Types of data
21 Dec 202224 minutes to read
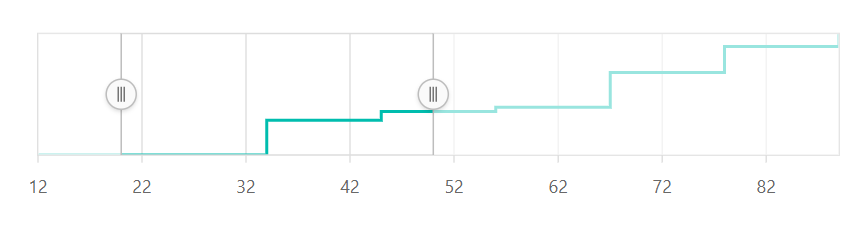
Numeric
The numeric scale is used to represent the numeric values of data in a Range Selector. By default, the valueType of a Range Selector is Double.
@(Html.EJS().RangeNavigator("container")
.ValueType(Syncfusion.EJ2.Charts.RangeValueType.DateTime)
.LabelFormat("MMM-yy")
.Series(sr =>
{
sr.XName("x").YName("y").DataSource(ViewBag.dataSource).Add();
}).Render()
)public IActionResult Index()
{
List <data> dataSource = new List<data>
{
new data { y = 12, y1 = 28 },
new data { y = 34, y1 = 44 },
new data { y = 45, y1 = 48 },
new data { y = 56, y1 = 50 },
new data { y = 67, y1 = 66 },
new data { y = 78, y1 = 78 },
new data { y = 89, y1 = 84 },
};
ViewBag.dataSource = dataSource;
return View();
}
public class data
{
public double y;
public double y1;
}
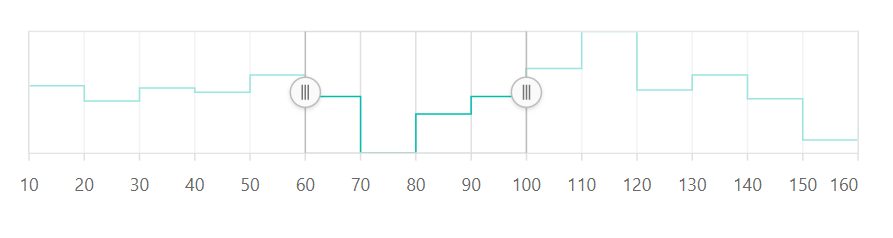
Range
The minimum and the maximum of the scale will be calculated automatically based on the provided data. It can be customized by using the minimum, maximum, and interval properties.
@(Html.EJS().RangeNavigator("container")
.ValueType(Syncfusion.EJ2.Charts.RangeValueType.DateTime)
.Minimum(10).
.Maximum(400)
.Series(sr =>
{
sr.XName("x").YName("y").DataSource(ViewBag.dataSource).Add();
}).Render()
)public IActionResult Index()
{
List <data> dataSource = new List<data>
{
new data { y = 12, y1 = 28 },
new data { y = 34, y1 = 44 },
new data { y = 45, y1 = 48 },
new data { y = 56, y1 = 50 },
new data { y = 67, y1 = 66 },
new data { y = 78, y1 = 78 },
new data { y = 89, y1 = 84 },
};
ViewBag.dataSource = dataSource;
return View();
}
public class data
{
public double y;
public double y1;
}
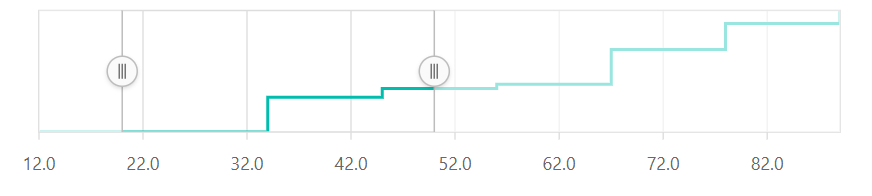
Label Format
The numeric labels can be formatted using the labelFormat property and it supports all the globalized formats.
