Virtualization in File Manager Control
3 Mar 202511 minutes to read
File Manager’s UI virtualization allows for the dynamic loading of a large number of directories and files in both the detailsView and largeIconsView without degrading performance.
Enable Virtualization
The virtualization of the File Manager control is based on the height and width of the viewport. The items will be loaded in both largeIconsView and detailsView based on the viewport size.
In order to enable virtualization, you must set the EnableVirtualization property to true.
The example below shows a large collection of files in the Documents and Text Documents folders.
<div class="control-section">
<div class="sample-container">
<!-- File Manager virtualization feature sample -->
@Html.EJS().FileManager("filemanager").AjaxSettings(
new Syncfusion.EJ2.FileManager.FileManagerAjaxSettings
{
Url = "https://ej2-aspcore-service.azurewebsites.net/api/Virtualization/FileOperations",
DownloadUrl = "https://ej2-aspcore-service.azurewebsites.net/api/Virtualization/Download",
UploadUrl = "https://ej2-aspcore-service.azurewebsites.net/api/Virtualization/Upload",
GetImageUrl = "https://ej2-aspcore-service.azurewebsites.net/api/Virtualization/GetImage"
}).EnableVirtualization(true).Render()
</div>
</div>using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web.Mvc;
//File Manager's base functions are available in the below package
using Syncfusion.EJ2.FileManager.Base;
//File Manager's operations are available in the below package
using Syncfusion.EJ2.FileManager.PhysicalFileProvider;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
// Use the package for hosting
using System.Web.Hosting;
namespace WebApplication.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
// Accessing the File Operations from File Manager package
PhysicalFileProvider operation = new PhysicalFileProvider();
public HomeController()
{
// Map the path of the files to be accessed with the host
var path = HostingEnvironment.MapPath("~/Content/Files");
// Assign the mapped path as root folder
operation.RootFolder(path);
}
public ActionResult FileOperations(FileManagerDirectoryContent args)
{
// Processing the File Manager operations
switch (args.Action)
{
case "read":
// Path - Current path; ShowHiddenItems - Boolean value to show/hide hidden items
return Json(operation.ToCamelCase(operation.GetFiles(args.Path, args.ShowHiddenItems)));
case "delete":
// Path - Current path where of the folder to be deleted; Names - Name of the files to be deleted
return Json(operation.ToCamelCase(operation.Delete(args.Path, args.Names)));
case "copy":
// Path - Path from where the file was copied; TargetPath - Path where the file/folder is to be copied; RenameFiles - Files with same name in the copied location that is confirmed for renaming; TargetData - Data of the copied file
return Json(operation.ToCamelCase(operation.Copy(args.Path, args.TargetPath, args.Names, args.RenameFiles, args.TargetData)));
case "move":
// Path - Path from where the file was cut; TargetPath - Path where the file/folder is to be moved; RenameFiles - Files with same name in the moved location that is confirmed for renaming; TargetData - Data of the moved file
return Json(operation.ToCamelCase(operation.Move(args.Path, args.TargetPath, args.Names, args.RenameFiles, args.TargetData)));
case "details":
if (args.Names == null)
{
args.Names = new string[] { };
}
// Path - Current path where details of file/folder is requested; Name - Names of the requested folders
return Json(operation.ToCamelCase(operation.Details(args.Path, args.Names)));
case "create":
// Path - Current path where the folder is to be created; Name - Name of the new folder
return Json(operation.ToCamelCase(operation.Create(args.Path, args.Name)));
case "search":
// Path - Current path where the search is performed; SearchString - String typed in the searchbox; CaseSensitive - Boolean value which specifies whether the search must be casesensitive
return Json(operation.ToCamelCase(operation.Search(args.Path, args.SearchString, args.ShowHiddenItems, args.CaseSensitive)));
case "rename":
// Path - Current path of the renamed file; Name - Old file name; NewName - New file name
return Json(operation.ToCamelCase(operation.Rename(args.Path, args.Name, args.NewName)));
}
return null;
}
// Processing the Upload operation
public ActionResult Upload(string path, IList<System.Web.HttpPostedFileBase> uploadFiles, string action)
{
FileManagerResponse uploadResponse;
//Invoking upload operation with the required paramaters
// path - Current path where the file is to uploaded; uploadFiles - Files to be uploaded; action - name of the operation(upload)
uploadResponse = operation.Upload(path, uploadFiles, action, null);
return Content("");
}
// Processing the Download operation
public ActionResult Download(string downloadInput)
{
FileManagerDirectoryContent args = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<FileManagerDirectoryContent>(downloadInput);
//Invoking download operation with the required paramaters
// path - Current path where the file is downloaded; Names - Files to be downloaded;
return operation.Download(args.Path, args.Names);
}
// Processing the GetImage operation
public ActionResult GetImage(FileManagerDirectoryContent args)
{
//Invoking GetImage operation with the required paramaters
// path - Current path of the image file; Id - Image file id;
return operation.GetImage(args.Path, args.Id, false, null, null);
}
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
}
}The output will look like the image below.
