ANATR", i + 2, "Brazil"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 3, "ANTON", i + 1, "Germany"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 4, "BLONP", i + 3, "Austria"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 5, "BOLID", i + 4, "Switzerland"));
code += 5;
}
}
return order;
}
[Key]
public int? OrderID { get; set; }
public string? CustomerID { get; set; }
public int? EmployeeID { get; set; }
public string? ShipCountry { get; set; }
}
}Step 5: Build the entity data model:
To construct the entity data model for your ODataV4 service, utilize the ODataConventionModelBuilder to define the model’s structure. Start by creating an instance of the ODataConventionModelBuilder, then register the entity set Orders using the EntitySet<T> method, where OrdersDetails represents the CLR type containing order details.
[program.cs]
using Microsoft.OData.ModelBuilder;
// Create an ODataConventionModelBuilder to build the OData model.
var modelBuilder = new ODataConventionModelBuilder();
// Register the orders entity set with the OData model builder.
modelBuilder.EntitySet<OrdersDetails>("Orders");Step 6: Register the ODataV4 services:
Once the entity data model is built, you need to register the ODataV4 services in your ASP.NET Core application. Here’s how:
// Add controllers with OData support to the service collection.
builder.Services.AddControllers().AddOData(
options => options
.Count()
.AddRouteComponents("odata", modelBuilder.GetEdmModel()));Step 7: Add controllers:
Finally, add controllers to expose the OData endpoints. Here’s an example:
using CustomAdaptor.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.OData.Query;
namespace CustomAdaptor.Controllers
{
[Route("[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class OrdersController : ControllerBase
{
/// <summary>
/// Retrieves all orders.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>The collection of orders.</returns>
[HttpGet]
[EnableQuery]
public IActionResult Get()
{
var data = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().AsQueryable();
return Ok(data);
}
}
}Step 8: Run the Application
Run the application in Visual Studio. It will be accessible on a URL like https://localhost:xxxx.
After running the application, you can verify that the server-side API controller is successfully returning the order data in the URL(https://localhost:xxxx/odata/Orders). Here xxxx denotes the port number.
Connecting Syncfusion EJ2 JavaScript Grid to an custom service extending the ODataV4 service
To integrate the Syncfusion EJ2 JavaScript Grid into your Javascript and ASP.NET Core project using Visual Studio, follow these steps:
Step 1: Create wwwroot folder:
Create a folder named wwwroot in the project root directory. This folder will contain static files served by the web server.
Step 2: Create JS folder:
Inside the wwwroot folder, create js folder to hold script file, respectively.
Step 3: Create index.html file:
Create an index.html file under the wwwroot folder and add the necessary HTML structure along with CSS and javaScript links to include Syncfusion EJ2 JavaScript Grid dependencies.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>EJ2 Grid</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta name="description" content="Javascript Grid Control">
<meta name="author" content="Syncfusion">
<link href="css/index.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-base/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-grids/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-buttons/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-popups/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-richtexteditor/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-navigations/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-dropdowns/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-lists/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-inputs/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-calendars/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-notifications/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/ej2-splitbuttons/styles/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet">
<script src="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/32.2.3/dist/ej2.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/ej2/syncfusion-helper.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="container">
<div id="Grid"></div>
</div>
<script type="module" src="js/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>Step 4: Adding custom adaptor:
Create a CustomAdaptor.js file under the wwwroot/js folder. Then extend the ej.data.ODataV4Adaptor class to define custom adaptor. This adaptor implements three key methods: processQuery, beforeSend, and processResponse.
-
The
processQuerymethod modifies the API endpoint URL and sets additional parameters required for executing the query. -
The
beforeSendmethod adds custom headers, such as theAuthorizationheader, before sending the request. -
The
processResponsemethod customizes the response by modifying data, such as adding a new field (SNo) to the dataset.
export class CustomAdaptor extends ej.data.ODataV4Adaptor {
processQuery(dm, query) {
dm.dataSource.url = 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/orders'; // Here xxxx represents the port number.
query.addParams('Syncfusion Grid', 'true'); // Add the additional parameter.
return super.processQuery.apply(this, arguments);
}
beforeSend(dm, request, settings) {
request.headers.set('Authorization', `true`);
super.beforeSend(dm, request, settings);
}
processResponse() {
let i = 0;
const original = super.processResponse.apply(this, arguments);
// Adding serial number.
if (original.result) {
original.result.forEach((item) => ej.base.setValue('SNo', ++i, item));
}
return original;
}
}Step 5: Adding Syncfusion Component:
Create a index.js file under the wwwroot/js folder. Create a DataManager instance specifying the URL of your API endpoint(https://localhost:xxxx/odata/Orders) using the url property. Then, set CustomAdaptor as the adaptor to handle data requests.
import { CustomAdaptor } from './CustomAdaptor.js';
var data = new ej.data.DataManager({
url: 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/orders', // Here xxxx represents the port number.
adaptor: new CustomAdaptor()
});
var grid = new ej.grids.Grid({
dataSource: data,
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, type: 'number' },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'EmployeeID', headerText: 'Employee ID', width: 140 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'ShipCountry', width: 140 }
]
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');Step 5: Run the project:
Now, run the project to see the Syncfusion EJ2 JavaScript Grid connected to the API service in action.
