How can I help you?
Layers
14 Nov 20229 minutes to read
The Maps component is rendered through Layers and any number of layers can be added to the Maps.
Multilayer
The Multilayer support allows loading multiple shape files and map providers in a single container, enabling Maps to display more information. The shape layer or map providers are the main layers of the Maps. Multiple layers can be added as SubLayer over the main layers using the Type property of Layers.
Sublayer
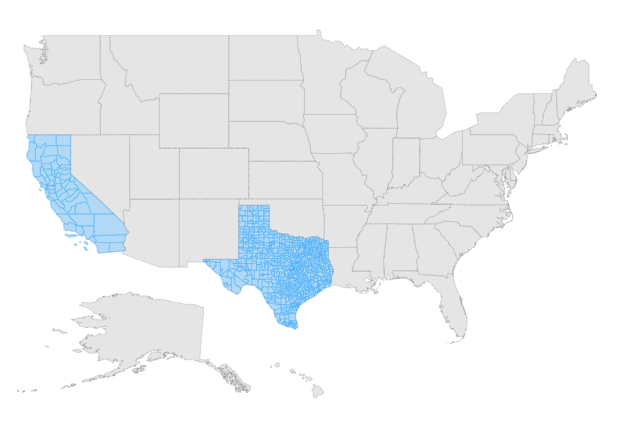
Sublayer is a type of shape file layer. It allows loading multiple shape files in a single map view. For example, a sublayer can be added over the main layer to view geographic features such as rivers, valleys and cities in a map of a country. Similar to the main layer, elements in the Maps such as markers, bubbles, color mapping and legends can be added to the sub-layer.
In this example, the United States map shape is used as shape data by utilizing usa.ts file, and texas.ts and california.ts files are used as sub-layers in the United States map.
@using Syncfusion.EJ2;
@Html.EJS().Maps("maps").Layers(l =>
{
l.ShapeSettings(ss => ss.Fill("#E5E5E5").Border(border => border.Color("black").Width(0.1).Opacity(1)))
.ShapeData(ViewBag.usamap).Add();
l.ShapeSettings(ss => ss.Fill("rgba(141, 206, 255, 0.6)").Border(border => border.Color("#1a9cff").Width(0.25).Opacity(1)))
.ShapeData(ViewBag.texasmap).Type(Syncfusion.EJ2.Maps.Type.SubLayer).Add();
l.ShapeSettings(ss => ss.Fill("rgba(141, 206, 255, 0.6)").Border(border => border.Color("#1a9cff").Width(0.25).Opacity(1)))
.ShapeData(ViewBag.californiamap).Type(Syncfusion.EJ2.Maps.Type.SubLayer).Add();
}).Render()using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using EJ2_Core_Application.Models;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using Syncfusion.EJ2.Charts;
namespace EJ2_Core_Application.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
public IActionResult Index()
{
ViewBag.usa = GetUSMap();
ViewBag.california = GetCaliforniaMap();
ViewBag.texas = GetTexasMap();
ViewBag.usamap = GetUSMaps();
ViewBag.californiamap = GetCaliforniaMaps();
ViewBag.texasmap = GetTexasMaps();
return View();
}
public object GetUSMap()
{
string allText = System.IO.File.ReadAllText("./wwwroot/USA.json");
return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(allText);
}
public object GetCaliforniaMap()
{
string allText = System.IO.File.ReadAllText("./wwwroot/California.json");
return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(allText);
}
public object GetTexasMap()
{
string allText = System.IO.File.ReadAllText("./wwwroot/Texas.json");
return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(allText);
}
public object GetUSMaps()
{
string allText = System.IO.File.ReadAllText(Server.MapPath("~/App_Data/USA.json"));
return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(allText, typeof(object));
}
public object GetCaliforniaMaps()
{
string allText = System.IO.File.ReadAllText(Server.MapPath("~/App_Data/California.json"));
return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(allText, typeof(object));
}
public object GetTexasMaps()
{
string allText = System.IO.File.ReadAllText(Server.MapPath("~/App_Data/Texas.json"));
return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(allText, typeof(object));
}
}
}Displaying different layer in the view
Multiple shape files and map providers can be loaded simultaneously in Maps. The BaseLayerIndex property is used to determine which layer on the user interface should be displayed. This property is used for the Maps drill-down feature, so when the BaseLayerIndex value is changed, the corresponding shape is loaded. In this example, two layers can be loaded with the World map and the United States map. Based on the given BaseLayerIndex value the corresponding shape will be loaded in the user interface. If the BaseLayerIndex value is set to 0, then the world map will be loaded.
@using Syncfusion.EJ2;
@Html.EJS().Maps("maps").BaseLayerIndex(1).Layers(l =>
{
l.ShapeData(ViewBag.worldMap).Add();
l.ShapeData(ViewBag.usaMap).Add();
}).Render()using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using EJ2_Core_Application.Models;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using Syncfusion.EJ2.Charts;
namespace EJ2_Core_Application.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
public IActionResult Index()
{
ViewBag.world_map = GetWorldMap();
ViewBag.usa = GetUSMap();
ViewBag.worldMap = GetWorldMaps();
ViewBag.usaMap = GetUSMaps();
return View();
}
public object GetUSMap()
{
string allText = System.IO.File.ReadAllText("./wwwroot/scripts/MapsData/USA.json");
return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(allText);
}
public object GetWorldMap()
{
string text = System.IO.File.ReadAllText("./wwwroot/scripts/MapsData/WorldMap.json");
return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(text);
}
public object GetWorldMaps()
{
string allText = System.IO.File.ReadAllText(Server.MapPath("~/App_Data/WorldMap.json"));
return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(allText, typeof(object));
}
public object GetUSMaps()
{
string allText = System.IO.File.ReadAllText(Server.MapPath("~/App_Data/USA.json"));
return JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(allText, typeof(object));
}
}
}Rendering custom shapes
Custom shapes (also known as custom maps) can be rendered in Maps to represent bus seat booking, cricket stadium, basic home plan/sketch, and so on. To accomplish this, a JSON file in GeoJSON format with proper geometries must be created manually or with the assistance of any online map vendor. The GeoJSON file created must be set to the ShapeData in the Maps layer, and the GeometryType must be set as GeometryType.Normal.
Refer this link for an example GeoJSON file containing information about bus seat selection.
Refer this link for more information and a live demonstration.