@(Html.EJS().RangeNavigator("container")
.ValueType(Syncfusion.EJ2.Charts.RangeValueType.DateTime)
.LabelFormat("MMM-yy")
.Series(sr =>
{
sr.XName("x").YName("y").DataSource(ViewBag.dataSource).Add();
}).Render()
)public IActionResult Index()
{
List <data> dataSource = new List<data>
{
new data { y = 12, y1 = 28 },
new data { y = 34, y1 = 44 },
new data { y = 45, y1 = 48 },
new data { y = 56, y1 = 50 },
new data { y = 67, y1 = 66 },
new data { y = 78, y1 = 78 },
new data { y = 89, y1 = 84 },
};
ViewBag.dataSource = dataSource;
return View();
}
public class data
{
public double y;
public double y1;
}
The following table describes the result of applying some commonly used label formats on numeric values.
| Label Value | Label Format property value | Result | Description |
| 1000 | n1 | 1000.0 | The Number is rounded to 1 decimal place |
| 1000 | n2 | 1000.00 | The Number is rounded to 2 decimal place |
| 1000 | n3 | 1000.000 | The Number is rounded to 3 decimal place |
| 0.01 | p1 | 1.0% | The Number is converted to percentage with 1 decimal place |
| 0.01 | p2 | 1.00% | The Number is converted to percentage with 2 decimal place |
| 0.01 | p3 | 1.000% | The Number is converted to percentage with 3 decimal place |
| 1000 | c1 | $1,000.0 | The Currency symbol is appended to number and number is rounded to 1 decimal place |
| 1000 | c2 | $1,000.00 | The Currency symbol is appended to number and number is rounded to 2 decimal place |
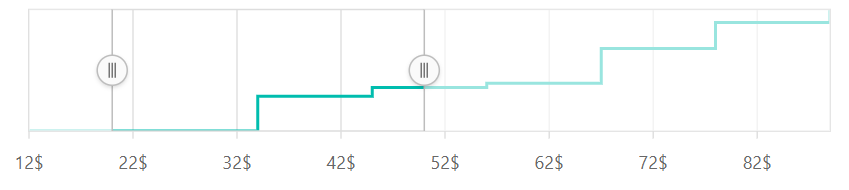
Custom Label Format
The Range Selector also supports the Custom Label formats using the placeholders such as {value}$, in which the value represents the axis label, e.g. 20$.
@(Html.EJS().RangeNavigator("container")
.ValueType(Syncfusion.EJ2.Charts.RangeValueType.DateTime)
.LabelFormat("MMM-yy")
.Series(sr =>
{
sr.XName("x").YName("y").DataSource(ViewBag.dataSource).Add();
}).Render()
)public IActionResult Index()
{
List <data> dataSource = new List<data>
{
new data { y = 12, y1 = 28 },
new data { y = 34, y1 = 44 },
new data { y = 45, y1 = 48 },
new data { y = 56, y1 = 50 },
new data { y = 67, y1 = 66 },
new data { y = 78, y1 = 78 },
new data { y = 89, y1 = 84 },
};
ViewBag.dataSource = dataSource;
return View();
}
public class data
{
public double y;
public double y1;
}
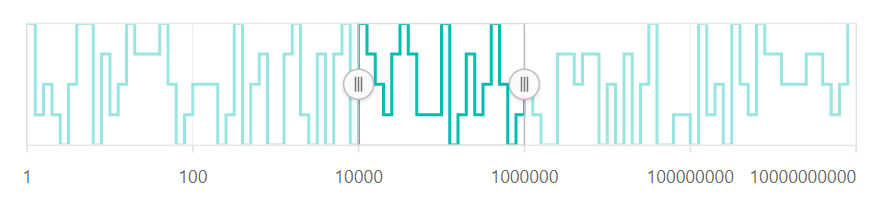
Logarithmic Axis
The Logarithmic supports the logarithmic scale, and it is used to visualize the data when the Range Selector has numerical values in both the lower (e.g.: 10-6) and the higher (e.g.: 106) orders of the magnitude.
@(Html.EJS().RangeNavigator("container")
.ValueType(Syncfusion.EJ2.Charts.RangeValueType.Logarithmic)
.Series(sr =>
{
sr.XName("y").YName("y1").DataSource(ViewBag.dataSource).Add();
}).Render()
)public IActionResult Index()
{
List <data> dataSource = new List<data>
{
new data { y = 12, y1 = 28 },
new data { y = 100, y1 = 44 },
new data { y = 500, y1 = 48 },
new data { y = 1000, y1 = 50 },
new data { y = 5000, y1 = 66 },
new data { y = 7000, y1 = 78 },
new data { y = 89, y1 = 84 },
};
ViewBag.dataSource = dataSource;
return View();
}
public class data
{
public double y;
public double y1;
}
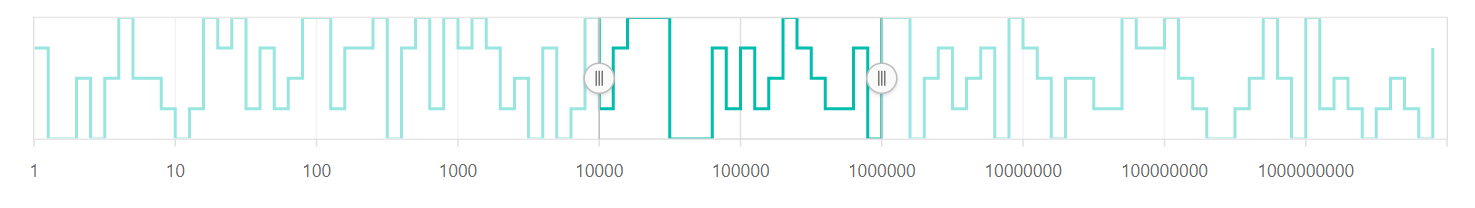
Range
The minimum and the maximum of the Range Selector will be calculated automatically based on the provided data. It can be customized by using the minimum, maximum, and interval properties.