Handling filtering operation
To enable filtering in your web application using the custom adaptor, extend the OData support in your service configuration. This involves adding the Filter method within the OData setup, allowing data to be filtered based on specified criteria. Once configured, clients can use the $filter query option in requests to retrieve specific data entries.
// Create a new instance of the web application builder.
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Create an ODataConventionModelBuilder to build the OData model.
var modelBuilder = new ODataConventionModelBuilder();
// Register the orders entity set with the OData model builder.
modelBuilder.EntitySet<OrdersDetails>("Orders");
// Add controllers with OData support to the service collection.
builder.Services.AddControllers().AddOData(
options => options
.Count()
.Filter() // Use Filter method for filtering.
.AddRouteComponents("odata", modelBuilder.GetEdmModel()));import { CustomAdaptor } from './CustomAdaptor.js';
ej.grids.Grid.Inject(ej.grids.Filter);
var data = new ej.data.DataManager({
url: 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/orders', // Here xxxx represents the port number.
adaptor: new CustomAdaptor()
});
var grid = new ej.grids.Grid({
dataSource: data,
allowFiltering: true,
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, type: 'number' },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'EmployeeID', headerText: 'Employee ID', width: 140 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'ShipCountry', width: 140 }
]
});
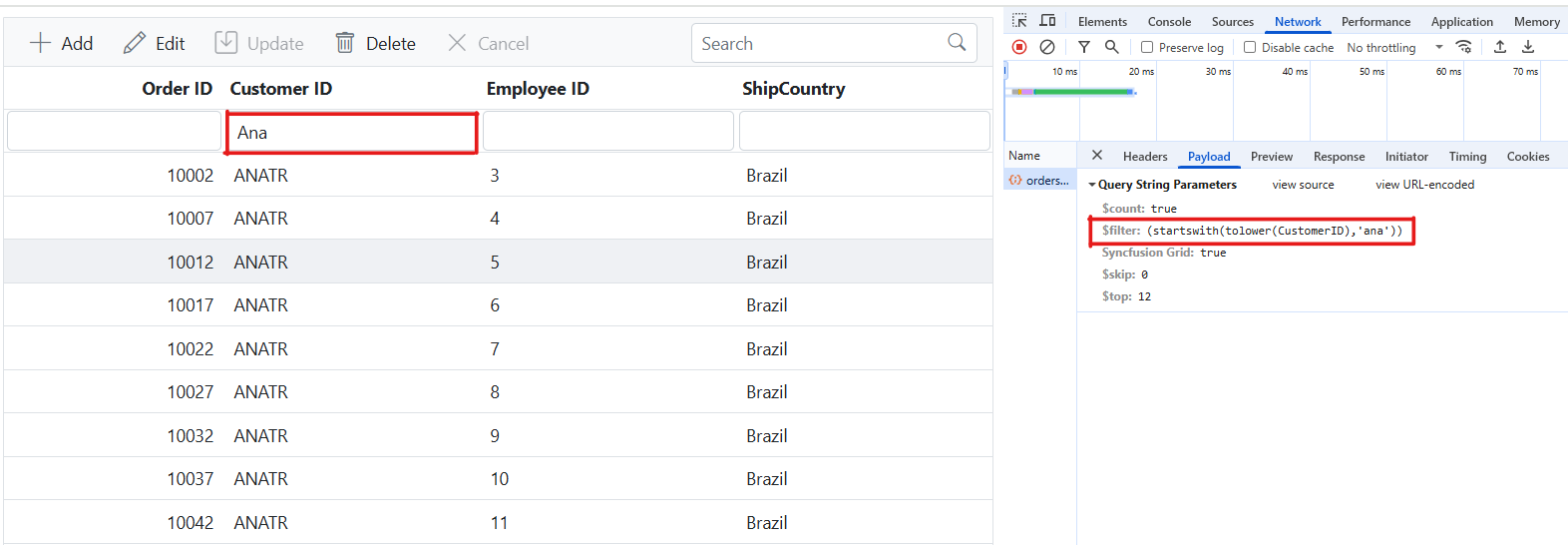
grid.appendTo('#Grid');Single column filtering
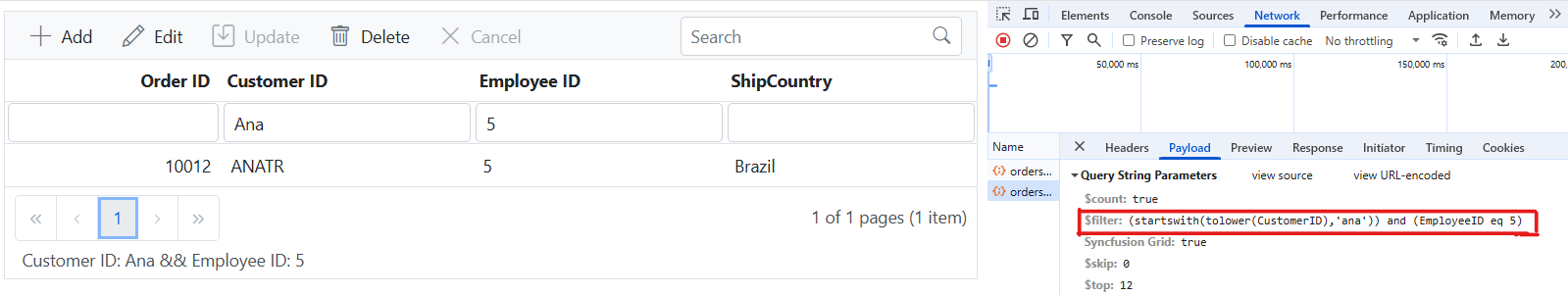
Multi column filtering
Handling searching operation
To enable search functionality in your web application using the custom adaptor, extend the OData support in your service configuration. This requires adding the Filter method within the OData setup, allowing data to be filtered based on specified criteria. Once configured, clients can use the $filter query option in their requests to search for specific data entries.