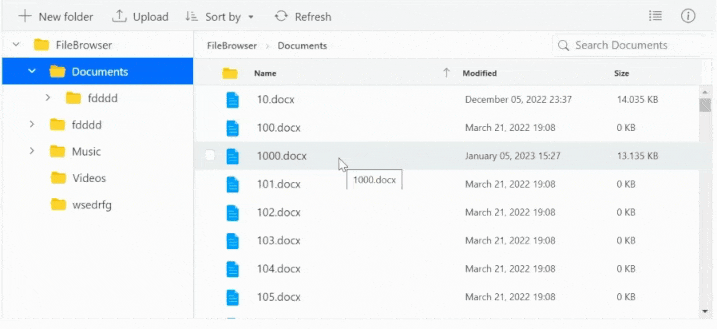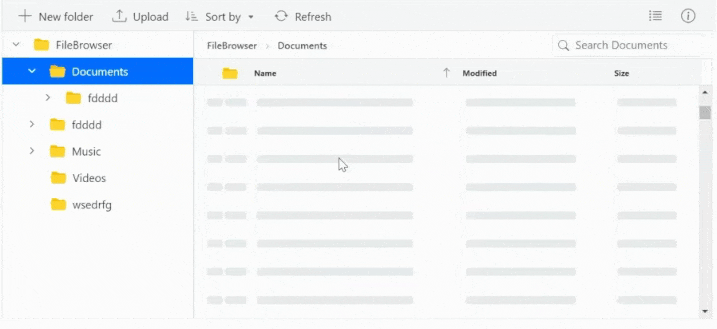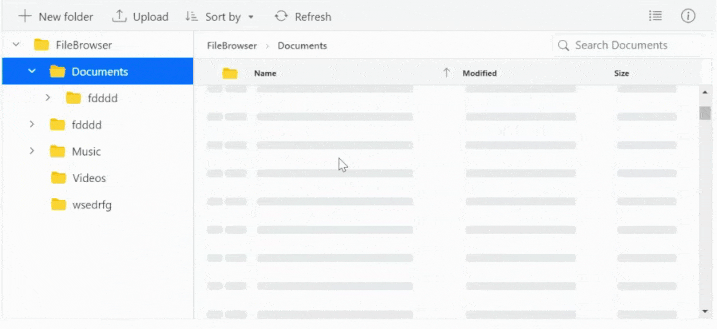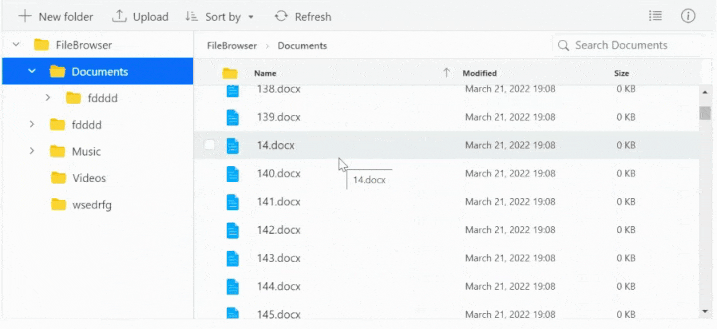
Limitations for Virtualization
-
Programmatic selection using the selectAll method is not supported with virtual scrolling.
-
The keyboard shortcut CTRL+A will only select the files and directories that are currently visible within the viewport, rather than selecting all files and directories in the entire directory tree.
-
Selected file items are not maintained while scrolling to ensure optimal control performance.