@(Html.EJS().RangeNavigator("container")
.ValueType(Syncfusion.EJ2.Charts.RangeValueType.Logarithmic)
.Minimum(10)
.Maximum(1000)
.Series(sr =>
{
sr.XName("y").YName("y1").DataSource(ViewBag.dataSource).Add();
}).Render()
)public IActionResult Index()
{
List <data> dataSource = new List<data>
{
new data { y = 12, y1 = 28 },
new data { y = 100, y1 = 44 },
new data { y = 500, y1 = 48 },
new data { y = 1000, y1 = 50 },
new data { y = 5000, y1 = 66 },
new data { y = 7000, y1 = 78 },
new data { y = 89, y1 = 84 },
};
ViewBag.dataSource = dataSource;
return View();
}
public class data
{
public double y;
public double y1;
}
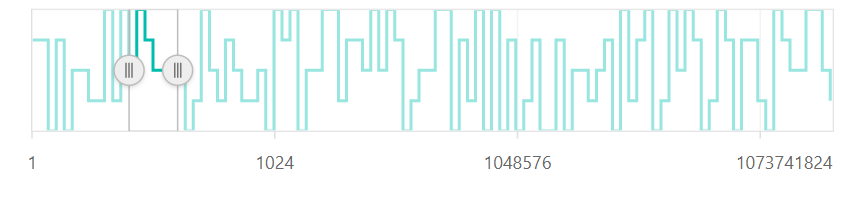
Logarithmic Base
The Logarithmic Base can be customized using the logBase property. The default value of this property is 10.
@(Html.EJS().RangeNavigator("container")
.ValueType(Syncfusion.EJ2.Charts.RangeValueType.Logarithmic)
.LogBase(10)
.Series(sr =>
{
sr.XName("y").YName("y1").DataSource(ViewBag.dataSource).Add();
}).Render()
)public IActionResult Index()
{
List <data> dataSource = new List<data>
{
new data { y = 12, y1 = 28 },
new data { y = 100, y1 = 44 },
new data { y = 500, y1 = 48 },
new data { y = 1000, y1 = 50 },
new data { y = 5000, y1 = 66 },
new data { y = 7000, y1 = 78 },
new data { y = 89, y1 = 84 },
};
ViewBag.dataSource = dataSource;
return View();
}
public class data
{
public double y;
public double y1;
}
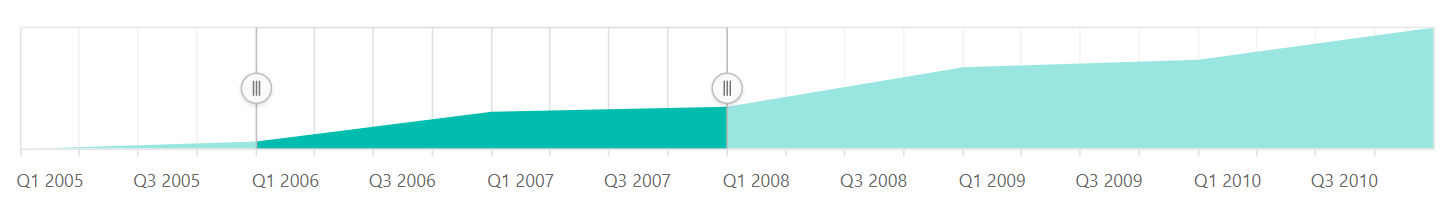
Date-time
The Range Selector supports the DateTime scale and displays the DateTime values as labels in the specified format.