// Create a new instance of the web application builder.
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Create an ODataConventionModelBuilder to build the OData model.
var modelBuilder = new ODataConventionModelBuilder();
// Register the orders entity set with the OData model builder.
modelBuilder.EntitySet<OrdersDetails>("Orders");
// Add controllers with OData support to the service collection.
builder.Services.AddControllers().AddOData(
options => options
.Count()
.Filter() // Use Filter method for searching.
.AddRouteComponents("odata", modelBuilder.GetEdmModel()));import { CustomAdaptor } from './CustomAdaptor.js';
ej.grids.Grid.Inject(ej.grids.Toolbar)
var data = new ej.data.DataManager({
url: 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/orders', // Here xxxx represents the port number.
adaptor: new CustomAdaptor()
});
var grid = new ej.grids.Grid({
dataSource: data,
toolbar: ['Search'],
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, type: 'number' },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'EmployeeID', headerText: 'Employee ID', width: 140 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'ShipCountry', width: 140 }
]
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');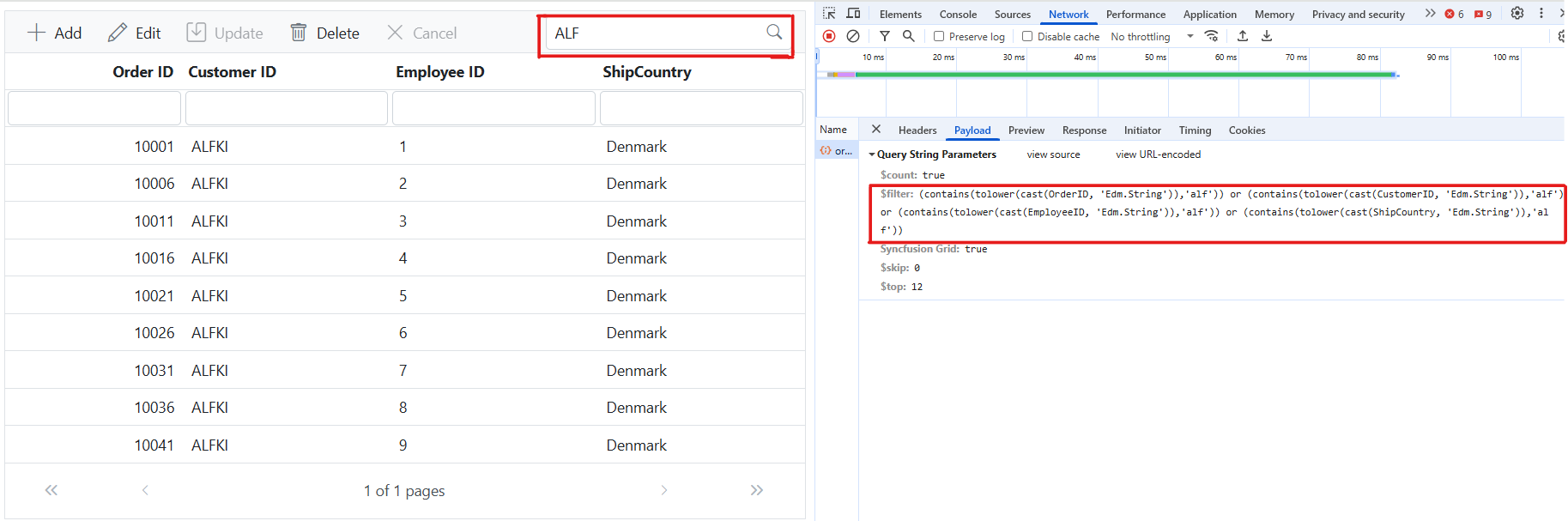
Handling sorting operation
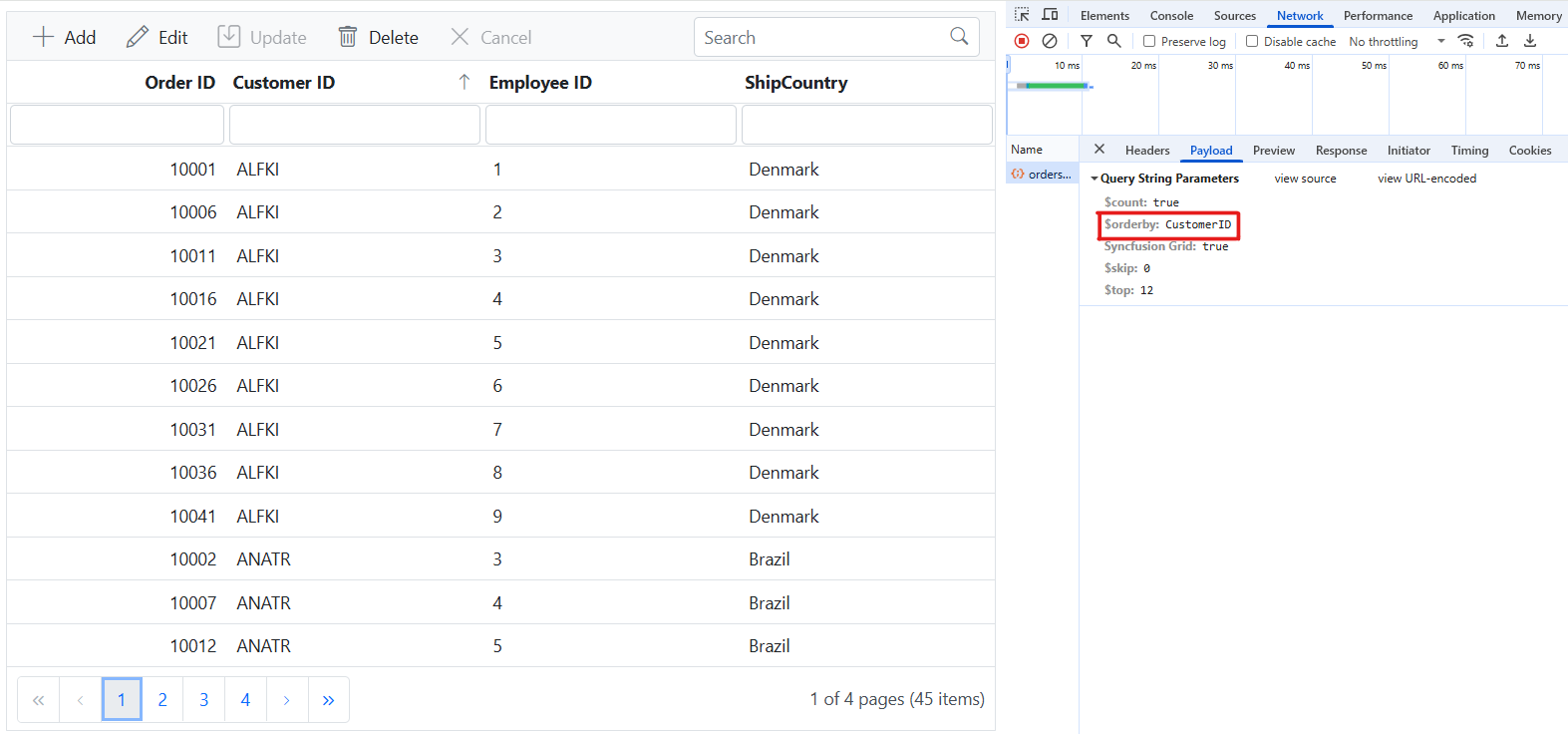
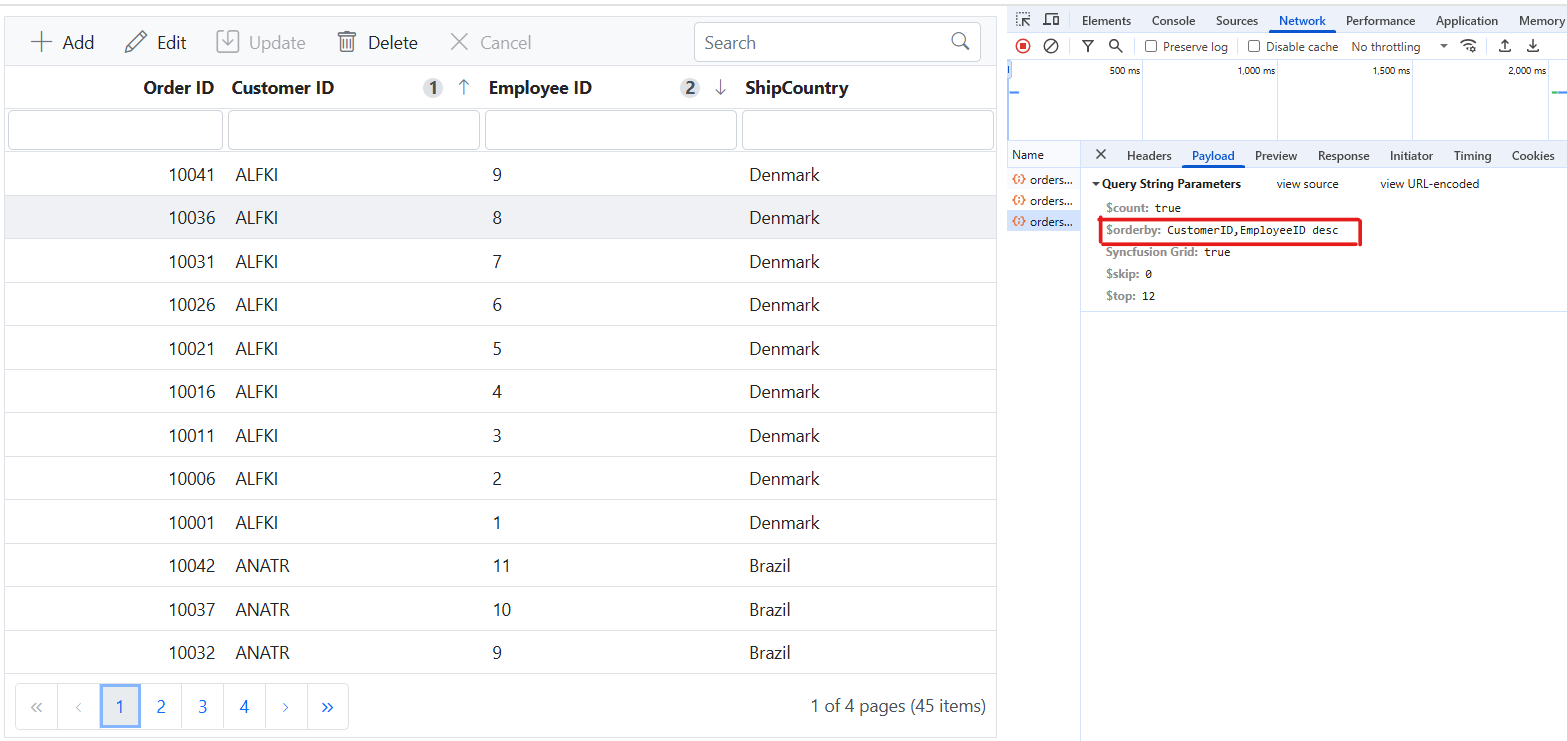
To enable sorting operations in your web application using the custom adaptor, first configure the custom adaptor to extend OData support in your service collection. This involves adding the OrderBy method within the OData setup, allowing data to be sorted based on specified criteria. Once enabled, clients can use the $orderby query option in their requests to sort data entries by desired attributes.
// Create a new instance of the web application builder.
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Create an ODataConventionModelBuilder to build the OData model.
var modelBuilder = new ODataConventionModelBuilder();
// Register the orders entity set with the OData model builder.
modelBuilder.EntitySet<OrdersDetails>("Orders");
// Add controllers with OData support to the service collection.
builder.Services.AddControllers().AddOData(
options => options
.Count()
.OrderBy() // Use this method for sorting.
.AddRouteComponents("odata", modelBuilder.GetEdmModel()));import { CustomAdaptor } from './CustomAdaptor.js';
ej.grids.Grid.Inject(ej.grids.Sort);
var data = new ej.data.DataManager({
url: 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/orders', // Here xxxx represents the port number.
adaptor: new CustomAdaptor()
});
var grid = new ej.grids.Grid({
dataSource: data,
allowSorting: true,
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, type: 'number' },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'EmployeeID', headerText: 'Employee ID', width: 140 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'ShipCountry', width: 140 }
]
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');Single column sorting
Multi column sorting
Handling paging operation
To implement paging in your web application using the CustomAdaptor with OData, use the SetMaxTop method in your OData setup to define the maximum number of records returned per request. Once configured, clients can utilize the $skip and $top query options to specify the number of records to skip and retrieve, respectively.
// Create a new instance of the web application builder.
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Create an ODataConventionModelBuilder to build the OData model.
var modelBuilder = new ODataConventionModelBuilder();
// Register the orders entity set with the OData model builder.
modelBuilder.EntitySet<OrdersDetails>("Orders");
// Add controllers with OData support to the service collection.
builder.Services.AddControllers().AddOData(
options => options
.Count()
.SetMaxTop(null)
.AddRouteComponents("odata", modelBuilder.GetEdmModel()));import { CustomAdaptor } from './CustomAdaptor.js';
ej.grids.Grid.Inject(ej.grids.Page);
var data = new ej.data.DataManager({
url: 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/orders', // Here xxxx represents the port number.