@(Html.EJS().RangeNavigator("container")
.ValueType(Syncfusion.EJ2.Charts.RangeValueType.DateTime)
.LabelFormat("MMM-yy")
.Series(sr =>
{
sr.XName("x").YName("y").DataSource(ViewBag.dataSource).Add();
}).Render()
)public IActionResult Index()
{
List <data> dataSource = new List<data>
{
new data { x = new DateTime(2005, 01, 01), y = 21, y1 = 28 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2006, 01, 01), y = 24, y1 = 44 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2007, 01, 01), y = 36, y1 = 48 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2008, 01, 01), y = 38, y1 = 50 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2009, 01, 01), y = 54, y1 = 66 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2010, 01, 01), y = 57, y1 = 78 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2011, 01, 01), y = 70, y1 = 84 },
};
ViewBag.dataSource = dataSource;
return View();
}
public class data
{
public DateTime x;
public double y;
public double y1;
}
NOTE
Date-time Range navigator supports date-time scale and displays date-time values as a labels in the specified format.
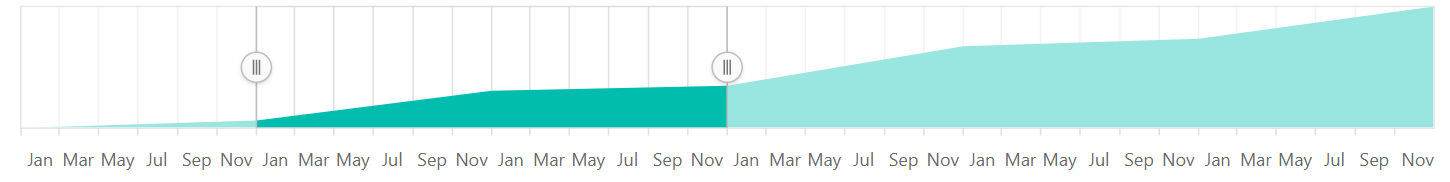
Interval Customization
The DateTime intervals can be customized using the interval and the intervalType properties of the Range Selector. For example, if the interval is set to 2 and the intervalType is set to years, the interval will be considered to be 2 years.
DateTime supports the following interval types:
- Auto
- Years
- Quarter
- Months
- Weeks
- Days
- Hours
- Minutes
@(Html.EJS().RangeNavigator("container")
.ValueType(Syncfusion.EJ2.Charts.RangeValueType.DateTime)
.LabelFormat("MMM-yy")
.IntervalType("Months")
.Series(sr =>
{
sr.XName("x").YName("y").DataSource(ViewBag.dataSource).Add();
}).Render()
)public IActionResult Index()
{
List <data> dataSource = new List<data>
{
new data { x = new DateTime(2005, 01, 01), y = 21, y1 = 28 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2006, 01, 01), y = 24, y1 = 44 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2007, 01, 01), y = 36, y1 = 48 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2008, 01, 01), y = 38, y1 = 50 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2009, 01, 01), y = 54, y1 = 66 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2010, 01, 01), y = 57, y1 = 78 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2011, 01, 01), y = 70, y1 = 84 },
};
ViewBag.dataSource = dataSource;
return View();
}
public class data
{
public DateTime x;
public double y;
public double y1;
}
Label Format
The labelFormat property is used to format and parse the date to all globalize format.
@(Html.EJS().RangeNavigator("container")
.ValueType(Syncfusion.EJ2.Charts.RangeValueType.DateTime)
.LabelFormat("'y/M/d")
.Series(sr =>
{
sr.XName("x").YName("y").Type(Syncfusion.EJ2.Charts.RangeNavigatorType.Area).DataSource(ViewBag.dataSource).Add();
}).Render()
)public ActionResult Index()
{
List<data> dataSource = new List<data>
{
new data { x = new DateTime(2005, 01, 01), y = 21, y1 = 28 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2006, 01, 01), y = 24, y1 = 44 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2007, 01, 01), y = 36, y1 = 48 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2008, 01, 01), y = 38, y1 = 50 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2009, 01, 01), y = 54, y1 = 66 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2010, 01, 01), y = 57, y1 = 78 },
new data { x = new DateTime(2011, 01, 01), y = 70, y1 = 84 },
};
ViewBag.dataSource = dataSource;
return View();
}
public class data
{
public DateTime x;
public double y;
public double y1;
}The following table shows the results of applying some common DateTime formats to the labelFormat property.
| Label Value | Label Format Property Value | Result | Description |
| new Date(2000, 03, 10) | EEEE | Monday | The Date is displayed in day format |
| new Date(2000, 03, 10) | yMd | 04/10/2000 | The Date is displayed in month/date/year format |
| new Date(2000, 03, 10) | MMM | Apr | The Shorthand month for the date is displayed |
| new Date(2000, 03, 10) | hm | 12:00 AM | Time of the date value is displayed as label |
| new Date(2000, 03, 10) | hms | 12:00:00 AM | The Label is displayed in hours:minutes:seconds format |