adaptor: new CustomAdaptor()
});
var grid = new ej.grids.Grid({
dataSource: data,
allowPaging:true,
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, type: 'number' },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'EmployeeID', headerText: 'Employee ID', width: 140 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'ShipCountry', width: 140 }
]
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');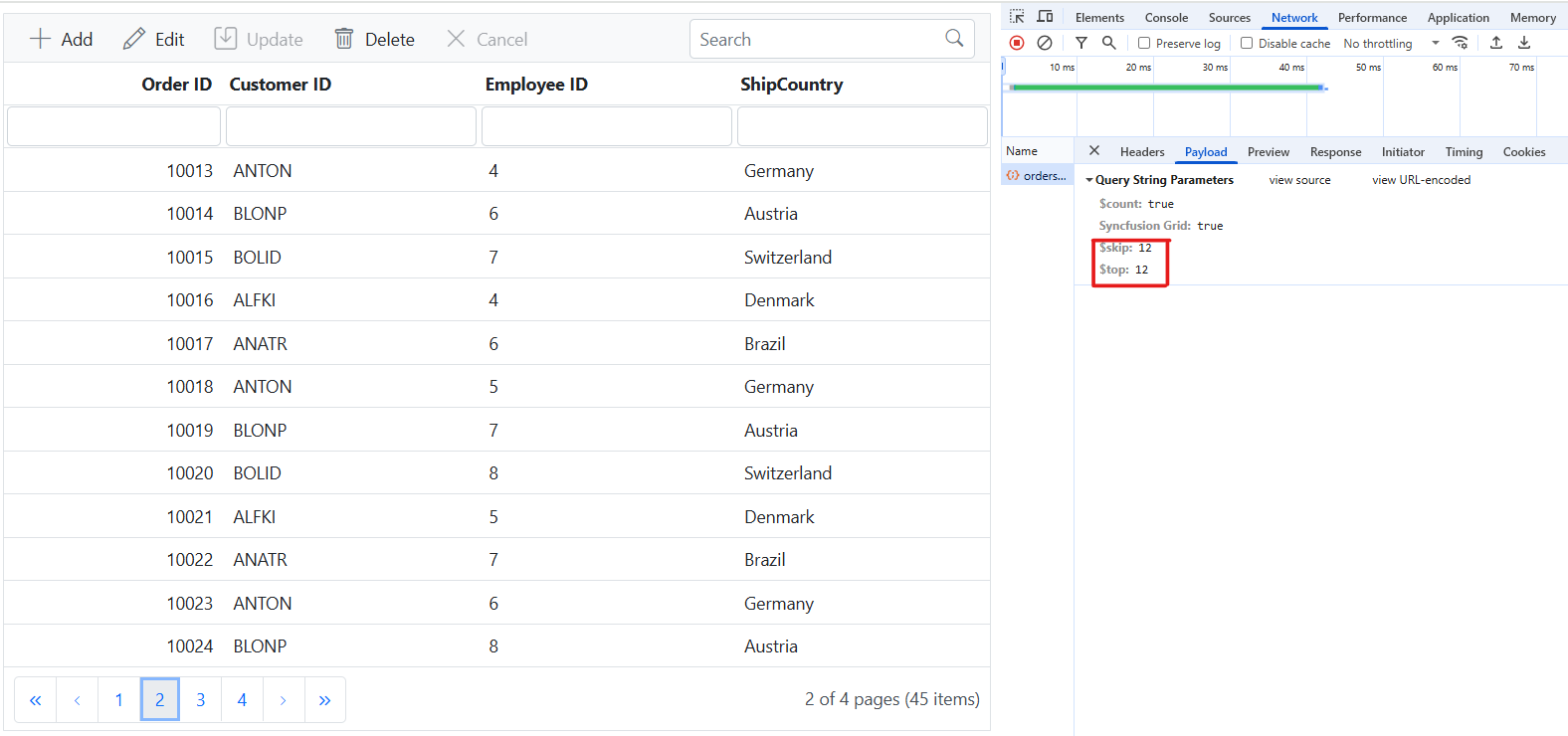
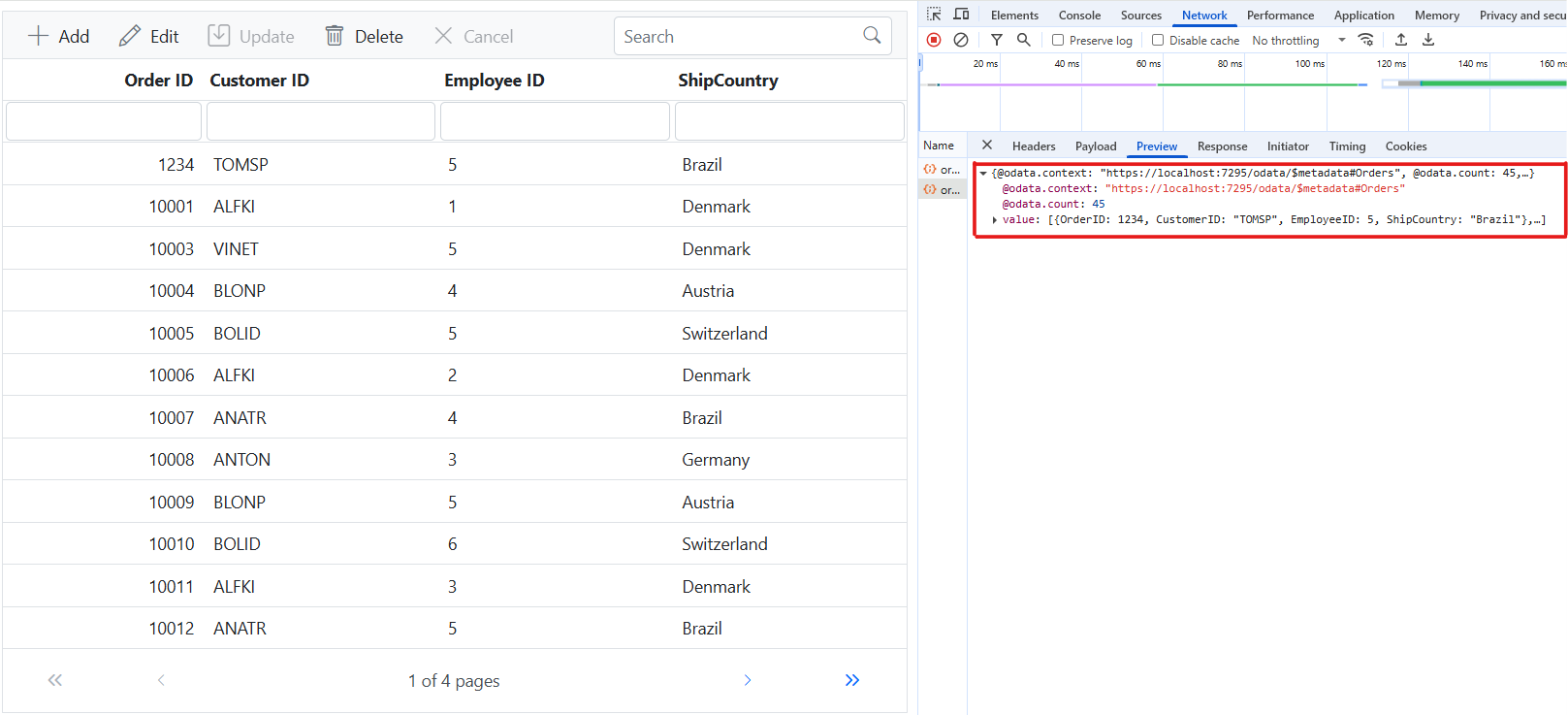
Handling CRUD operations
To manage CRUD (Create, Read, Update, and Delete) operations using CustomAdaptor, follow the provided guide for configuring the Syncfusion EJ2 JavaScript Grid for editing and utilize the sample implementation of the OrdersController in your server application. This controller processes HTTP requests for CRUD operations, including GET, POST, PATCH, and DELETE.
To enable CRUD operations in the Syncfusion EJ2 JavaScript Grid within an Angular application, follow the below steps:
import { CustomAdaptor } from './CustomAdaptor.js';
ej.grids.Grid.Inject(ej.grids.Toolbar,ej.grids.Edit);
var data = new ej.data.DataManager({
url: 'https://localhost:xxxx/odata/orders', // Here xxxx represents the port number.
adaptor: new CustomAdaptor()
});
var grid = new ej.grids.Grid({
dataSource: data,
toolbar: ['Add', 'Edit', 'Update', 'Delete', 'Cancel'],
editSettings: { allowAdding: true, allowDeleting: true, allowEditing: true },
columns: [
{ field: 'OrderID', headerText: 'Order ID', textAlign: 'Right', width: 120, isPrimaryKey: true, type: 'number' },
{ field: 'CustomerID', width: 140, headerText: 'Customer ID', type: 'string' },
{ field: 'EmployeeID', headerText: 'Employee ID', width: 140 },
{ field: 'ShipCountry', headerText: 'ShipCountry', width: 140 }
]
});
grid.appendTo('#Grid');Normal/Inline editing is the default edit mode for the Syncfusion EJ2 JavaScript Grid. To enable CRUD operations, ensure that the isPrimaryKey property is set to true for a specific Grid column, ensuring that its value is unique.
Insert Record
To insert a new record into your Syncfusion EJ2 JavaScript Grid, you can utilize the HttpPost method in your server application. Below is a sample implementation of inserting a record using the OrdersController:
/// <summary>
/// Inserts a new order to the collection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="addRecord">The order to be inserted.</param>
/// <returns>It returns the newly inserted record detail.</returns>
[HttpPost]
[EnableQuery]
public IActionResult Post([FromBody] OrdersDetails addRecord)
{
if (order == null)
{
return BadRequest("Null order");
}
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Insert(0, addRecord);
return Ok(addRecord);
}
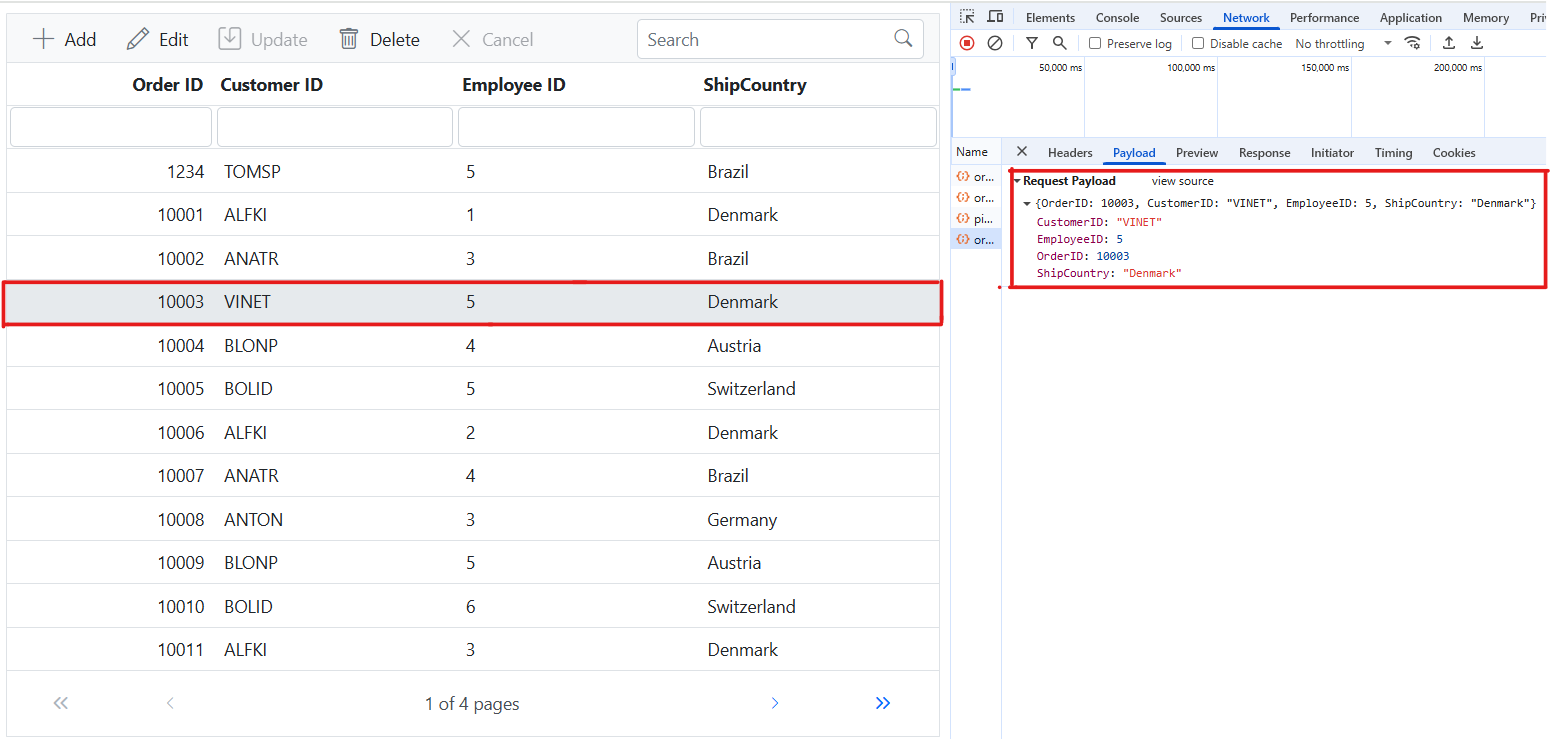
Update Record
Updating a record in the Syncfusion EJ2 JavaScript Grid can be achieved by utilizing the HttpPatch method in your controller. Here’s a sample implementation of updating a record:
/// <summary>
/// Updates an existing order.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">The ID of the order to update.</param>
/// <param name="updateRecord">The updated order details.</param>
/// <returns>It returns the updated order details.</returns>
[HttpPatch("{key}")]
public IActionResult Patch(int key, [FromBody] OrdersDetails updatedOrder)
{
if (updatedOrder == null)
{
return BadRequest("No records");
}
var existingOrder = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().FirstOrDefault(o => o.OrderID == key);
if (existingOrder != null)
{
// If the order exists, update its properties.
existingOrder.CustomerID = updatedOrder.CustomerID ?? existingOrder.CustomerID;
existingOrder.EmployeeID = updatedOrder.EmployeeID ?? existingOrder.EmployeeID;
existingOrder.ShipCountry = updatedOrder.ShipCountry ?? existingOrder.ShipCountry;
}
return Ok(existingOrder);
}
Delete Record
To delete a record from your Syncfusion EJ2 JavaScript Grid, you can utilize the HttpDelete method in your controller. Below is a sample implementation:
/// <summary>
/// Deletes an order.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">The key of the order to be deleted.</param>
/// <returns>The deleted order.</returns>
[HttpDelete("{key}")]
public IActionResult Delete(int key)
{
var order = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().FirstOrDefault(o => o.OrderID == key);
if (order != null)
{
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Remove(order);
}
return Ok(order);
}